Artificial neural networks (ANNs) traditionally lack the adaptability and plasticity seen in biological neural networks. This limitation poses a significant challenge for their application in dynamic and unpredictable environments. The inability of ANNs to continuously adapt to new information and changing conditions hinders their effectiveness in real-time applications such as robotics and adaptive systems. Developing ANNs that can self-organize, learn from experiences, and adapt throughout their lifetime is crucial for advancing the field of artificial intelligence (AI).
Current methods addressing neural plasticity include meta-learning and developmental encodings. Meta-learning techniques, such as gradient-based methods, aim to create adaptable ANNs but often come with high computational costs and complexity. Developmental encodings, including Neural Developmental Programs (NDPs), show potential in evolving functional neural structures but are confined to pre-defined growth phases and lack mechanisms for continuous adaptation. These existing methods are limited by computational inefficiency, scalability issues, and an inability to handle non-stationary environments, making them unsuitable for many real-time applications.
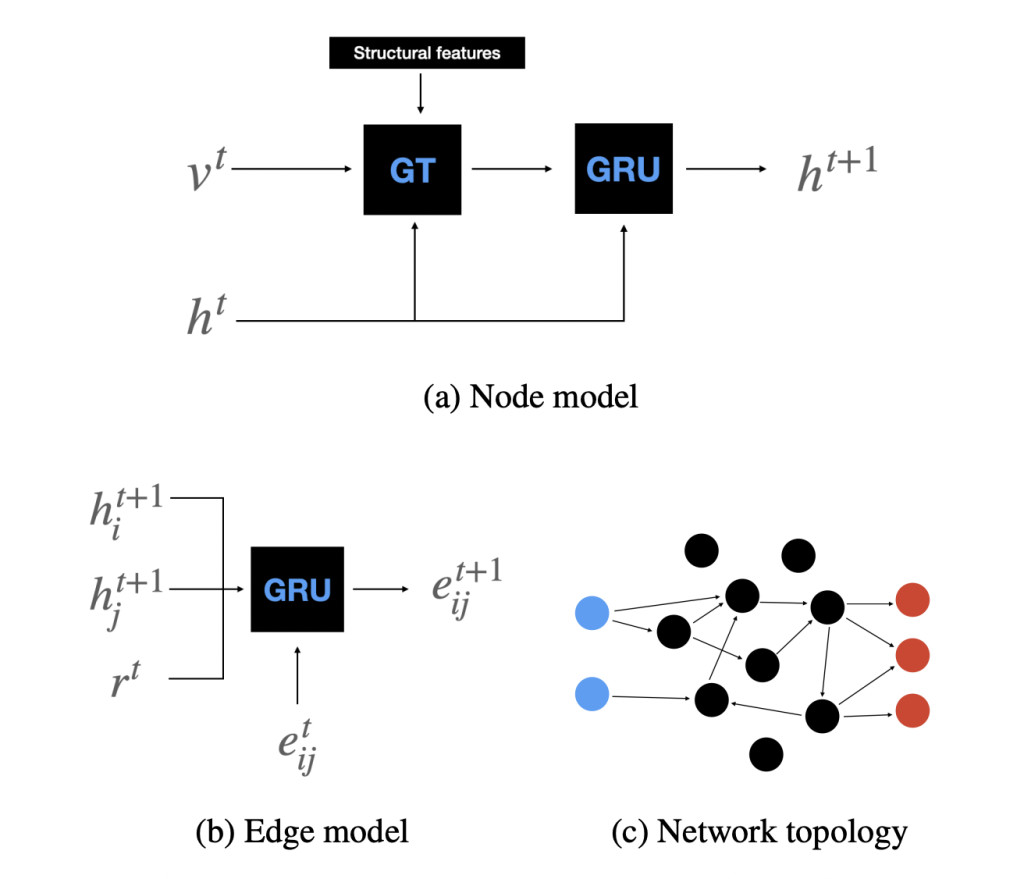
The researchers from the IT University of Copenhagen introduce Lifelong Neural Developmental Programs (LNDPs), a novel approach extending NDPs to incorporate synaptic and structural plasticity throughout an agent’s lifetime. LNDPs utilize a graph transformer architecture combined with Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) to enable neurons to self-organize and differentiate based on local neuronal activity and global environmental rewards. This approach allows dynamic adaptation of the network’s structure and connectivity, addressing the limitations of static and pre-defined developmental phases. The introduction of spontaneous activity (SA) as a mechanism for pre-experience development further enhances the network’s ability to self-organize and develop innate skills, making LNDPs a significant contribution to the field.
LNDPs involve several key components: node and edge models, synaptogenesis, and pruning functions, all integrated into a graph transformer layer. Nodes’ states are updated using the output of the graph transformer layer, which includes information about node activations and structural features. Edges are modeled with GRUs that update based on pre-and post-synaptic neuron states and received rewards. Structural plasticity is achieved through synaptogenesis and pruning functions that dynamically add or remove connections between nodes. The framework is implemented using various reinforcement learning tasks, including Cartpole, Acrobot, Pendulum, and a foraging task, with hyperparameters optimized using the Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolutionary Strategy (CMA-ES).
The researchers demonstrate the effectiveness of LNDPs across several reinforcement learning tasks, including Cartpole, Acrobot, Pendulum, and a foraging task. The below key performance metrics from the paper show that networks with structural plasticity significantly outperform static networks, especially in environments requiring rapid adaptation and non-stationary dynamics. In the Cartpole task, LNDPs with structural plasticity achieved higher rewards in initial episodes, showcasing faster adaptation capabilities. The inclusion of spontaneous activity (SA) phases greatly enhanced performance, enabling networks to develop functional structures before interacting with the environment. Overall, LNDPs demonstrated superior adaptation speed and learning efficiency, highlighting their potential for developing adaptable and self-organizing AI systems.
In conclusion, LNDPs represent a framework for evolving self-organizing neural networks that incorporate lifelong plasticity and structural adaptability. By addressing the limitations of static ANNs and existing developmental encoding methods, LNDPs offer a promising approach for developing AI systems capable of continuous learning and adaptation. This proposed method demonstrates significant improvements in adaptation speed and learning efficiency across various reinforcement learning tasks, highlighting its potential impact on AI research. Overall, LNDPs represent a substantial step towards more naturalistic and adaptable AI systems.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter.Â
Join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 46k+ ML SubReddit
The post Researchers at IT University of Copenhagen Propose Self-Organizing Neural Networks for Enhanced Adaptability appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ