Language modeling in artificial intelligence focuses on developing systems that can understand, interpret, and generate human language. This field encompasses various applications, such as machine translation, text summarization, and conversational agents. Researchers aim to create models that mimic human language abilities, allowing for seamless interaction between humans and machines. The advancements in this field have led to the development of increasingly complex and large models that require substantial computational resources.
The increasing complexity and size of large language models (LLMs) result in significant training and inference costs. These costs arise from the necessity to encode vast amounts of knowledge into model parameters, which are both resource-intensive and computationally expensive. As the demand for more powerful models grows, the challenge of managing these costs becomes more pronounced. Addressing this problem is crucial for the sustainable development of language modeling technologies.
Existing methods to mitigate these costs involve optimizing various aspects of LLMs, such as their architecture, data quality, and parallelization. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) models, for instance, use external knowledge bases to reduce the load on model parameters. However, these models still depend heavily on large parameter sizes, which limits their efficiency. Other approaches include improving data quality and using advanced hardware, but these solutions only partially address the underlying issue of high computational costs.
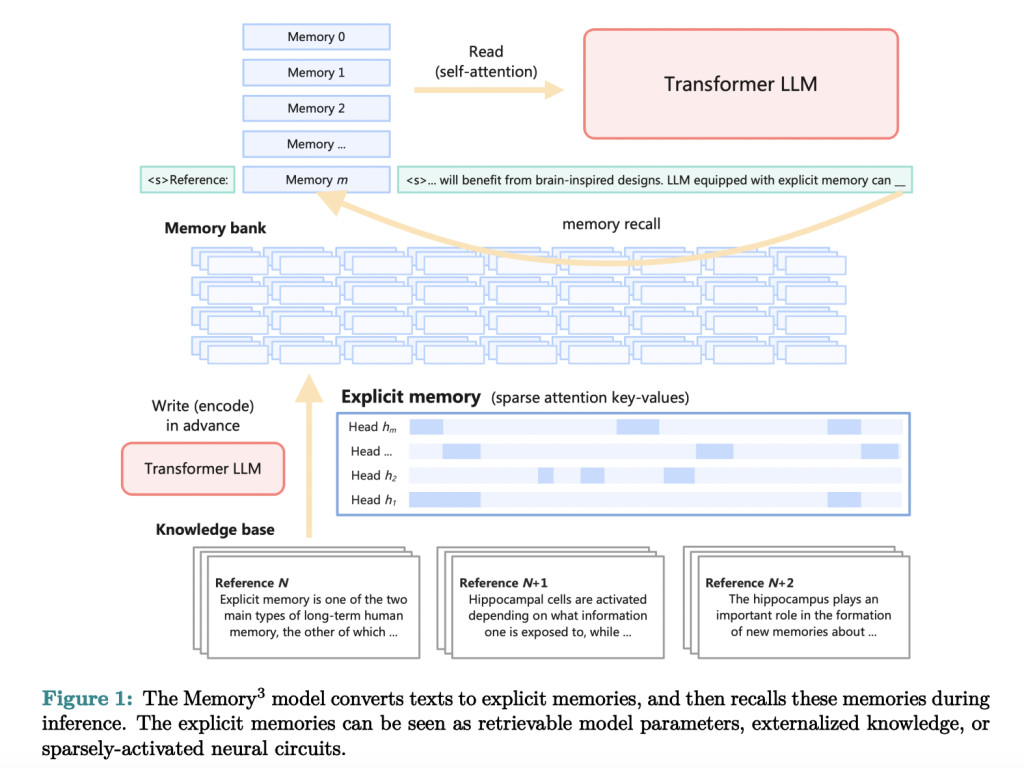
Researchers from the Institute for Advanced Algorithms Research in Shanghai, Moqi Inc., and the Center for Machine Learning Research at Peking University have introduced the Memory3 model. This novel approach incorporates explicit memory into LLMs. This model externalizes a significant portion of knowledge, allowing the LLM to maintain a smaller parameter size. Introducing explicit memory represents a paradigm shift in how language models store and retrieve knowledge.
Memory3 utilizes explicit memories, which are cheaper to store and recall than traditional model parameters. This design includes a memory sparsification mechanism and a two-stage pretraining scheme to facilitate efficient memory formation. The model converts texts into explicit memories, which can be retrieved during inference, reducing overall computational costs. The Memory3 architecture is designed to be compatible with existing Transformer-based LLMs, requiring minimal fine-tuning. This adaptability ensures that the Memory3 model can be widely adopted without extensive system modifications. The knowledge base comprises 1.1 × 108 text chunks, each with a length of up to 128 tokens, efficiently stored and processed.
The Memory3 model, with 2.4 billion non-embedding parameters, outperformed larger LLMs and RAG models. It achieved better benchmark performance, demonstrating superior efficiency and accuracy. Specifically, Memory3 showed a decoding speed higher than RAG models, as it did not rely on extensive text retrieval processes. Furthermore, the performance on professional tasks, which involved high-frequency retrieval of explicit memories, showcased the model’s robustness and adaptability to various applications. The integration of explicit memories significantly reduced the computational load, allowing for faster and more efficient processing.
The Memory3 model demonstrated impressive results. It showed a 2.51% boost in average scores due to explicit memory compared to models without this feature. In specific tasks, the Memory3 model scored 83.3 on HellaSwag and 80.4 on BoolQ, surpassing a larger 9.1B parameter model, which scored 70.6 and 70.7, respectively. The model’s decoding speed was 35.2% slower without using memory, indicating efficient memory use. Moreover, the explicit memory mechanism reduced the total memory storage requirement from 7.17PB to 45.9TB, making it more practical for large-scale applications.
To conclude, the Memory3 model represents a significant advancement in reducing the cost and complexity of training and operating large language models. The researchers offer a more efficient, scalable solution that maintains high performance and accuracy by externalizing some knowledge into explicit memories. This innovative approach addresses the pressing issue of computational costs in language modeling, paving the way for more sustainable and accessible AI technologies.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter.Â
Join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 46k+ ML SubReddit
The post Memory3: A Novel Architecture for LLMs that Introduces an Explicit Memory Mechanism to Improve Efficiency and Performance appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ