Traditional AI inference systems often rely on centralized servers, which pose scalability limitations, privacy risks, and require trust in centralized authorities for reliable execution. These centralized models are also at risk to single points of failure and data breaches, limiting widespread adoption and innovation in AI applications. Meet Rakis: an open-source, permissionless inference network that addresses key challenges in AI inference by focusing on decentralization and verifiability.
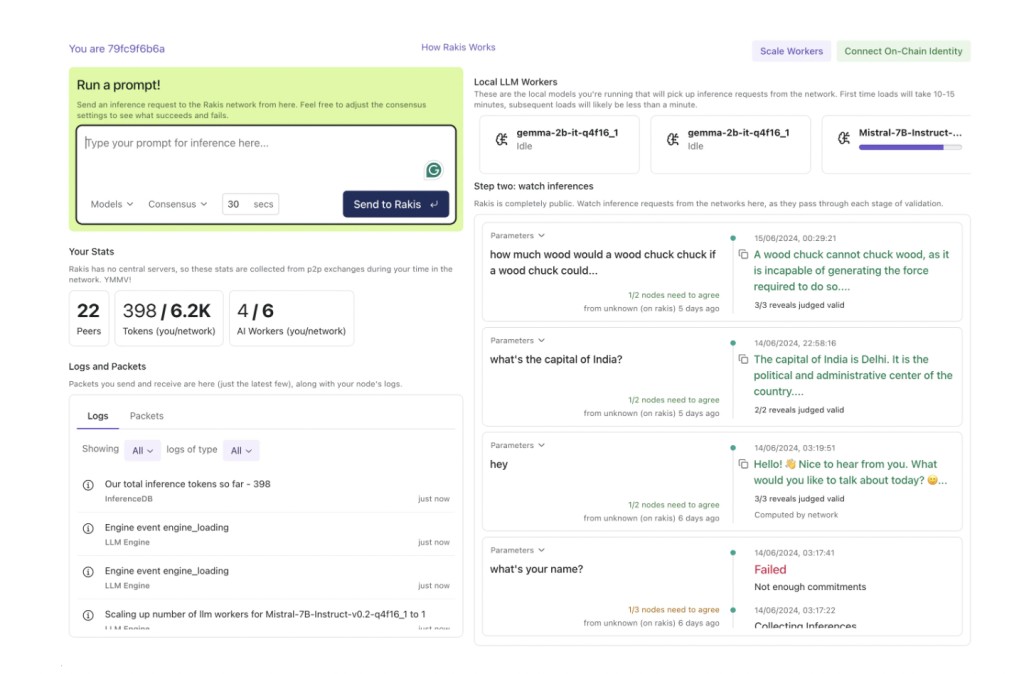
Current AI systems predominantly operate within centralized architectures, where computation is concentrated on servers managed by single entities. In contrast, Rakis introduces a decentralized approach that leverages the collective computational power of interconnected browsers. The peer-to-peer network model democratizes access to AI capabilities, allowing anyone with a web browser to participate without special permissions. By utilizing technologies like WebRTC for NAT traversal and multiple peer networks such as NKN and GunDB for robust message delivery, Rakis ensures redundancy and reliability in communication channels. This decentralized setup not only enhances scalability but also mitigates privacy risks associated with centralized data storage and processing.
Rakis employs a layered architecture to efficiently manage decentralized AI inference tasks namely P2P and Peering, Inference, Coordination, Consensus, and Persistence layer.
Key features of these layers are:
Peer-to-Peer Networking: Utilizes multiple networks for redundant message delivery and employs WebRTC for NAT hole punching to establish direct connections between peers.
Inference Layer: Manages AI inference requests, worker scheduling, and result processing using Web Workers for parallel computation.
Consensus Mechanism: Implements a novel consensus approach based on embeddings and a commit-reveal process. This mechanism ensures deterministic AI outputs despite inherent randomness in AI algorithms by clustering results in high-dimensional spaces and reaching consensus based on specified security parameters.
Integration with Blockchains: Integrates with various blockchains like Ethereum and Arbitrum for persistent storage of inference results and incentivization mechanisms.
Performance-wise, Rakis dynamically scales worker instances based on demand, optimizes resource utilization through efficient queuing mechanisms, and supports multiple AI models to cater to diverse application needs. By decentralizing AI inference, Rakis enhances privacy, security, and transparency, which is crucial for applications ranging from financial transactions to creative projects.
In conclusion, Rakis represents a significant advancement towards democratizing access to AI capabilities through decentralization. By shifting AI inference tasks from centralized servers to a distributed network of browsers, Rakis improves scalability and privacy as well as fosters innovation and collaboration within the AI and blockchain communities. The consensus mechanism ensures reliable and transparent AI outputs, allowing applications such as self-executing smart contracts and decentralized AI agents.Â
Check out the Github, Docs, and Details. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter.Â
Join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 45k+ ML SubReddit
The post Meet Rakis: A Decentralized Verifiable Artificial Intelligence AI Network in the Browser appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ