The paper addresses the challenge of ensuring that large language models (LLMs) generate accurate, credible, and verifiable responses by correctly citing reliable sources. Existing methods often need help with errors and hallucinations, leading to incorrect or misleading information in generated responses. This research aims to improve the accuracy and reliability of LLM outputs by introducing a novel verification framework. As LLMs have become increasingly powerful and prevalent, it is crucial to investigate how their performance scales with model size and training data. The authors aim to provide insights into the scaling properties of LLMs and how they differ from smaller models.Â
Currently, LLMs are used for tasks requiring information retrieval and generation, emphasizing grounding responses in verifiable sources. Standard approaches include retrieval-augmented generation, where LLMs are instructed to generate responses along with corresponding sources in a single inference run. More sophisticated methods involve preprocessing steps, such as summarizing relevant documents or extracting key information to enrich the input query. However, these approaches face challenges in maintaining accuracy and citation quality due to the complexity of processing large volumes of data in one go and the risk of error propagation from preprocessing steps.
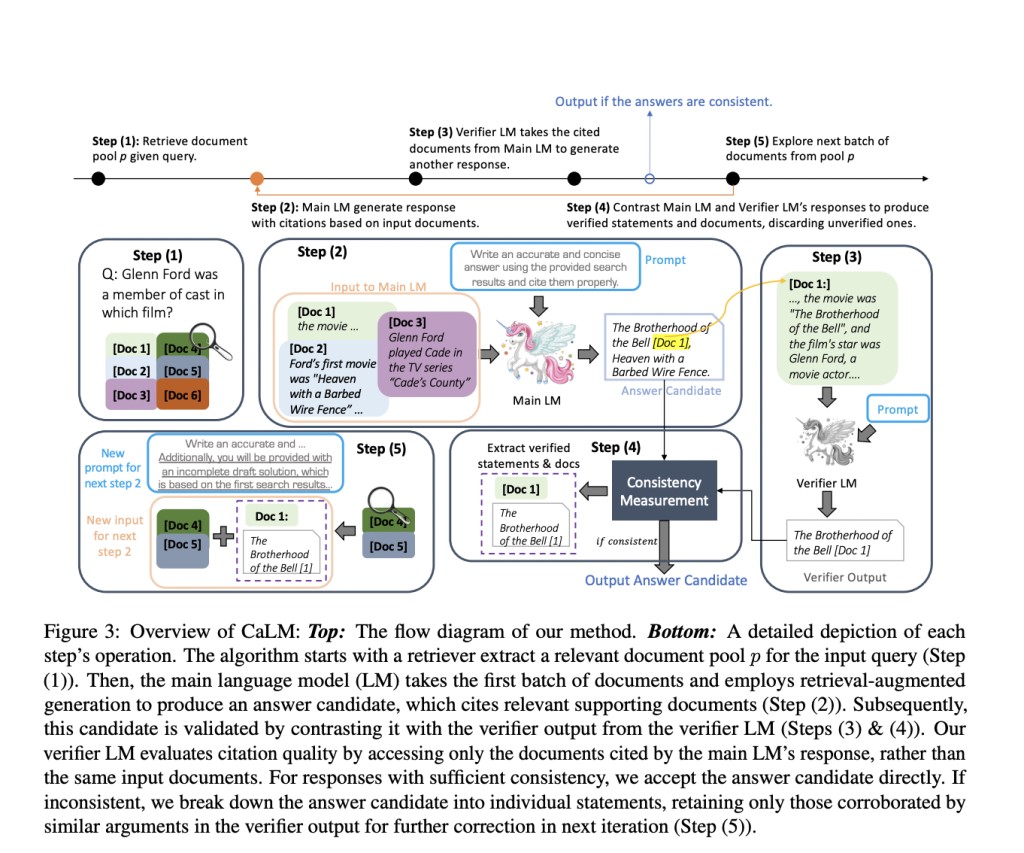
The proposed solution, CaLM (Contrasting Large and Small Language Models), leverages the complementary strengths of large and small LMs. CaLM employs a post-verification approach, where a smaller LM validates the outputs of a larger LM. The smaller LM scrutinizes the cited documents to confirm the accuracy of the larger LM’s citations. If the responses align, the large LM’s answer is verified; CaLM iteratively refines the response using a feedback loop if discrepancies are found. This method enhances the grounded generation capabilities of large LMs without requiring model fine-tuning.
CaLM’s verification process involves using a smaller LM to cross-reference the output of a larger LM with the cited documents. The smaller LM, which relies less on parametric memory and excels at processing relevant information, assesses whether the larger LM’s response is consistent with the information from the cited sources. This method capitalizes on the smaller LM’s sensitivity to input relevance, ensuring any inconsistencies are identified and corrected. The iterative feedback loop allows for continuous refinement of the response, significantly improving citation accuracy and overall answer quality.
Experiments conducted on three open-domain question-answering datasets (QAMPARI, ASQA, and ELI5) demonstrated substantial performance gains using CaLM. The method improved answer accuracy and citation quality, outperforming state-of-the-art methods by 1.5% to 7% on average. The framework proved robust even in challenging scenarios with less powerful retrieval systems, highlighting its effectiveness in enhancing the grounded generation capabilities of LLMs.
The CaLM framework effectively addresses the problem of ensuring accurate and verifiable responses from LLMs by leveraging the strengths of both large and small language models. By employing a post-verification approach and iterative refinement, CaLM significantly improves the quality and reliability of LLM outputs, making it a valuable advancement in the field of language model research. The findings suggest that while LLMs offer significant performance improvements, their scaling behavior is complex and task-dependent. This research contributes to a better understanding of the capabilities and limitations of large language models, which is crucial for their effective deployment in real-world applications.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter.Â
Join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 45k+ ML SubReddit
The post CaLM: Bridging Large and Small Language Models for Credible Information Generation appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ