A significant challenge in the realm of large language models (LLMs) is the high computational cost associated with multi-agent debates (MAD). These debates, where multiple agents communicate to enhance reasoning and factual accuracy, often involve a fully connected communication topology. This means each agent references the solutions generated by all other agents, leading to expanded input contexts and increased computational demands. Addressing this challenge is crucial for improving the scalability and efficiency of AI systems, making them more viable for real-time applications and environments with limited computational resources.
Current methods for multi-agent debate involve fully connected topologies where each agent can access and reference the solutions generated by all other agents. While this approach has shown improvements in reasoning tasks, it is computationally expensive. Techniques such as Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting and self-consistency have been employed to enhance LLM performance by structuring their reasoning processes. However, these methods also suffer from limitations, including increased complexity and the need for extensive computational resources to handle the expanded input context generated by multiple agents communicating extensively.
The researchers from Google DeepMind introduce a novel approach using sparse communication topology in multi-agent debates. By limiting the number of reference solutions visible to each agent, they aim to maintain or even improve the performance of MAD while significantly reducing computational costs. This approach involves systematic investigation and implementation of neighbor-connected communication strategies, where agents communicate with a limited set of peers rather than all agents. This innovation addresses the computational inefficiencies of existing methods by reducing the input context size, making the debate process more scalable and resource-efficient.
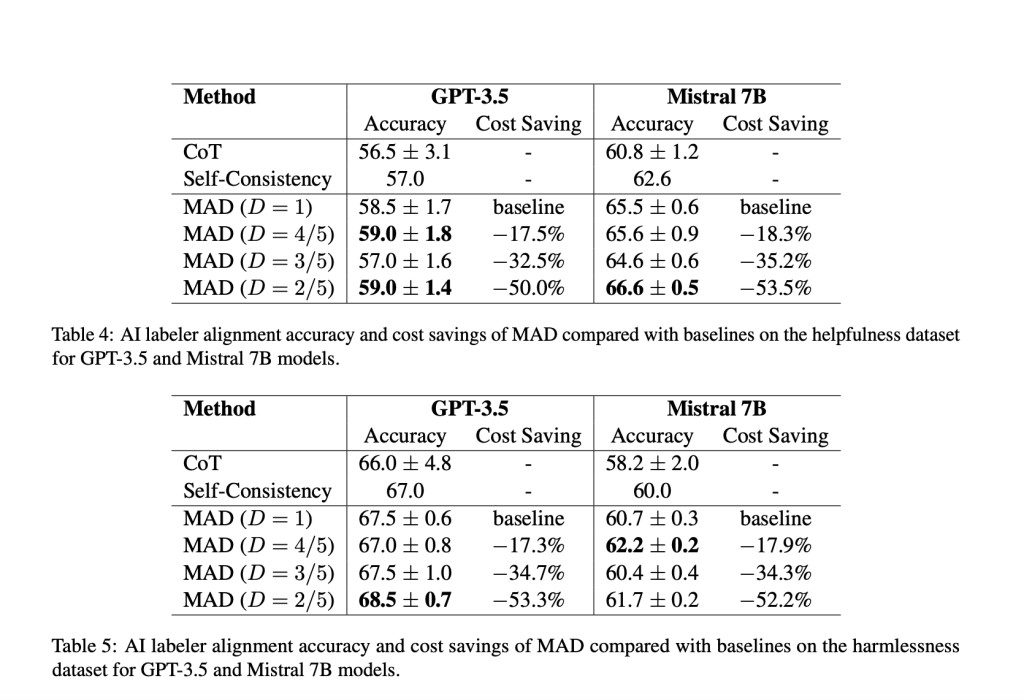
This innovative method utilizes static graphs to represent communication topologies among agents, quantified by a sparsity ratio. In experiments, the focus is on configurations with six agents, examining various degrees of sparsity. The agents, instantiated with models like GPT-3.5 and Mistral 7B, engage in multiple rounds of debate, incorporating responses from their connected peers to refine their answers. For reasoning tasks, datasets such as MATH and GSM8K are used, while alignment labeling tasks employ the Anthropic-HH dataset. The experimental setup includes performance metrics like accuracy and cost savings, and variance reduction techniques are applied to ensure robust results.
The approach using sparse communication topology in MAD achieved notable improvements in both performance and computational efficiency. On the MATH dataset, a neighbor-connected topology improved accuracy by 2% over fully connected MAD while reducing the average input token cost by over 40%. For alignment labeling tasks using the Anthropic-HH dataset, sparse MAD configurations showed improvements in helpfulness and harmlessness metrics by 0.5% and 1.0%, respectively, while halving the computational costs. These results demonstrate that sparse communication topologies can deliver comparable or superior performance to fully connected topologies with significantly reduced computational overhead.
In conclusion, this research presents a significant advancement in the field of AI by introducing sparse communication topology in multi-agent debates. This approach effectively addresses the computational inefficiencies of existing methods, offering a scalable and resource-efficient solution. The experimental results highlight the potential impact of this innovation on AI research, showcasing its ability to enhance performance while reducing costs, thereby advancing the practical applicability of multi-agent systems.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter.Â
Join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 45k+ ML SubReddit
Create, edit, and augment tabular data with the first compound AI system, Gretel Navigator, now generally available! [Advertisement]
The post This AI Paper from Google DeepMind Explores the Effect of Communication Connectivity in Multi-Agent Systems appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ