Large language models (LLMs) have the potential to lead users to make poor decisions, especially when these models provide incorrect information with high confidence, which is called hallucination. This confident misinformation has the potential to be very dangerous since it might persuade people to act based on erroneous assumptions, which could have negative consequences.
A potential solution to this problem could be for LMs to state clearly the likelihood that their assertions are true. LMs can give users a greater idea of the information’s dependability by including confidence ratings in their responses. However, current language models do not produce long-form writing with calibrated confidence claims. Long-form generated content contains intricate and subtle details that are challenging to balance appropriately throughout a lengthy story. The majority of models and calibration methods currently in use are intended for brief, discrete outputs and do not sufficiently satisfy the requirement for calibrated confidence in lengthier, more in-depth answers.
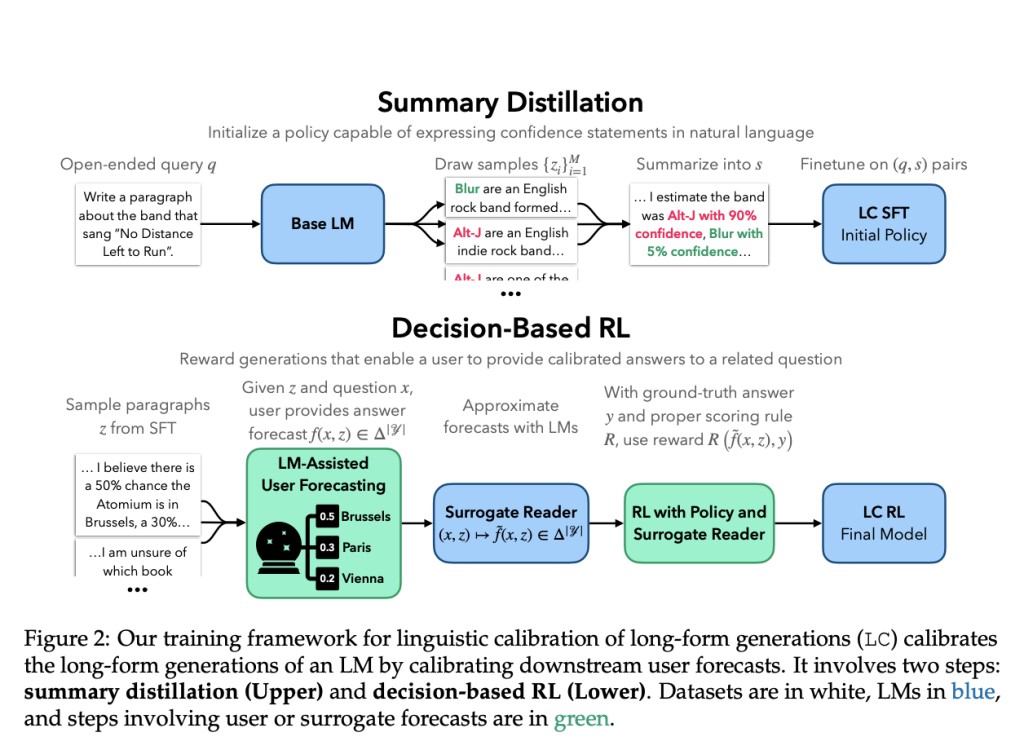
To achieve linguistic calibration, a team of researchers from Stanford has proposed a two-step training framework in recent research, which is as follows.Â
Supervised Finetuning: In this preliminary stage, the LM is trained to produce long-form content that includes embedded confidence statements. The LM gains the ability to respond with statements such as “I am positive that…†or “I estimate a 30% chance of…â€
Reinforcement Learning: The model is further refined using reinforcement learning after the finetuning stage. In this step, the LM is rewarded for producing replies that let users give calibrated answers to linked queries. The goal is to ensure that users are able to make precise probabilistic predictions using the LM’s information and confidence levels.
This method’s effectiveness has been evaluated using the Llama 2 7B model. The outcomes demonstrated that the LM could provide long-form responses with comparable accuracy but a large increase in calibration over strong finetuned factuality baselines through this two-step training approach. This enhancement was validated by both automatic and human assessments.
The results showed that even with large domain alterations, the calibrated LM continued to perform better. It was put to the test on subjects related to science and biology in addition to a completely held-out activity that involved writing biographies of individuals. This generalization implies that the linguistic calibrating approach is resilient to variations in subject areas and content kinds.
The team has summarized their primary contributions as follows.
For long-form generations, the team has defined linguistic calibration as an LM that is considered calibrated if it helps users make optimal decisions by helping them generate meaningful and accurate probabilistic projections.
A two-phase training framework has been developed: reinforcement learning to incentivize text production that contributes to calibrated predictions and supervised finetuning to include confidence claims.
The framework applied to Llama 2 7B yields notable calibration improvements over robust factual baselines while preserving accuracy, as confirmed by evaluations conducted by humans and APIs.
Without more training, the calibrated LM performs well on tasks outside of its domain, such as creating biographies and responding to scientific questions.
During decision-making, the method builds an objective based on users’ predictions, utilizing appropriate scoring methods for efficient end-to-end calibration of long-form text creation.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our Telegram Channel, Discord Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 44k+ ML SubReddit
The post Researchers at Stanford Introduce a Two-Step Framework for Linguistic Calibration of Long-Form Generations appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ