A security researcher discovered an exploitable timing leak in the Kyber key encapsulation mechanism (KEM) that’s in the process of being adopted by NIST as a post-quantum cryptographic standard.
Antoon Purnal of PQShield detailed his findings in a blog post and on social media, and noted that the problem has been fixed with the help of the Kyber team. The issue was found in the reference implementation of the Module-Lattice-Based Key-Encapsulation Mechanism (ML-KEM) that’s in the process of being adopted as a NIST post-quantum key encapsulation standard.
Clang Compiler Introduces Side-Channel Vulnerability
“A key part of implementation security is resistance against side-channel attacks, which exploit the physical side-effects of cryptographic computations to infer sensitive information,†Purnal wrote.
To secure against side-channel attacks, cryptographic algorithms must be implemented in a way so that “no attacker-observable effect of their execution depends on the secrets they process,†he wrote. In the ML-KEM reference implementation, “we’re concerned with a particular side channel that’s observable in almost all cryptographic deployment scenarios: time.â€
The vulnerability can occur when a compiler optimizes the code, in the process silently undoing “measures taken by the skilled implementer.â€
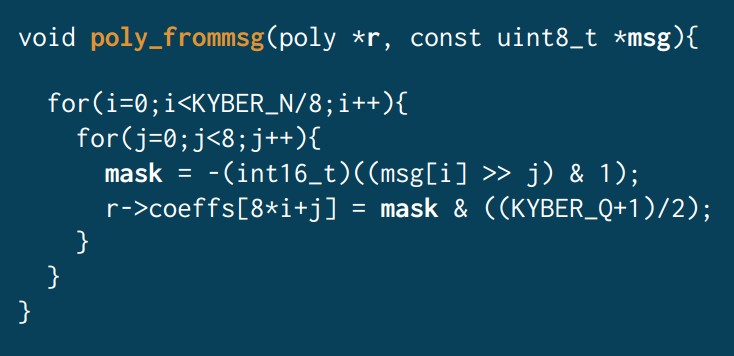
In Purnal’s analysis, the Clang compiler was found to emit a vulnerable secret-dependent branch in the poly_frommsg function of the ML-KEM reference code needed in both key encapsulation and decapsulation, corresponding to the expand_secure implementation.
“In decapsulation, poly_frommsg is used once. The whole decapsulation takes more than 100K cycles. Surely the timing difference produced by this one branch is too small to matter?†Purnal asked rhetorically.
“…sophisticated local attackers can perform high-resolution cache attacks, target the branch predictor to learn which branches are taken, or slow down the library to amplify the timing difference,†he answered. “So the prudent approach is to patch.â€
Measuring the time it takes for a complete decapsulation “is enough for an attacker to piece together the key,†he said.
Purnal published a demo on GitHub called “clangover†showing the role of the timing vulnerability in the recovery of an ML-KEM 512 secret encryption key. “The demo terminates successfully in less than 10 minutes on the author’s laptop,†he wrote.
A Critical Post-Quantum Key Vulnerability
Purnal noted that while not all compilers, options and platforms are affected, “if a given binary is affected, the security impact may be critical. Therefore, the conservative approach is to take this issue seriously, and look out for patches from your cryptography provider.â€
The reference implementation was patched by implementing the relevant conditional move as a function in a separate file. “This change prevents Clang from recognizing the binary nature of the condition flag, and hence from applying the optimization,†he said.
“It’s important to note that this does not rule out the possibility that other libraries, which are based on the reference implementation but do not use the poly_frommsg function verbatim, may be vulnerable – either now or in the future,†he concluded.
Source: Read More