Large language models (LLMs) have shown their potential in many natural language processing (NLP) tasks, like summarization and question answering using zero-shot and few-shot prompting approaches. However, prompting alone is not enough to make LLMs work as agents who can navigate environments to solve complex and multi-step. Fine-tuning LLMs for these tasks is also impractical due to the unavailability of training data. Collecting data for tasks that require decision-making and complex interactions is both time-consuming and costly. Also, the automatic sequence evaluation of actions taken by an agent is challenging, and the bad metrics make it hard to check whether the agent’s performance is improving or getting worse.Â
For self-improving LLMs, various methods have been proposed that contain self-distillation where the teacher and student are the same models. LLM Agent’s performance can be improved using multiple prompting approaches but shows orthogonality to self-improvement fine-tuning. Further, agents of self-improving show how complex robotics tasks can be solved by learning and improving on their own. A method discussed in this paper shows filtering trajectories and fine-tuning. However, importance is given to the supervised filtering that does not explore generating novel tasks and synthetic data
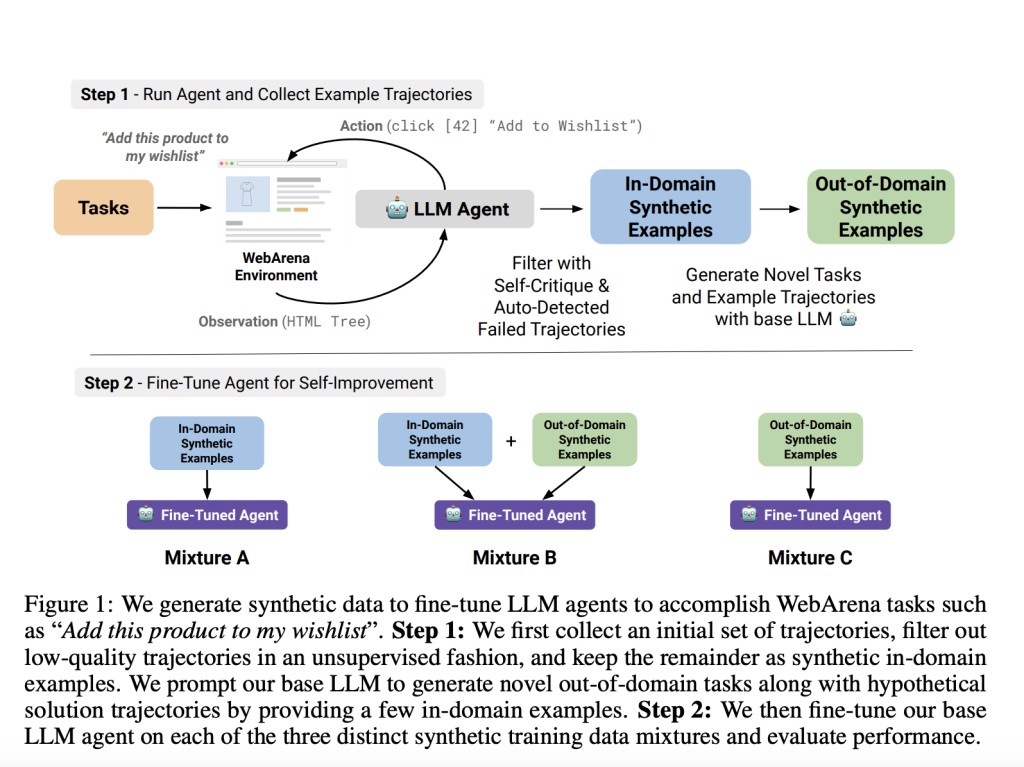
Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, ExtensityAI, Johannes Kepler University Linz, and NXAI introduced new techniques that allow LLM agents to solve complex and multistep tasks through self-improvement. All the distinct techniques for self-improvement involve fine-tuning the LLM agent and releasing a signal to learn through unsupervised methods such as self-critique to filter training examples. For a detailed understanding of the impact of self-improvement, two auxiliary metrics are introduced: (a) a measure to analyze capabilities gained and lost by the agent, and (b) an extension of the VERTEX score to measure the quality of agent trajectories of different lengths.Â
The metrics used in understanding the impact of self-improvement allow for small changes, both good and bad, better than the overall benchmark scores. Moreover, researchers performed multiple experiments to fine-tune agent models on the synthetic training data mixtures and determine the self-improvement of the agent model over the base agent model through evaluation metrics. The performance of the baseline agent is measured and a trivial agent is implemented that always outputs stop [N/A]. The trivial agent baseline helps to recognize the completed tasks that contribute to an agent, which has the potential to calculate the capability score.
The result of the experiment shows that models can self-improve at web agent tasks and enhance overall benchmark performance with the best-performing mixture by solving 18 tasks correctly with a relative improvement of 31%. Further, the results also show that the self-improved agents can gain new capabilities with the help of self-improvement while losing a few abilities to perform some capabilities. In this case, two mixtures are fine-tuned to enhance the capability score and show 5 more capabilities than the base agent model, with a relative improvement of 24%.
In conclusion, researchers introduced new techniques that allow LLM agents to solve complex and multistep tasks through self-improvement. Self-improvement helps to enhance the performance of agent models and allows to gain new capabilities, having minimal decrease in the quality of trajectories to provide these benefits. However, this paper possesses some limitations in fine-tuning techniques for self-improvement. Their performance is improved by reinforcing correct actions and decisions of an underlying model, however, these techniques can further reinforce incorrect actions and biases of the underlying model. This limitation can be reduced with the help of human or supervised filtering.Â
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our Telegram Channel, Discord Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 43k+ ML SubReddit | Also, check out our AI Events Platform
The post This AI Paper Explores the Extent to which LLMs can Self-Improve their Performance as Agents in Long-Horizon Tasks in a Complex Environment Using the WebArena Benchmark appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ