In Neural Networks, understanding how to optimize performance with a given computational budget is crucial. More processing power devoted to training neural networks usually results in better performance. However, choosing between expanding the training dataset and raising the model’s parameters is crucial when scaling computer resources. In order to optimize performance, these two factors must be balanced within a set computing budget. Scaling rules can help determine the best way to allocate resources.
These scaling rules for neural language models (LMs) have been studied in previous research, in which it was discovered that scaling the parameter count and training token count proportionately, ideally at a 1-to-1 ratio, would maximize performance. However, the majority of these scaling principles come from training transformers on a very specific kind of data, which is the web-scraped text.Â
This brings the question of whether other kinds of data can be used to generalize such scaling principles. The careful selection and blending of training data is typically the key to top industrial labs’ success in creating amazing Large Language Models (LLMs). This selection procedure is important because it has been demonstrated that LM performance is much improved by enhancing data quality.Â
In a recent research, a team of researchers from Reworkd AI has adjusted the syntactic features of probabilistic context-free grammars (PCFGs) to produce training datasets with different levels of complexity in order to study this. The research has provided two important insights, which are as follows.
Sensitivity to Data Complexity: The training data’s complexity affects the stated scaling rules. This indicates that the scaling principles are not always valid across various data types without modification, as they alter in parallel with the complexity of the data.
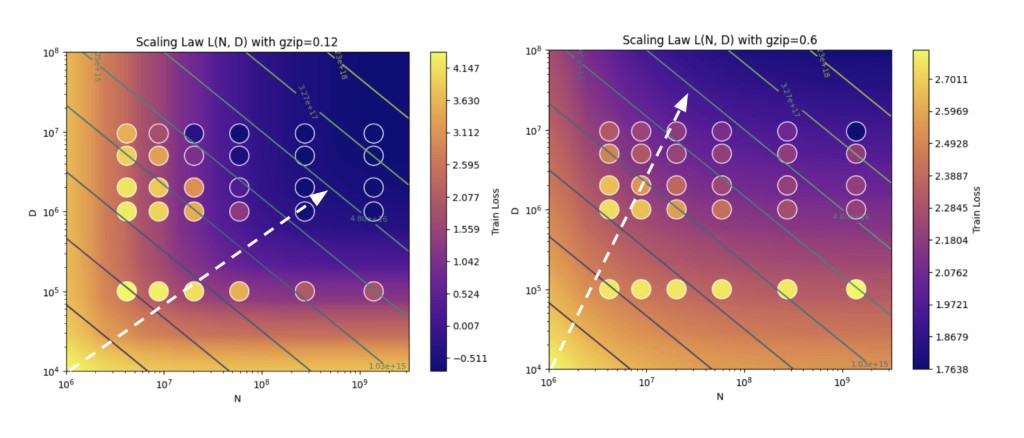
Compression as a Complexity Indicator: Using the popular compression technology gzip, the team was able to accurately forecast how the scaling qualities are influenced by the complexity of the data. In particular, the degree of data complexity is reflected in gzip’s capacity to compress data. The scaling rules are affected differently by more complicated data, which is more difficult to compress than by simpler, more compressible data.
The team has used these results to propose a new data-dependent scaling law for language models that takes into account the training data’s compressibility as determined by gzip. According to this new law, increasing the amount of the dataset rather than just increasing the number of parameters in the model should be the optimal use of computational resources as training data gets more difficult to compress.
The findings have emphasized how crucial it is to take data complexity into account when implementing scaling laws for neural language models. By accounting for the gzip compressibility of the training data, these models can be more accurately forecasted and maximized, assuring a more effective use of computational resources.
In conclusion, this study shows that neural network scaling laws depend on the characteristics of the training data, including complexity. This can help in more effectively allocating computational resources for neural network training, especially when handling data kinds other than plain old web text.
Check out the Paper and GitHub. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our Telegram Channel, Discord Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 43k+ ML SubReddit | Also, check out our AI Events Platform
The post Data Complexity and Scaling Laws in Neural Language Models appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ