Maintaining the accuracy of Large Language Models (LLMs), such as GPT, is crucial, particularly in cases requiring factual accuracy, like news reporting or educational content creation. Despite their impressive capabilities, LLMs are prone to generating plausible but nonfactual information, known as “hallucinations,†usually when faced with open-ended queries that require broad world knowledge. Google AI Researchers introduced AGREE to address the issue of “hallucination,†where LLMs generate a response that is factually incorrect, nonsensical, or disconnected from the input prompt.
Existing approaches to preventing hallucinations in LLMs primarily include two methods: post-hoc citing and prompting-based grounding. Post-hoc citing involves adding citations after generating responses, often using natural language inference (NLI) models. However, this method relies heavily on the knowledge within the LLM’s embeddings and faces challenges with facts beyond its training data. While prompting-based grounding leverages the instruction-following and in-context learning capabilities of LLMs, but its often ineffective, particularly in real-world scenarios requiring high factual accuracy.
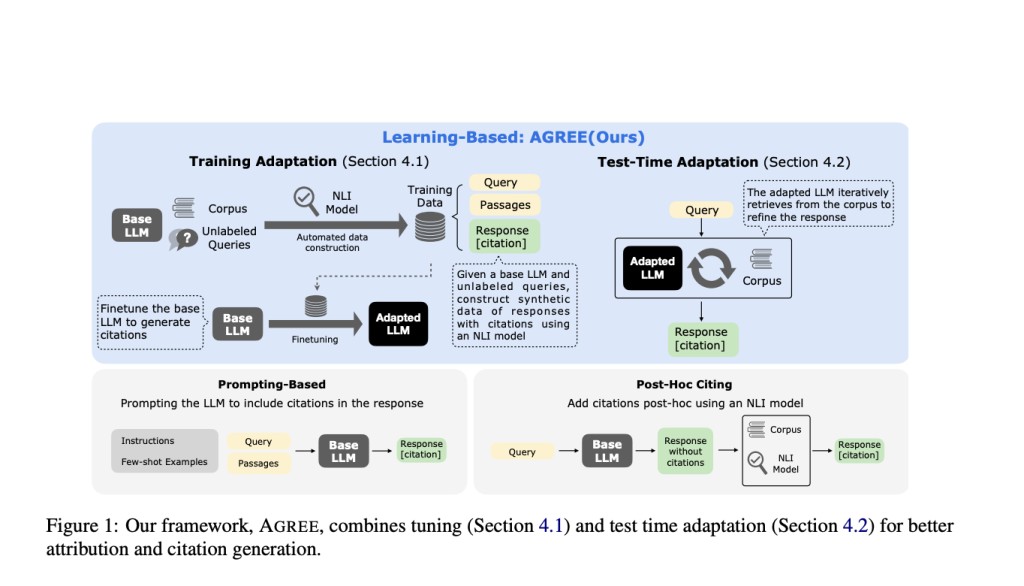
The proposed solution, AGREE (Adaptation for GRounding EnhancEment), introduces a learning-based framework that enables LLMs to self-ground their responses and provide accurate citations. AGREE takes a holistic approach by combining both learning-based adaptation and test-time adaptation (TTA). During training, AGREE fine-tunes LLMs using synthetic data from unlabeled queries, enabling them to self-ground their claims by adding citations to their responses. AGREE uses an iterative inference strategy during test time, which lets LLMs actively seek more information based on self-generated citations, which helps them improve their answers over and over again.
At the training stage, AGREE involves collecting synthetic data from unlabeled queries, retrieving relevant passages from reliable sources using a retriever model, and fine-tuning a base LLM to self-ground its claims. The fine-tuning process utilizes an NLI model to judge the support for each claim and add citations accordingly. Experiments across five datasets demonstrate AGREE’s effectiveness in improving grounding and citation precision compared to baseline methods. AGREE outperforms prompting-based and post-hoc citing approaches, achieving relative improvements of over 30% in grounding quality. Additionally, AGREE can work with out-of-domain data, suggesting its robustness across different question types, including knowledge out-of-domain. The inclusion of TTA in AGREE also leads to improvements in both grounding and answer correctness.
In conclusion, AGREE has effectively improved the issue of hallucination in LLMs by working on their factuality and verifiability. By enabling LLMs to self-ground their responses and provide accurate citations, AGREE enhances their reliability, particularly in domains requiring high factual accuracy. AGREE’s approach of combining learning-based adaptation with test-time adaptation provides a strong solution that works better than current approaches and can be used across a wide range of datasets. Overall, AGREE possesses the potential to promote reliable language models suitable for real-world applications requiring high factual accuracy.
Check out the Paper and Blog. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our Telegram Channel, Discord Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 43k+ ML SubReddit | Also, check out our AI Events Platform
The post Google AI Introduce AGREE: A Machine Learning Framework that Enables LLMs to Self-Ground the Claims in their Responses and to Provide Precise Citations appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ