Language models (LMs) are a cornerstone of artificial intelligence research, focusing on the ability to understand and generate human language. Researchers aim to enhance these models to perform various complex tasks, including natural language processing, translation, and creative writing. This field examines how LMs learn, adapt, and scale their capabilities with increasing computational resources. Understanding these scaling behaviors is essential for predicting future capabilities and optimizing the resources required for training and deploying these models.
The primary challenge in language model research is understanding how model performance scales with the amount of computational power and data used during training. This scaling is crucial for predicting future capabilities and optimizing resource use. Traditional methods require extensive training across multiple scales, which is computationally expensive and time-consuming. This creates a significant barrier for many researchers and engineers who need to understand these relationships to improve model development and application.
Existing research includes various frameworks and models for understanding language model performance. Notable among these are compute scaling laws, which analyze the relationship between computational resources and model capabilities. Tools like the Open LLM Leaderboard, LM Eval Harness, and benchmarks like MMLU, ARC-C, and HellaSwag are commonly used. Moreover, models such as LLaMA, GPT-Neo, and BLOOM provide diverse examples of how scaling laws can be practiced. These frameworks and benchmarks help researchers evaluate and optimize language model performance across different computational scales and tasks.
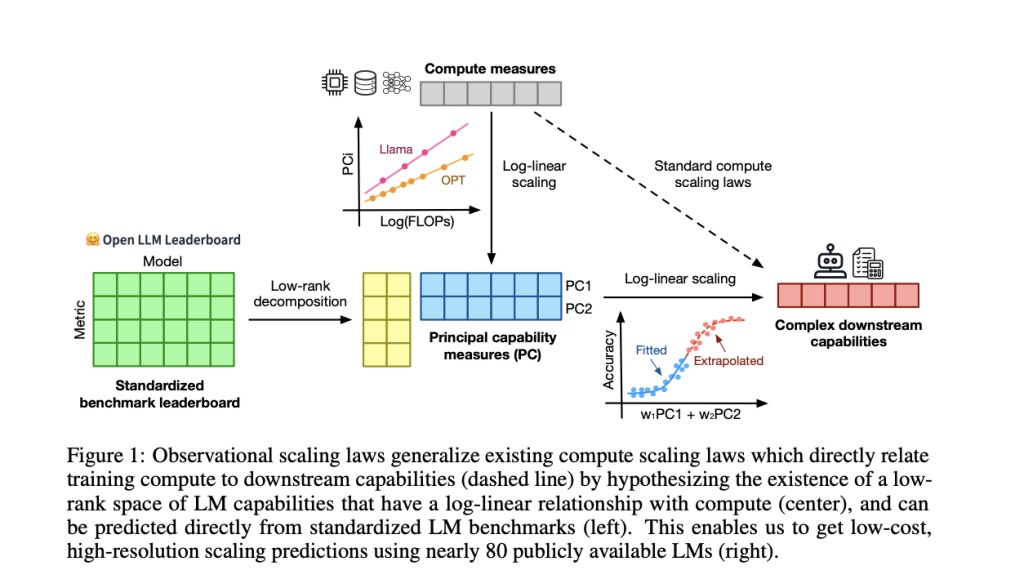
Researchers from Stanford University, University of Toronto, and Vector Institute introduced observational scaling laws to improve language model performance predictions. This method uses publicly available models to create scaling laws, reducing the need for extensive training. By leveraging existing data from approximately 80 models, the researchers could build a generalized scaling law that accounts for variations in training compute efficiencies. This innovative approach offers a cost-effective and efficient way to predict model performance across different scales and capabilities, setting it apart from traditional scaling methods.
The methodology analyzes performance data from about 80 publicly available language models, including the Open LLM Leaderboard and standardized benchmarks such as MMLU, ARC-C, and HellaSwag. The researchers hypothesized that model performance could be mapped to a low-dimensional capability space. They developed a generalized scaling law by examining variations in training compute efficiencies among different model families. This process involved using principal component analysis (PCA) to identify key capability measures and fitting these measures into a log-linear relationship with compute resources, enabling accurate and high-resolution performance predictions.
The research demonstrated significant success with observational scaling laws. For instance, using simpler models, the method accurately predicted the performance of advanced models like GPT-4. Quantitatively, the scaling laws showed a high correlation (R² > 0.9) with actual performance across various benchmarks. Emergent phenomena, such as language understanding and reasoning abilities, followed a predictable sigmoidal pattern. The results also indicated that the impact of post-training interventions, like Chain-of-Thought and Self-Consistency, could be reliably predicted, showing performance improvements of up to 20% in specific tasks.
To conclude, the research introduces observational scaling laws, leveraging publicly available data from around 80 models to predict language model performance efficiently. By identifying a low-dimensional capability space and using generalized scaling laws, the study reduces the need for extensive model training. The results showed high predictive accuracy for advanced model performance and post-training interventions. This approach saves computational resources and enhances the ability to forecast model capabilities, offering a valuable tool for researchers and engineers in optimizing language model development.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our Telegram Channel, Discord Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 42k+ ML SubReddit
The post This Machine Learning Paper from Stanford and the University of Toronto Proposes Observational Scaling Laws: Highlighting the Surprising Predictability of Complex Scaling Phenomena appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ