The robotics field has historically vacillated between two primary architectural paradigms: modular hierarchical policies and end-to-end policies. Modular hierarchies employ rigid layers such as symbolic planning, trajectory generation, and tracking, while end-to-end policies utilize high-capacity neural networks to map sensory input directly to actions. The emergence of large language models (LLMs) has renewed interest in hierarchical control architectures, with recent studies utilizing LLMs to replace symbolic planners, achieving significant feats like mobile object rearrangement based on open-vocabulary instructions. However, hierarchical architectures still face challenges in defining control primitives and establishing interfaces between layers, particularly in coordinating diverse human-like movements beyond semantic action verbs.
The rise of LLMs has sparked interest in their application to robotics, particularly in hierarchical control architectures. Previous studies have demonstrated utilizing LLMs for high-level reasoning through various approaches such as few-shot prompts, function coding, and interaction with humans via language. Integrating LLMs into task planning and reasoning requires calling lower-level skills, achievable through language-conditioned policies. Also, there’s a growing trend in repurposing large models originally trained for vision or language tasks for robotics applications.
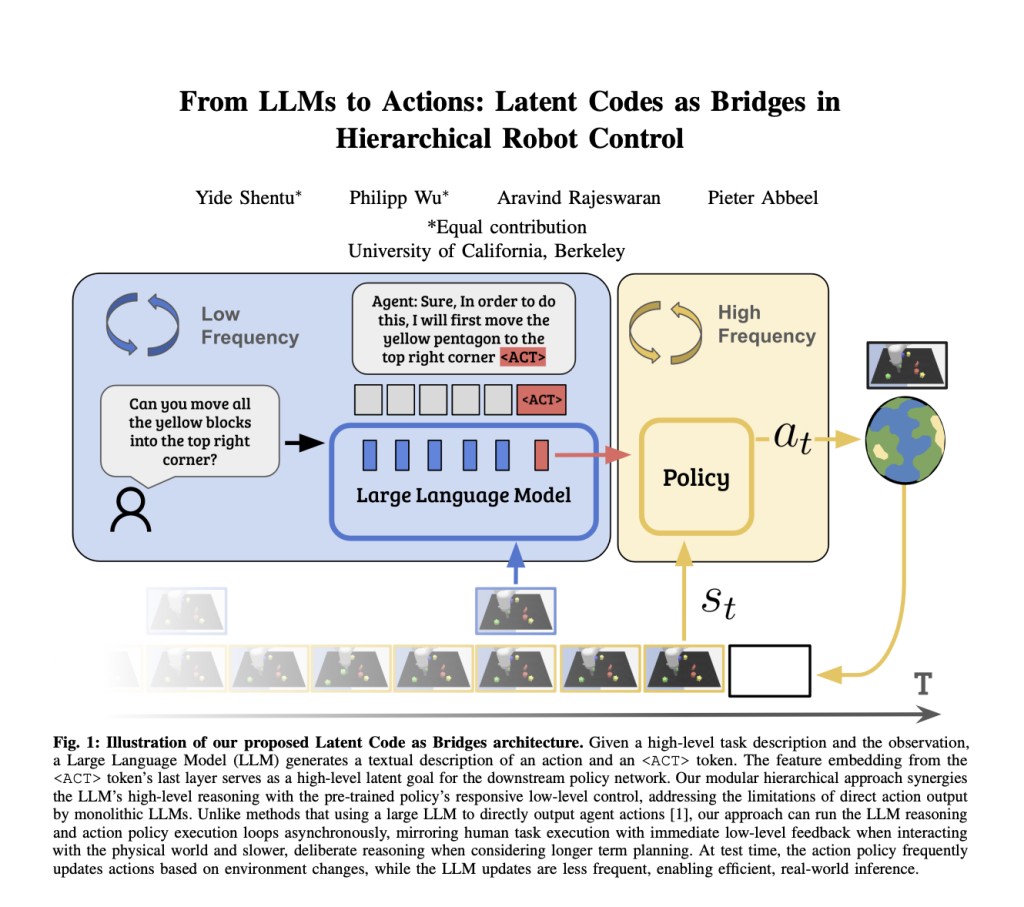
Researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, introduced Latent Codes as Bridges (LCB), a robust policy architecture for control. LCB combines the strengths of modular hierarchical architectures with end-to-end learning. It allows direct utilization of LLMs for high-level reasoning alongside pre-trained skills for low-level control, enhancing them through end-to-end learning. By incorporating a <ACT> token at the interface layer to modulate low-level policies, LCB surpasses the limitations of relying solely on language, which struggles to describe certain behaviors. Also, by employing a separate <ACT> token, LCB preserves the core language generation and reasoning capabilities of LLMs during fine-tuning.
The proposed architecture, LCB, integrates the advantages of modular hierarchical architectures and end-to-end learning. It employs an additional latent code to bridge high-level reasoning with low-level language-conditioned policy, preserving both abstract goals and language embedding space. This approach addresses the limitations of existing methods, offering improved flexibility and preservation of language understanding during fine-tuning. The architecture comprises a pretrained Multimodal LLM and a pretrained policy, facilitating multimodal understanding and action output based on environment observations and conditioning latent. Data processing involves generating conversational-style interactions to train the model for language-guided action execution.
Experiments on Language Table and CALVIN benchmarks reveal LCB’s superiority over baselines, including those with GPT-4V, in tasks necessitating reasoning and multi-step behaviors. LCB’s integration of the vision language model enhances task performance by extracting features effectively.
Summary
This work presents LCB, a robust method merging large language model reasoning with low-level action policies.Â
Unlike prior approaches, LCB integrates these capabilities seamlessly through a learned latent interface.Â
Evaluation on Language Table and CALVIN benchmarks demonstrate LCB’s proficiency in interpreting and executing diverse reasoning and long-horizon tasks.Â
The hierarchical flexibility enabled by LCB holds potential for practical applications in robotics.
Check out the Paper and Project. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our Telegram Channel, Discord Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 42k+ ML SubReddit
The post UC Berkeley Researchers Introduce Learnable Latent Codes as Bridges (LCB): A Novel AI Approach that Combines the Abstract Reasoning Capabilities of Large Language Models with Low-Level Action Policies appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ