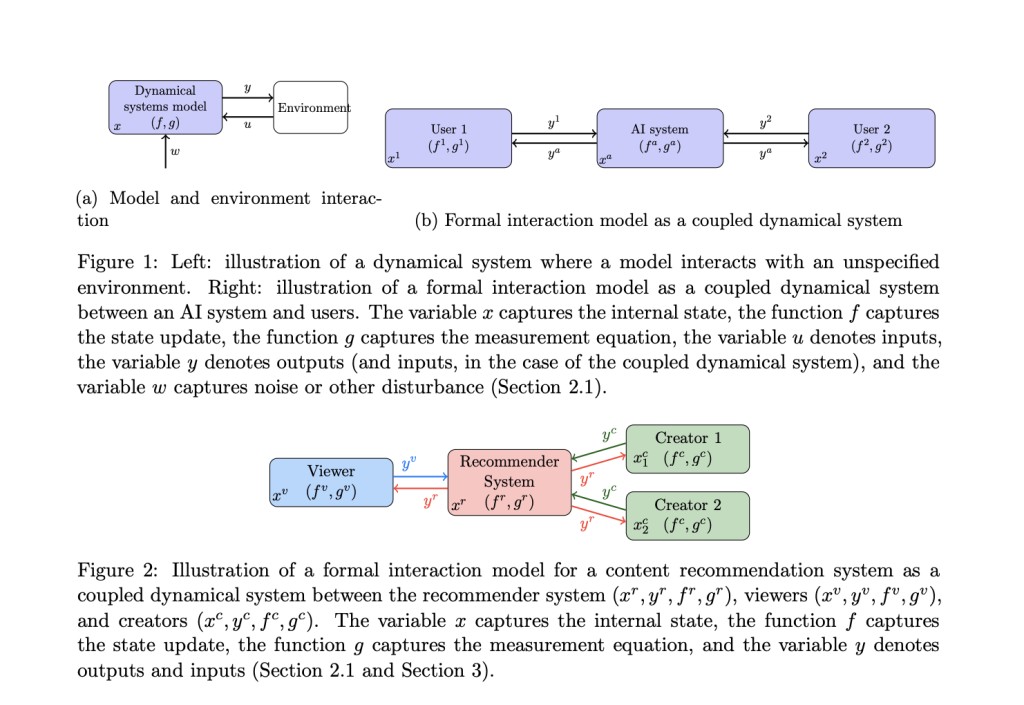
Machine learning has become an important domain that has contributed to developing platforms and products that are data-driven, adaptive, and intelligent. The AI systems help to shape the users, and in turn, users shape these systems. A popular method, Content Recommender Systems (CRS), can interact with viewers and creators and facilitate algorithmic curation and personalization. The CRS interactions can affect downstream recommendations by shaping viewer preferences and content available on the platform. Its old design helps users to navigate songs and videos over email lists, whereas large online platforms use the modern design.
Although these AI systems are helpful, their design and evaluation do not highlight how these systems and users shape one another, and this problem can be seen in multiple learning algorithms. For example, when a large static dataset is trained using supervised learning settings, it fails to prove how the AI system transforms the environment where it operates. Besides, deploying AI systems can harm performance and society on a large scale through distribution shifts. Another problem arises from Reinforcement Learning (RL), which fails to capture key interactions and dynamics between the AI system and users. This paper resolved all these shortcomings of AI systems.
Researchers from Cornell University, the University of California, Princeton University, and the University of Texas at Austin proposed Formal Interaction Models (FIM). This mathematical model formalizes how AI and users shape one another. FIM is a coupled dynamic system between the AI system and users that enhances the AI system’s design and evaluation. It includes four major use cases: (a) it specifies interactions for implementation, (b) it monitors interactions with the help of empirical analysis, (c) it anticipates societal impacts using counterfactual analysis, and (d) it controls societal impacts through interventions. Design axes such as style, granularity, mathematical complexity, and measurability are considered carefully during the model’s design.
FIM helps to create new metrics that capture these societal impacts that lead to benefits in the design of objectives. These new metrics can be optimized through supervised learning or RL-based algorithms to control the societal effects. Few societal impacts can be evaluated directly with the help of a single parameter of FIM, but other effects may arise as complex combinations of multiple parameters. For example, one should emphasize measuring value instead of engagement during a metrics proposal. This paper discusses the optimization of downstream user welfare and ecosystem health with the help of tools from mechanism design to recommender systems design.
Researchers performed analyses, solving various limitations and mostly focusing on anticipating societal impacts and controlling the societal effects. The model designs used during analysis are fairly homogeneous within each interaction type and have a large separation between viewer and creator interactions. Moreover, dynamic models are not used because they create feedback loops due to the feedback of viewers fed into the recommender system regarding the used product from recommended content and use viewer feedback to estimate viewer utilities.
In conclusion, Researchers from four universities proposed Formal Interaction Models (FIM), a mathematical model that formalizes how AI and users shape one another. FIM is a coupled dynamical system between the AI system and users that enhances AI system design and evaluation. This paper mentions four major use cases of FIM and discusses the role of model style, granularity, mathematical complexity, and measurability. Researchers used the dynamical systems language to highlight the limitations in the use cases for future work.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our Telegram Channel, Discord Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 40k+ ML SubReddit
For Content Partnership, Please Fill Out This Form Here..
The post Formal Interaction Model (FIM): A Mathematics-based Machine Learning Model that Formalizes How AI and Users Shape One Another appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ