Google AI recently released Patchscopes to address the challenge of understanding and interpreting the inner workings of Large Language Models (LLMs), such as those based on autoregressive transformer architectures. These models have seen remarkable advancements, but limitations in their transparency and reliability still exist. There are flaws in the reasoning and no clear understanding of how these models make their predictions, which shows that we need tools and frameworks to better understand how they work.Â
Current methods for interpreting LLMs often involve complex techniques that may need to provide more intuitive and human-understandable explanations of the models’ internal representations. The proposed method, Patchscopes, aims to address this limitation by using LLMs themselves to generate natural language explanations of their hidden representations. Unlike previous methods, Patchscopes unifies and extends a broad range of existing interpretability techniques, enabling insights into how LLMs process information and arrive at their predictions. By providing human-understandable explanations, Patchscopes enhances transparency and control over LLM behavior, facilitating better comprehension and addressing concerns related to their reliability.
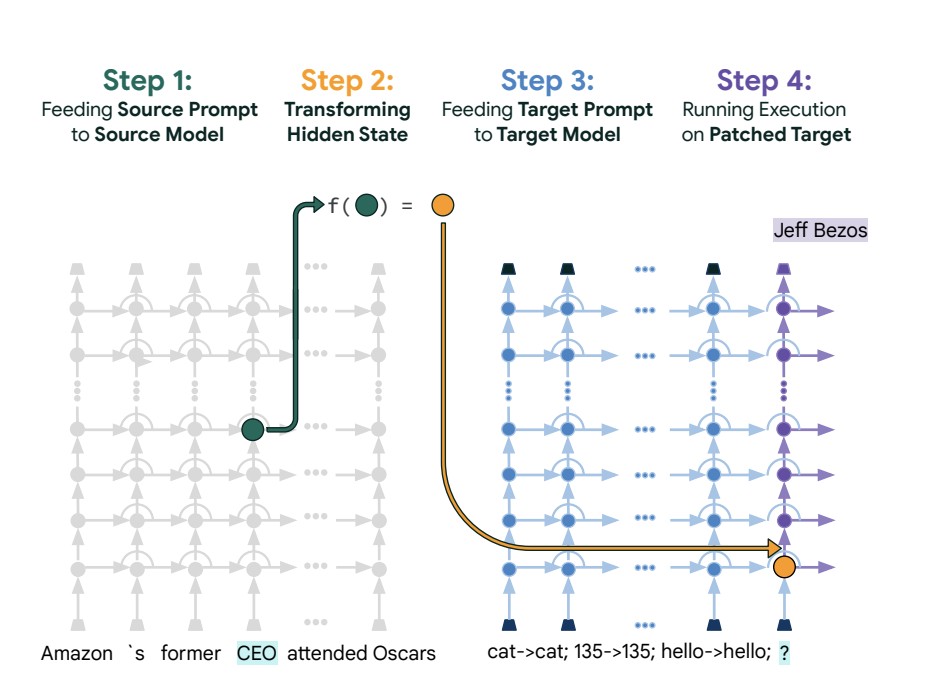
Patchscopes inject hidden LLM representations into target prompts and process the added input to create explanations that humans can understand of how the model understands things internally. For example, in co-reference resolution, Patchscopes can reveal how an LLM understands pronouns like “it†within specific contexts. Patchscopes can shed light on the progression of information processing and reasoning within the model by the examination of hidden representations that are located at various layers of the model. The results of the experiments demonstrate that Patchscopes is effective in a variety of tasks, including next-token prediction, fact extraction, entity explanation, and error correction. These results have demonstrated the versatility and performance of Patchscopes across a wide range of interpretability tasks.
In conclusion, Patchscopes proved to be a significant step forward in understanding the inner workings of LLMs. By leveraging the models’ language abilities to provide intuitive explanations of their hidden representations, Patchscopes enhances transparency and control over LLM behavior. The framework’s versatility and effectiveness in various interpretability tasks, combined with its potential to address concerns related to LLM reliability and transparency, make it a promising tool for researchers and practitioners working with large language models.
Check out the Paper and Blog. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our Telegram Channel, Discord Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 40k+ ML SubReddit
Want to get in front of 1.5 Million AI Audience? Work with us here
The post Google AI Introduces Patchscopes: A Machine Learning Approach that Trains LLMs to Provide Natural Language Explanations of Their Hidden Representations appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ