Large Language Models (LLMs) have transformed Natural Language Processing, but the dominant Transformer architecture suffers from quadratic complexity issues. While techniques like sparse attention have aimed to reduce this complexity, a new breed of models is achieving impressive results through innovative core architectures.Â
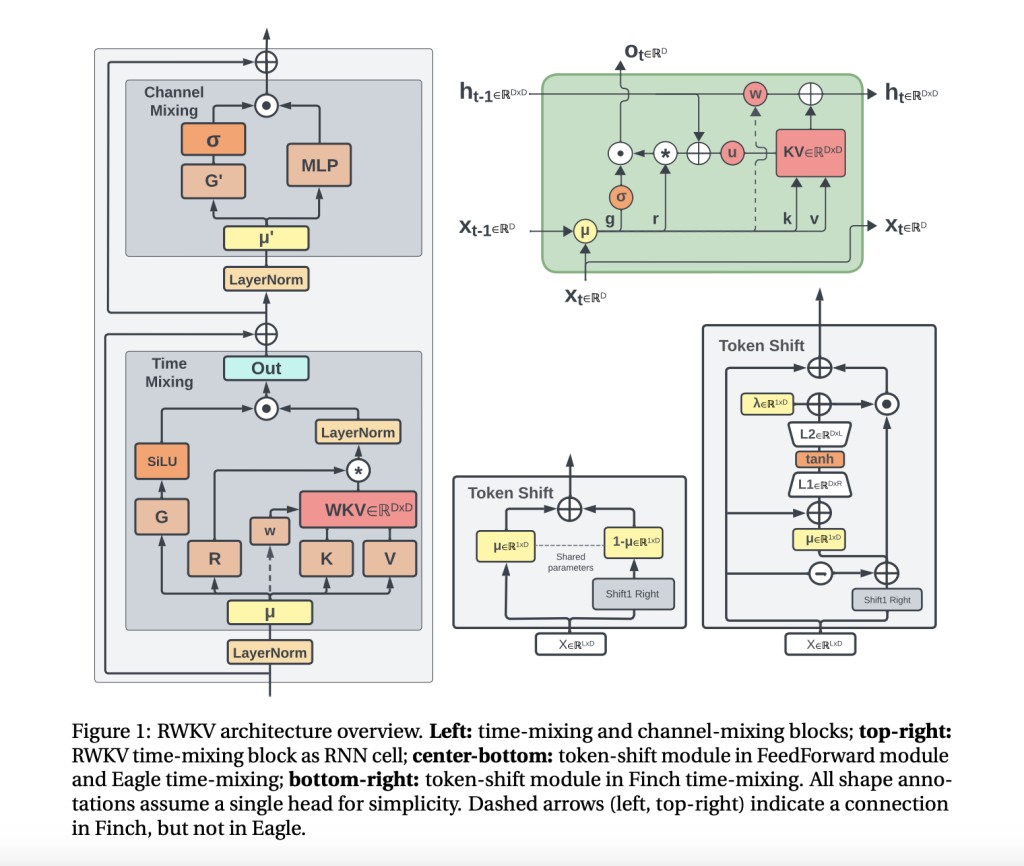
Researchers have introduced Eagle (RWKV-5) and Finch (RWKV-6) in this paper, novel architectures that replace the Transformer’s attention mechanism with efficient recurrence modules. Building upon RWKV-4, Eagle introduces multi-headed matrix-valued states, reformulated receptance, and additional gating. Finch takes it further, with data-dependent functions for time-mixing and token-shifting, allowing for more expressive and flexible modeling.
What makes these models truly unique is their dynamic, data-driven recurrence. In Eagle, the time-mixing weights are static but learned uniquely per channel, accumulating information over time. With Finch, these weights become time-varying and data-dependent, allowing each channel to adapt its memory dynamics based on the input context. This novel approach is augmented by techniques like Low Rank Adaptation, which efficiently adjusts the recurrence parameters.
To bolster performance on diverse data, the researchers also introduce the RWKV World Tokenizer and the massive 1.12 trillion token RWKV World v2 dataset, with a strong emphasis on multilinguality and code.
The results speak for themselves. On multilingual benchmarks, Eagle and Finch significantly outperform comparably-sized models, representing a substantial improvement to the accuracy-compute Pareto frontier. They excel at tasks like associative recall, long context modeling, and the comprehensive Bamboo benchmark. What’s more, their efficient architectures enable faster inference and reduced memory usage compared to sparse Transformer variants.
But these models aren’t just language specialists. The team demonstrates Eagle’s capabilities on music modeling, with a 2% improvement over the previous RWKV-4 architecture. VisualRWKV, an instruction-tuned multimodal variant, achieves impressive results on visual understanding benchmarks, matching or outperforming much larger models.
While Eagle and Finch have their limitations, such as challenges with text embedding tasks, they represent a significant leap forward in efficient and high-performing language modeling. By departing from the traditional Transformer architecture and introducing dynamic, data-driven recurrence mechanisms, these models achieve impressive results across a wide range of benchmarks while maintaining computational efficiency.
Check out the Paper, Github, and HF Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our Telegram Channel, Discord Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 40k+ ML SubReddit
Want to get in front of 1.5 Million AI Audience? Work with us here
The post Eagle (RWKV-5) and Finch (RWKV-6): Marking Substantial Progress in Recurrent Neural Networks-Based Language Models by Integrating Multiheaded Matrix-Valued States and Dynamic Data-Driven Recurrence Mechanisms appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ