In Large Language Models (LLMs), reasoning involves dissecting a problem’s logical structure and turning it into a sequence of logical steps that lead to a solution. For LLMs, this procedure has proven difficult, particularly in algorithmic reasoning where intricate logical patterns must be interpreted and transformed into a series of processes.
Understanding patterns inside an issue and decomposing them into a series of logical stages to arrive at a solution are key components of algorithmic thinking. Although a variety of reasoning tasks have demonstrated the potential of LLMs, algorithmic reasoning remains difficult because of its complex structure.Â
In order to convey the reasoning required to solve a particular instance or topic, recent studies have tried to address this challenge by employing programming languages like Python. It is challenging to write executable code that faithfully captures the reasoning in a single inference call and does it in real-time. Even if two instances need the same logic, the code created for one cannot be utilized for another.
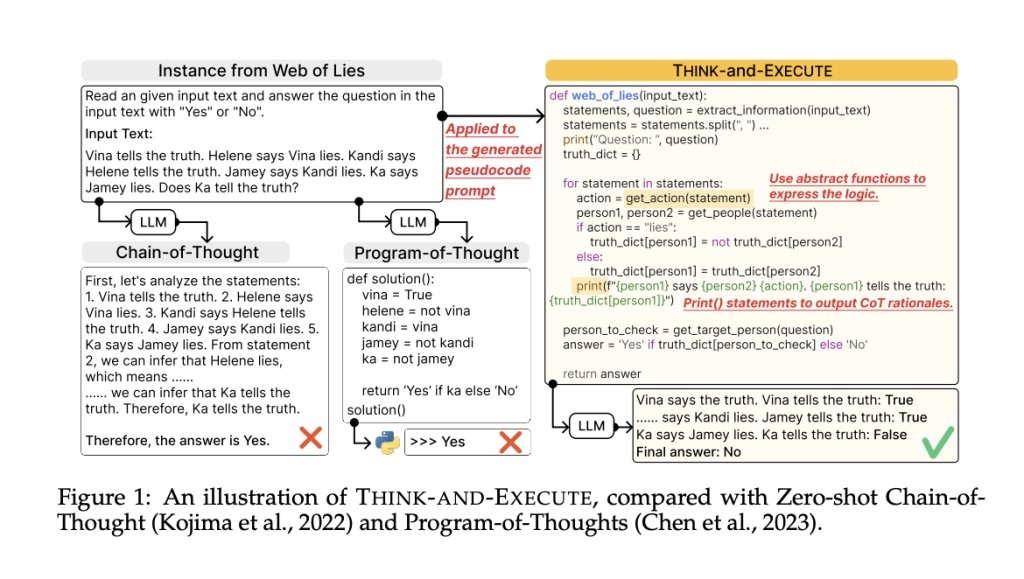
In recent research, a team of researchers from Yonsei University and KAIST AI has presented THINK-AND-EXECUTE, a unique architecture that splits the language model reasoning process into two parts to get over the limitations. The two parts are as follows.Â
THINK: The framework looks for a task-level logic in this phase that is shared by all instances of a certain task. Next, pseudocode, which offers a more adaptive and flexible representation than programming languages like Python, has been used to express the shared logic.Â
EXECUTE: The framework adapts the task-level logic to each unique instance after it has been defined and stated in pseudocode. Subsequently, it emulates the pseudocode execution for every occurrence, efficiently utilizing the found logic to resolve the issue.
The effectiveness of THINK-AND-EXECUTE has been shown through comprehensive trials on seven algorithmic thinking tasks. The framework beats multiple robust baselines, including Program-of-Thought (PoT) and Chain-of-Thought (CoT), which rely on instance-specific reasoning techniques. This implies that learning task-level logic can help LLMs become more proficient reasoners. Even though these models have been trained to follow instructions in regular language, the results have demonstrated that pseudocode is a more useful tool for directing LLM thinking than natural language.Â
The team has summarized their primary contributions as follows.
A new and unique thinking paradigm known as THINK-AND-EXECUTE has been suggested. This framework encapsulates the common logical structure of a given job using pseudocode. The method allows for more efficient reasoning in LLMs by utilizing pseudocode, which provides flexibility and adaptability.Â
The team has shown that THINK-AND-EXECUTE outperforms well-established baselines like Chain-of-Thought and Program-of-Thought prompting, based on substantial research on a variety of algorithmic tasks inside the Big-Bench Hard dataset. This demonstrates how well the system works to improve reasoning abilities in a variety of issue domains.
Utilizing THINK-AND-EXECUTE, the team has demonstrated the effectiveness of the method by effectively transferring the pseudocode produced by an LLM to smaller language models. This indicates that the approach is both generalizable and scalable, meaning it can be applied to a variety of model topologies and sizes.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our Telegram Channel, Discord Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 40k+ ML SubReddit
The post ‘Think-and-Execute’: A Machine Learning Framework that Encapsulates the Common Logical Structure of a Job Using Pseudocode for Efficient Reasoning in Large Language Models (LLMs) appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ