We’ve been working a lot with Filament since 2023. After publishing many tutorials on this website, we decided to dedicate…
Libraries & Frameworks
In this tutorial, we will walk through how to perform migration with MongoDB in Laravel The post Laravel Migration With…
An opinionated Laravel starter kit with Vue.js, Inertia.js, and Tailwind CSS including authentication, admin dashboard, and essential features for building…
A Test Automation Center of Excellence (TA CoE) centralizes and scales QA processes, driving higher software quality, faster releases, and lower risk. This blog explores its components, strategic benefits, a case study from the insurance sector, and why select Tx to set up your TA CoE.
The post Breaking the QA Barrier: Build a Test Automation CoE That Scales Excellence first appeared on TestingXperts.
Laravel UI Components using TailwindCSS, Blade Templates and vanilla Javascript Source: Read MoreÂ
In the digital era where speed, quality, and agility define success, test automation has become essential to software development lifecycles. Organizations must deliver faster without compromising on quality, and manual testing often becomes a bottleneck. Enter Tosca a comprehensive continuous testing platform from Tricentis that enables enterprises to automate testing at scale efficiently. Tosca stands
The post Tosca : Guidelines and Best Practices appeared first on Codoid.
Tired of constantly wrestling with type errors in API responses? Fluent methods offer a type-safe, boilerplate-free way to streamline your…
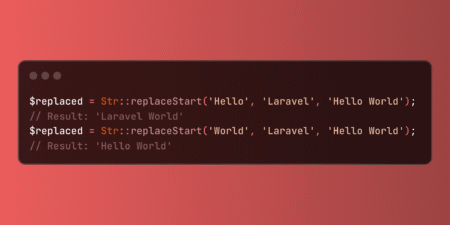
Laravel’s Str::replaceStart method enables precise prefix replacement by modifying strings only when they begin with specific content. This utility excels…
The Fathom Analytics package for Laravel Livewire provides Alpine.js directives and helpers for seamless Fathom Analytics event tracking in Blade…
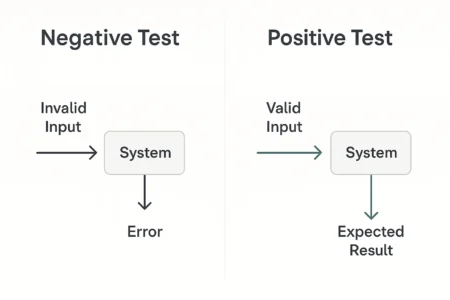
When every click behaves exactly as a product owner expects, it is tempting to believe the release is rock‑solid. However, real users and real attackers rarely follow the script. They mistype email addresses, paste emojis into form fields, lose network connectivity halfway through checkout, or probe your APIs with malformed JSON. Negative testing exists precisely
The post Negative Scenarios in Testing: Proven Ways to Bulletproof Your Software appeared first on Codoid.
The OpenRouter package for Laravel helps you integrate OpenRouter into your Laravel applications. OpenRouter is a unified interface for Large…
Useful Laravel links to read/watch for this week of June 5, 2025. Source: Read MoreÂ
In Laravel, you often need to check things before users reach the Controller. For that, you would use Middleware. Let…
Feeling overwhelmed by the clutter of managing optional form fields? The ‘When Has’ method is your solution. It streamlines your…
Laravel’s Str::is method now supports case-insensitive pattern matching through a third boolean parameter. This enhancement enables more flexible string comparisons…
Laravel’s whereDoesntHaveRelation methods simplify querying records that lack specific relationships. These utilities eliminate complex closure syntax for negative relation queries,…
The Laravel team released v12.16.0, with an “AsUri” model cast, contextual service container binding using PHP 8 attributes, and more.…
When generating a PDF with DomPDF package, you may need a PDF with more than one page. For such cases,…
Spatie has a modern package spatie/laravel-pdf for generating PDF files with some design customizations. This tutorial will show how to…
A simple CLI tool for managing a project’s git hooks across multiple members. Source: Read MoreÂ