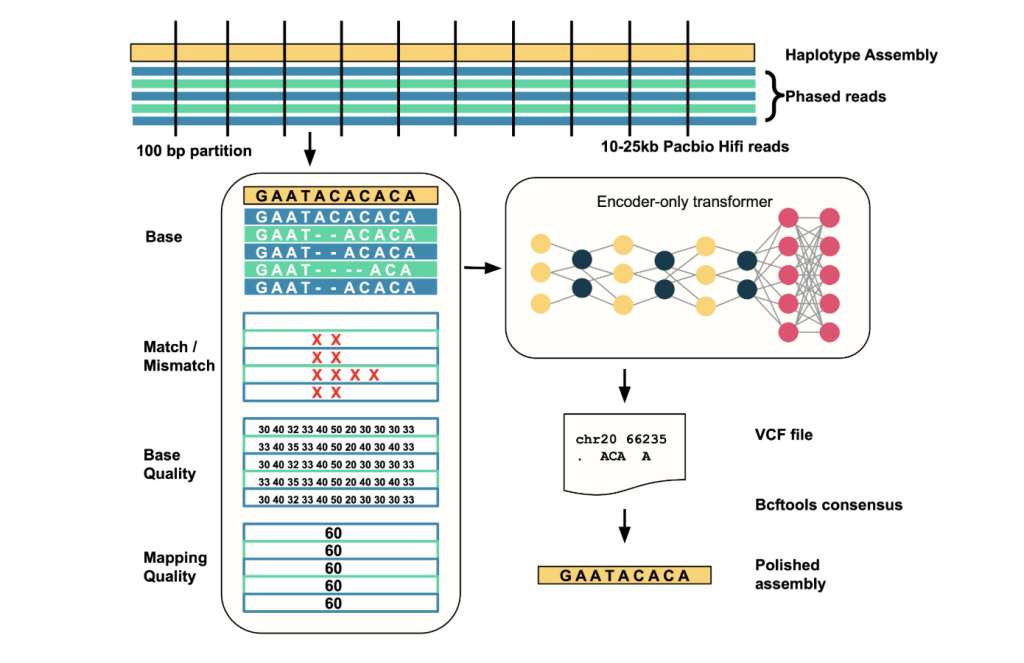
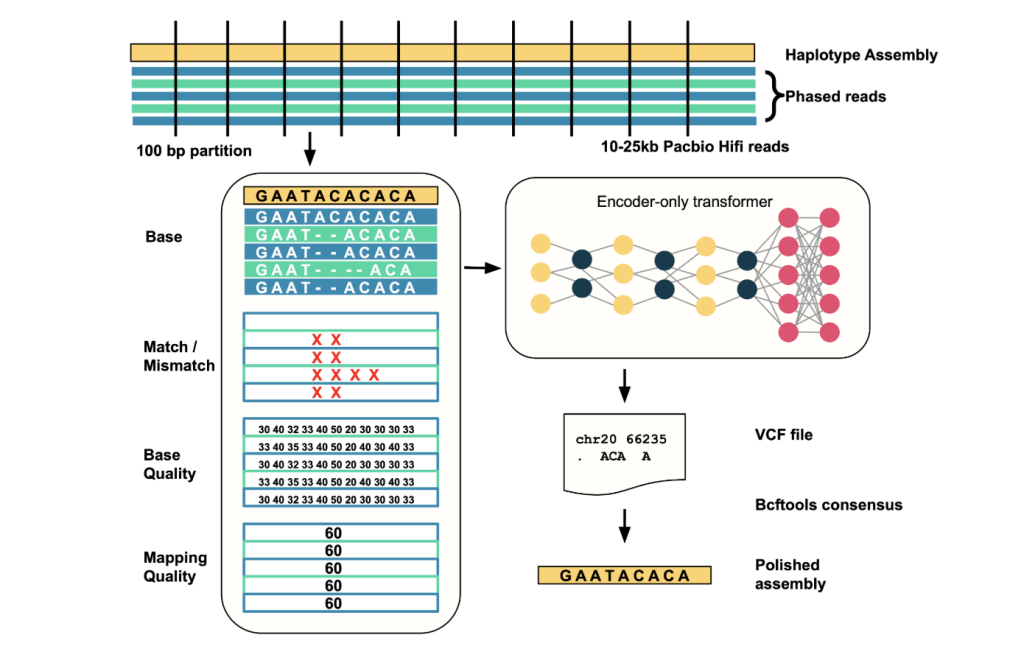
Google AI, in collaboration with the UC Santa Cruz Genomics Institute, has introduced DeepPolisher, a cutting-edge deep learning tool designed to substantially improve the accuracy of genome assemblies by correcting base-level errors. Its notable efficacy was recently demonstrated in advancing the Human Pangenome Reference, a major milestone in genomics research.
The Challenge of Accurate Genome Assembly
A reference genome is an essential foundation for understanding genetic diversity, heredity, disease mechanisms, and evolutionary biology. Modern sequencing technologies, including those developed by Illumina and Pacific Biosciences, have dramatically improved sequencing accuracy and throughput—but even with technological breakthroughs, assembling an error-free human genome (comprising over 3 billion nucleotides) remains immensely challenging. Even a minuscule per-base error rate can result in thousands of errors which can obscure key genetic variations or mislead downstream analyses.
What Is DeepPolisher?
DeepPolisher is an open-source, transformer-based sequencing correction tool. Building on advances from DeepConsensus, it takes advantage of transformer deep learning architectures to further reduce errors in genome assembly, particularly insertion and deletion (indel) errors, which have a profound impact by shifting reading frames and can cause important genes or regulatory elements to be missed during annotation.
- Technology: Encoder-only transformer, adapting proven techniques in natural language processing for genomics.
- Training data: Leveraged a human cell line extensively characterized by NIST and NHGRI, sequenced with various platforms to ensure near-complete accuracy (~99.99999% correctness, between 300–1,000 errors in 6 billion bases).
How Does It Work? (Technical Overview)
- Input Alignment: Takes aligned PacBio HiFi reads against a haplotype-resolved genome assembly as input.
- Error Site Detection: Scans the assembly in 25kb windows; identifies candidate error sites where read evidence deviates from the assembly.
- Data Encoding: For each window containing putative errors (<100bp), it creates a multi-channel tensor representation of read alignment features such as base, base quality, mapping quality, and match/mismatch status.
- Model Inference: Feeds these tensors into the transformer, which predicts corrected sequences for these regions.
- Output Correction: Outputs differences in VCF format, which are then applied to the assembly to produce a polished, highly accurate sequence using tools like bcftools.
Performance and Impact
DeepPolisher delivers substantial improvements:
- Total error reduction: ~50%
- Indel error reduction: >70%
- Error rates: Achieves an error rate as low as one base error per 500,000 assembled bases in real-world deployment with the Human Pangenome Reference Consortium (HPRC).
- Genomic Q-score improvement: Raises assembly quality from Q66.7 to Q70.1 on average (Q-score is a logarithmic measure of per-base error rate; higher is better. Q70.1 implies <1 error per 12 million nucleotides)
- Every sample tested by HPRC showed improvement.
These advances directly impact the reliability and accuracy of derived references, such as in the Human Pangenome Reference, which saw a fivefold data expansion and substantial error reduction due to DeepPolisher.

Deployment and Applications
- Integrated in major projects: Used in HPRC’s second data release, providing high-accuracy reference assemblies for 232 individuals, ensuring broad ancestral diversity in genomic references.
- Open-source access: Available via GitHub, with case studies and Dockerized workflows for use on assemblies produced by tools like HiFiasm and sequenced with PacBio HiFi reads.
- Generalizability: While initially focused on human genomes, the structure and approach are adaptable to other organisms and sequencing platforms, fostering accuracy across the genomics community.
Practical Workflow Example
A typical workflow using DeepPolisher might involve:
- Input: HiFiasm diploid assembly and PacBio HiFi reads, phase-aligned using the PHARAOH pipeline.
- Running: Dockerized commands for image creation, inference, and correction application.
- Output: Separate VCF files for maternal and paternal assemblies, polished FASTAs after bcftools consensus step.
- Assessment: Use of benchmarking tools (e.g., dipcall, Hap.py) to quantify improvements in error rates and variant accuracy.
Conclusion and Future Directions
DeepPolisher represents a leap forward in genome polishing technology—sharply reducing error rates and unlocking higher resolution for functional genomics, rare variant discovery, and clinical applications. By targeting the remaining barrier to perfect genome assemblages, it enables more accurate diagnosis, population-level genetic studies, and paves the way for next-generation reference projects benefiting biomedical research and medicine.
Check out the Technical details, GitHub Page and Paper. Feel free to check out our GitHub Page for Tutorials, Codes and Notebooks. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post Google AI Releases DeepPolisher: A New Deep Learning Tool that Improves the Accuracy of Genome Assemblies by Precisely Correcting Base-Level Errors appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ