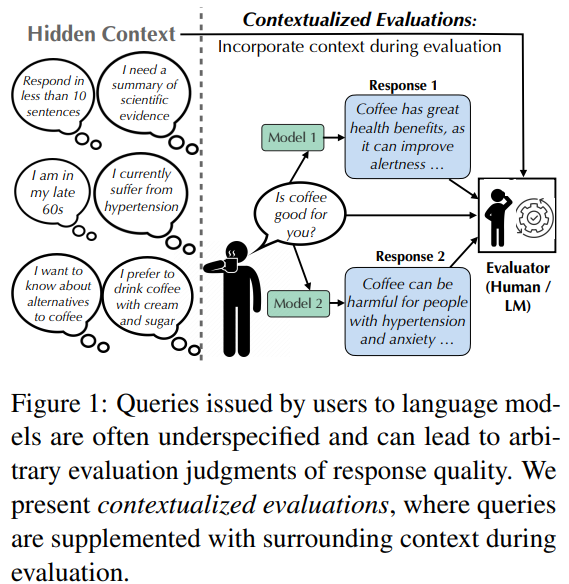
Language model users often ask questions without enough detail, making it hard to understand what they want. For example, a question like “What book should I read next?” depends heavily on personal taste. At the same time, “How do antibiotics work?” should be answered differently depending on the user’s background knowledge. Current evaluation methods often overlook this missing context, resulting in inconsistent judgments. For instance, a response praising coffee might seem fine, but could be unhelpful or even harmful for someone with a health condition. Without knowing the user’s intent or needs, it’s difficult to fairly assess a model’s response quality.
Prior research has focused on generating clarification questions to address ambiguity or missing information in tasks such as Q&A, dialogue systems, and information retrieval. These methods aim to improve the understanding of user intent. Similarly, studies on instruction-following and personalization emphasize the importance of tailoring responses to user attributes, such as expertise, age, or style preferences. Some works have also examined how well models adapt to diverse contexts and proposed training methods to enhance this adaptability. Additionally, language model-based evaluators have gained traction due to their efficiency, although they can be biased, prompting efforts to improve their fairness through clearer evaluation criteria.
Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, the Allen Institute for AI, and the University of Maryland, College Park have proposed contextualized evaluations. This method adds synthetic context (in the form of follow-up question-answer pairs) to clarify underspecified queries during language model evaluation. Their study reveals that including context can significantly impact evaluation outcomes, sometimes even reversing model rankings, while also improving agreement between evaluators. It reduces reliance on superficial features, such as style, and uncovers potential biases in default model responses, particularly toward WEIRD (Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich, Democratic) contexts. The work also demonstrates that models exhibit varying sensitivities to different user contexts.
The researchers developed a simple framework to evaluate how language models perform when given clearer, contextualized queries. First, they selected underspecified queries from popular benchmark datasets and enriched them by adding follow-up question-answer pairs that simulate user-specific contexts. They then collected responses from different language models. They had both human and model-based evaluators compare responses in two settings: one with only the original query, and another with the added context. This allowed them to measure how context affects model rankings, evaluator agreement, and the criteria used for judgment. Their setup offers a practical way to test how models handle real-world ambiguity.
Adding context, such as user intent or audience, greatly improves model evaluation, boosting inter-rater agreement by 3–10% and even reversing model rankings in some cases. For instance, GPT-4 outperformed Gemini-1.5-Flash only when context was provided. Without it, evaluations focus on tone or fluency, while context shifts attention to accuracy and helpfulness. Default generations often reflect Western, formal, and general-audience biases, making them less effective for diverse users. Current benchmarks that ignore context risk produce unreliable results. To ensure fairness and real-world relevance, evaluations must pair context-rich prompts with matching scoring rubrics that reflect the actual needs of users.
In conclusion, Many user queries to language models are vague, lacking key context like user intent or expertise. This makes evaluations subjective and unreliable. To address this, the study proposes contextualized evaluations, where queries are enriched with relevant follow-up questions and answers. This added context helps shift the focus from surface-level traits to meaningful criteria, such as helpfulness, and can even reverse model rankings. It also reveals underlying biases; models often default to WEIRD (Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich, Democratic) assumptions. While the study uses a limited set of context types and relies partly on automated scoring, it offers a strong case for more context-aware evaluations in future work.
Check out the Paper, Code, Dataset and Blog. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. SUBSCRIBE NOW to our AI Newsletter
The post Why Context Matters: Transforming AI Model Evaluation with Contextualized Queries appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ