What is Databricks Lakebase?
Databricks Lakebase is a Postgres OLTP engine, integrated into Databricks Data Intelligence Platform. A database instance is a compute type that provides fully managed storage and compute resources for a postgres database. Lakebase leverages an architecture that separates compute and storage, which allows independent scaling while supporting low latency (<10ms) and high concurrency transactions.
Databricks has integrated this powerful postgres engine along with sophisticated capabilities that are benefited by Databricks recent acquisition of Neon. Lakebase is fully managed by Databricks, which means no infrastructure has to be provisioned and maintained separately. In addition to traditional OLTP engine, Lakebase comes with below features,
- Openness: Lakebase are built on open-source standards
- Storage and compute separation: Lakebase stores data in data lakes in open format. It enables scaling storage and compute independently.
- Serverless: Lakebase is lightweight, meaning it can scale instantly up and down based on the load. It can scale down to zero, at which the cost of the lakebase is just for the storage of data only. No compute cost will be applied.
- Modern development workflow: Branching a database is as simple as branching a code repository. It is done near instantly.
- Built for AI Agents: Lakebases are designed to support a large number of AI agents. It’s branching and checkpointing capabilities enable AI agents to experiment and rewind to any point in time.
- Lakehouse Integration: Lakebase make it easy to combine operational, analytical and AI systems without complex ETL pipelines.
In this article, we shall discuss in detail about how database branching feature works in Lakebase.
Database Branching
Database branching is one of the unique features introduced in Lakebase, that enables to branch out a database. It resembles the exact behavior of how code branch could be branched out from an existing branch.
Branching database is beneficial for an isolated test environment or point in time recovery. Lakebase uses copy-on-write branching mechanism to create an instant zero-copy clone of the database, with dedicated compute to operate on that branch. With zero-copy clone, it enables to create a branch of parent database of any size instantly.
The child branch is managed independently of the parent branch. With child isolated database branch, one can perform testing/debugging in the production copy of data. Though both parent and child databases appear separate, physically both instances would be pointing to same data pages. Under the hood, child database will be pointing to the actual data pages which parent is pointing to. When a change occurs in any of the data in child branch, then a new data page will be created with the new changes, and it will be available only to the branch. Any changes done in branch will not reflect in parent branch.
How branching works
The below diagrams represent how database branching works under the hood,


Lakebase in action
Here is the demonstration of how Lakebase instance can be created, branch out an instance and how table changes behave,
To create Lakebase instance, login Databricks and navigate to Compute -> OLTP Database tab -> Click “Create New Instance” button,

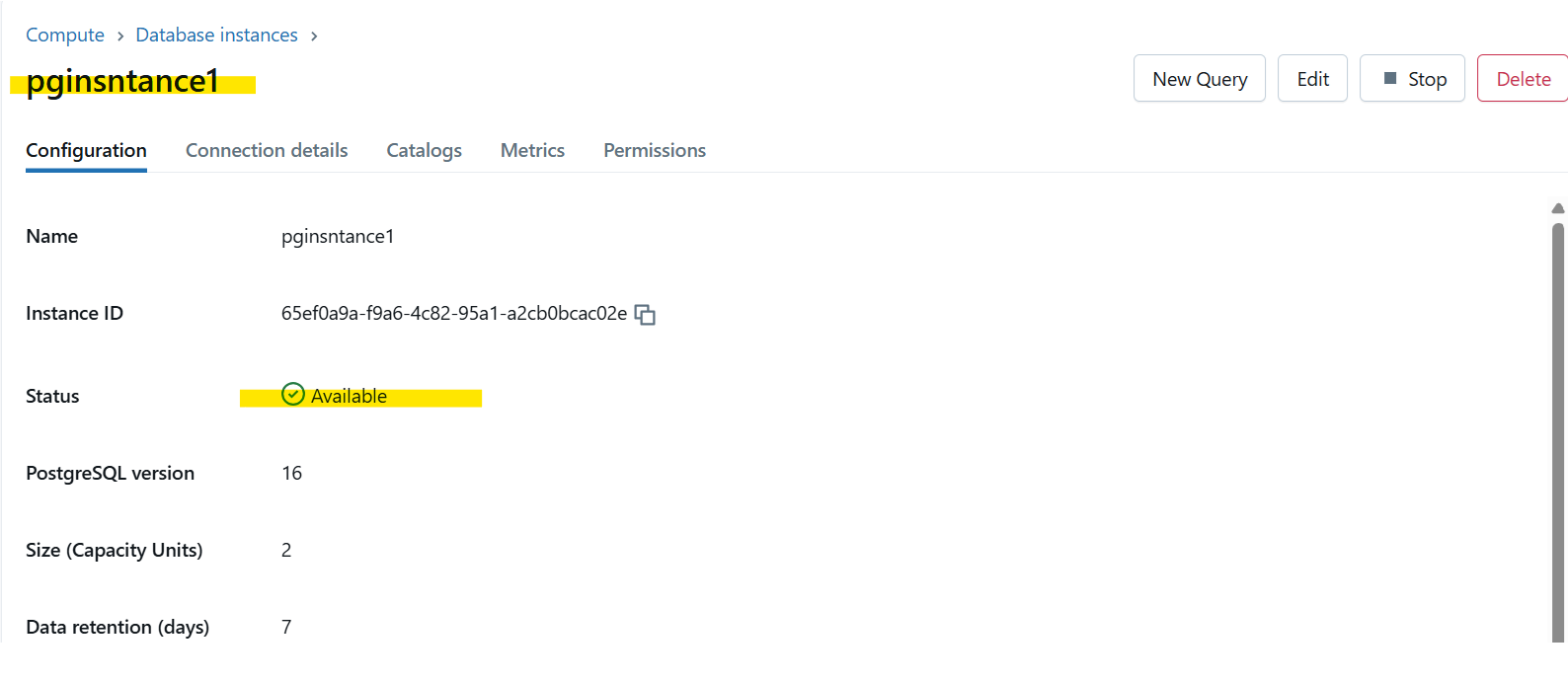
Click “New Query” to launch SQL Editor for PostgreSQL Database. In current instance, let’s create a new table and add some records.
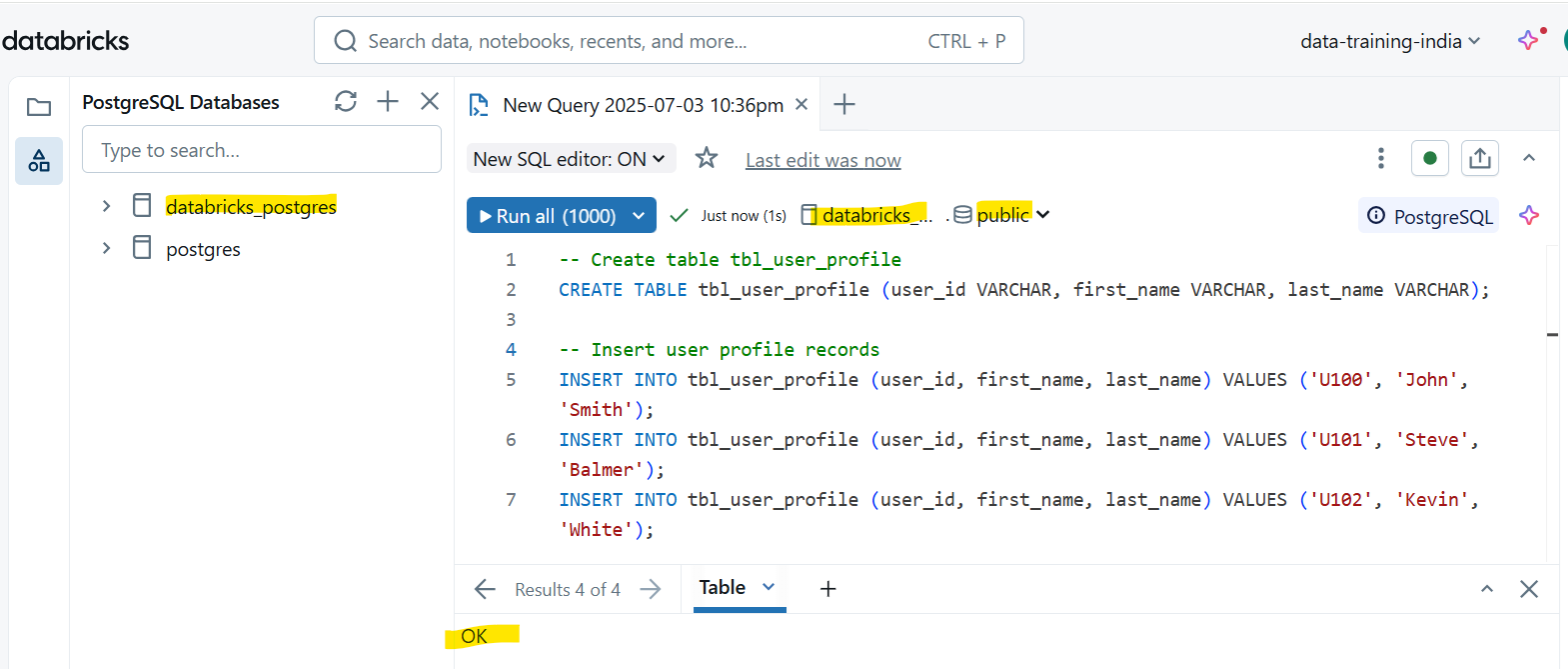
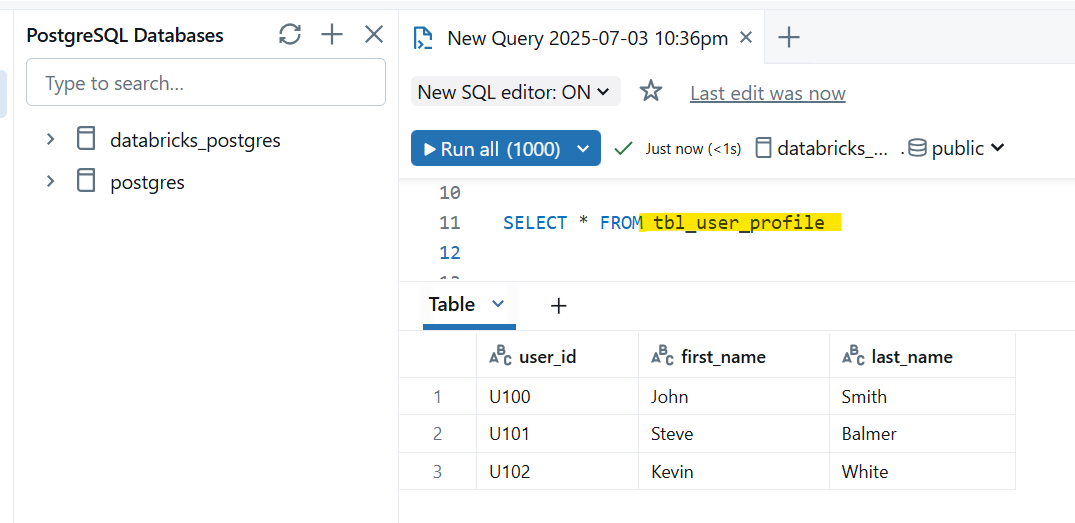
Let’s create a database branch “pginstance2” from instance “pginstance1”. Goto Compute –> OLTP Database –> Create Database instance
Enter new instance name and expand “Advanced Settings” -> Enable “Create from parent” option -> Enter the source instance name “pginstance1”.
Under “Include data from parent up to”, select “Current point in time” option. Here, we can choose any specific point in time instance too.

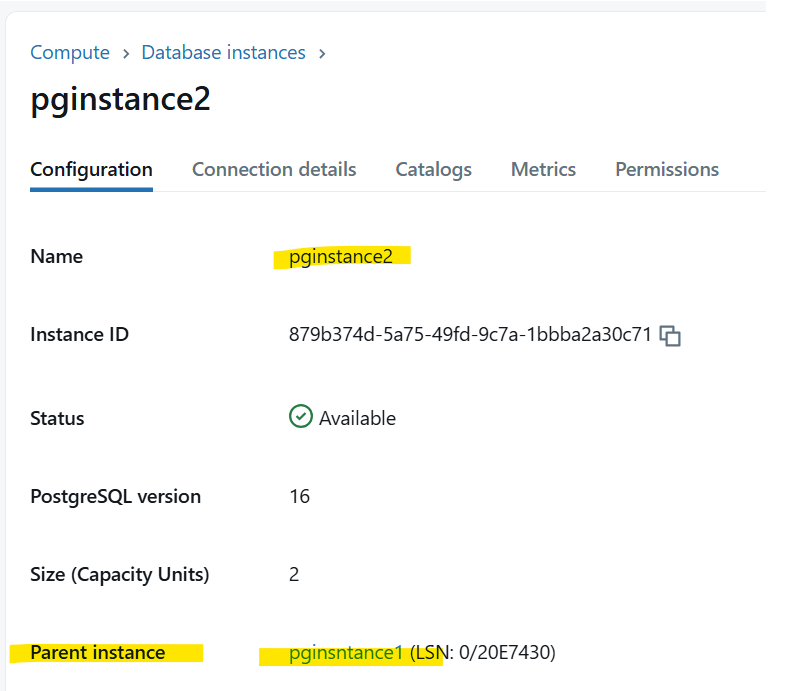
Launch SQL Editor from pginstance2 database instance and query tbl_user_profile table

Now, let’s insert new record and update an existing record in the tbl_user_profile table in pginstance2,

Now, let’s switch back to parent database instance pginsntance1 and query tbl_user_profile table. The table in pginsntance1 should still be only 3 records. All the changes done in tbl_user_profile table should be available only in pginstance2.

Conclusion
Database changes that are done in one branch will not impact/reflect in another branch, thereby provide clear isolation of database at scale. Currently Lakebase do not have a feature to merge database branch. However, Databricks is committed and working towards database merge capability in near future.
Source: Read MoreÂ
