Redefining Job Execution with AI Agents
AI agents are reshaping how jobs are performed by offering tools that execute complex, goal-directed tasks. Unlike static algorithms, these agents combine multi-step planning with software tools to handle entire workflows across various sectors, including education, law, finance, and logistics. Their integration is no longer theoretical—workers are already applying them to support a variety of professional duties. The result is a labor environment in transition, where the boundaries of human and machine collaboration are being redefined on a daily basis.
Bridging the Gap Between AI Capability and Worker Preference
A persistent problem in this transformation is the disconnect between what AI agents can do and what workers want them to do. Even if AI systems are technically capable of taking over a task, workers may not support that shift due to concerns about job satisfaction, task complexity, or the importance of human judgment. Meanwhile, tasks that workers are eager to offload may lack mature AI solutions. This mismatch presents a significant barrier to the responsible and effective deployment of AI in the workforce.

Beyond Software Engineers: A Holistic Workforce Assessment
Until recently, assessments of AI adoption often centered on a handful of roles, such as software engineering or customer service, limiting understanding of how AI impacts broader occupational diversity. Most of these approaches also prioritized company productivity over worker experience. They relied on an analysis of current usage patterns, which does not provide a forward-looking view. As a result, the development of AI tools has lacked a comprehensive foundation grounded in the actual preferences and needs of people performing the work.
Stanford’s Survey-Driven WORKBank Database: Capturing Real Worker Voices
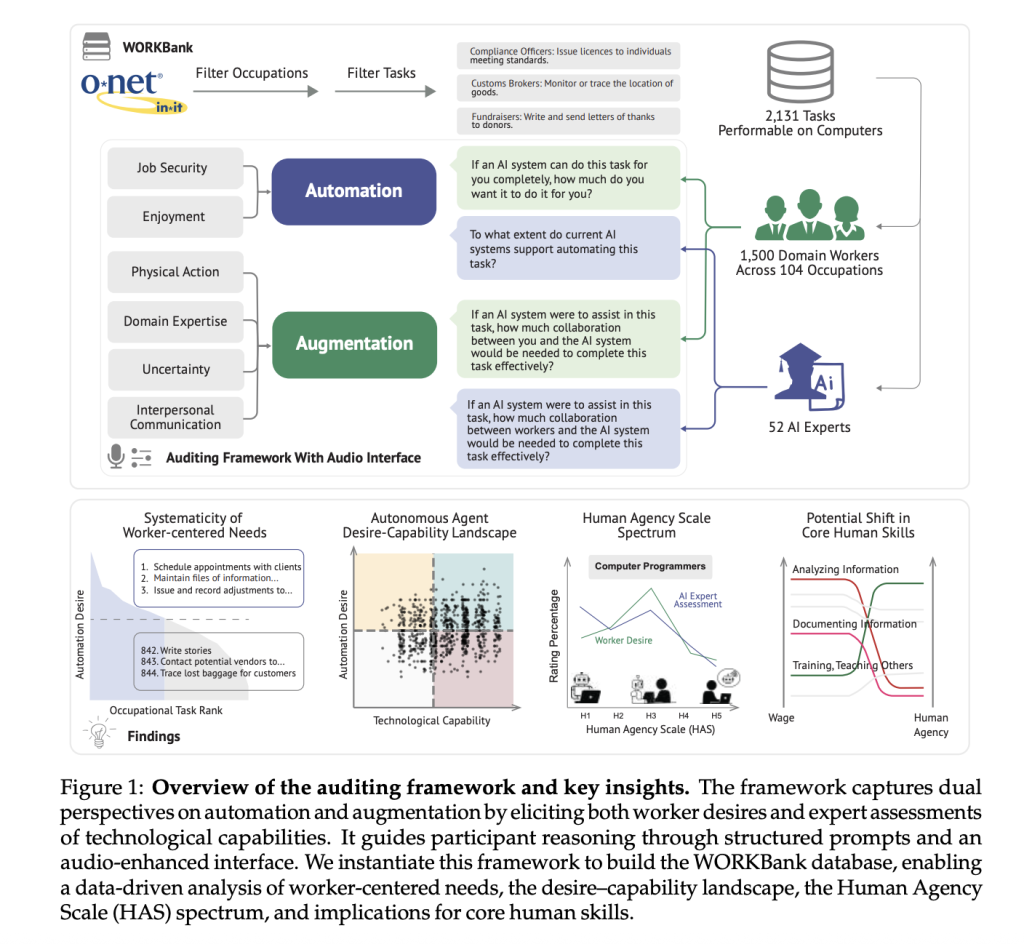
The research team from Stanford University introduced a survey-based auditing framework that evaluates which tasks workers would prefer to see automated or augmented and compares this with expert assessments of AI capability. Using task data from the U.S. Department of Labor’s O*NET database, researchers created the WORKBank, a dataset based on responses from 1,500 domain workers and evaluations from 52 AI experts. The team employed audio-supported mini-interviews to collect nuanced preferences. It introduced the Human Agency Scale (HAS), a five-level metric that captures the desired extent of human involvement in task completion.

Human Agency Scale (HAS): Measuring the Right Level of AI Involvement
At the center of this framework is the Human Agency Scale, which ranges from H1 (full AI control) to H5 (complete human control). This approach recognizes that not all tasks benefit from full automation, nor should every AI tool aim for it. For example, tasks rated H1 or H2—like transcribing data or generating routine reports—are well-suited for independent AI execution. Meanwhile, tasks such as planning training programs or participating in security-related discussions were often rated at H4 or H5, reflecting the high demand for human oversight. The researchers gathered dual inputs: workers rated their desire for automation and preferred HAS level for each task, while experts evaluated AI’s current capability for that task.
Insights from WORKBank: Where Workers Embrace or Resist AI
The results from the WORKBank database revealed clear patterns. Approximately 46.1% of tasks received a high desire for automation from workers, particularly those viewed as low-value or repetitive. Conversely, significant resistance was found in tasks involving creativity or interpersonal dynamics, regardless of AI’s technical ability to perform them. By overlaying worker preferences and expert capabilities, tasks were divided into four zones: the Automation “Green Light” Zone (high capability and high desire), Automation “Red Light” Zone (high capability but low desire), R&D Opportunity Zone (low capability but high desire), and Low Priority Zone (low desire and low capability). 41% of tasks aligned with companies funded by Y Combinator fell into the Low Priority or Red Light zones, indicating a potential misalignment between startup investments and worker needs.
Toward Responsible AI Deployment in the Workforce
This research offers a clear picture of how AI integration can be approached more responsibly. The Stanford team uncovered not only where automation is technically feasible but also where workers are receptive to it. Their task-level framework extends beyond technical readiness to encompass human values, making it a valuable tool for AI development, labor policy, and workforce training strategies.
TL;DR:
This paper introduces WORKBank, a large-scale dataset combining worker preferences and AI expert assessments across 844 tasks and 104 occupations, to evaluate where AI agents should automate or augment work. Using a novel Human Agency Scale (HAS), the study reveals a complex automation landscape, highlighting a misalignment between technical capability and worker desire. Findings show that workers welcome automation for repetitive tasks but resist it in roles requiring creativity or interpersonal skills. The framework offers actionable insights for responsible AI deployment aligned with human values.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post New AI Framework Evaluates Where AI Should Automate vs. Augment Jobs, Says Stanford Study appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ