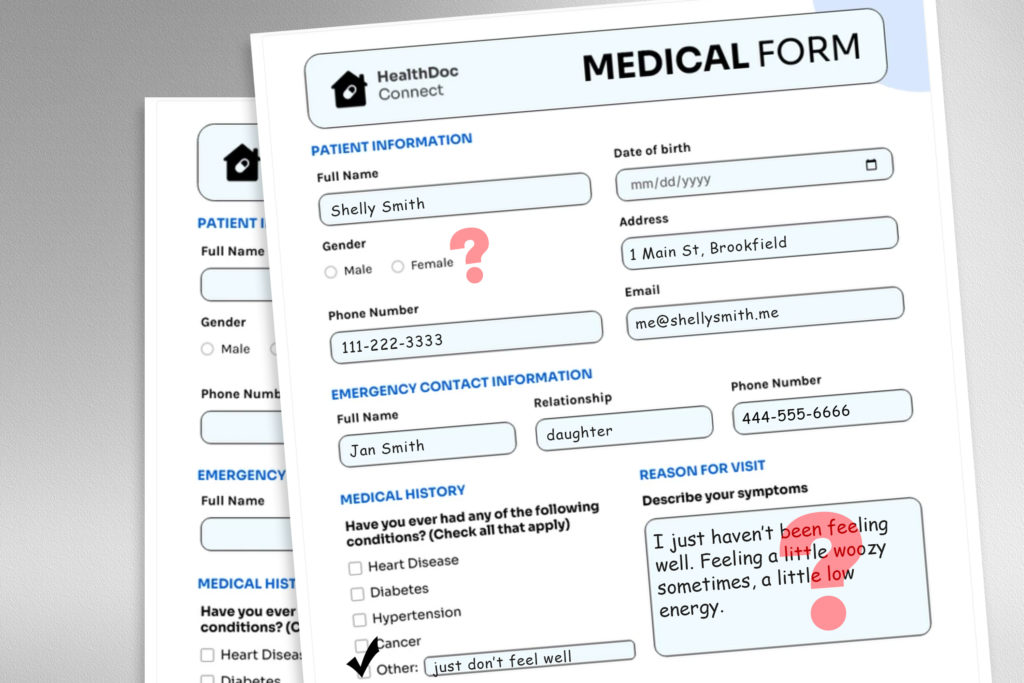
A large language model (LLM) deployed to make treatment recommendations can be tripped up by nonclinical information in patient messages, like typos, extra white space, missing gender markers, or the use of uncertain, dramatic, and informal language, according to a study by MIT researchers.
They found that making stylistic or grammatical changes to messages increases the likelihood an LLM will recommend that a patient self-manage their reported health condition rather than come in for an appointment, even when that patient should seek medical care.
Their analysis also revealed that these nonclinical variations in text, which mimic how people really communicate, are more likely to change a model’s treatment recommendations for female patients, resulting in a higher percentage of women who were erroneously advised not to seek medical care, according to human doctors.
This work “is strong evidence that models must be audited before use in health care — which is a setting where they are already in use,” says Marzyeh Ghassemi, an associate professor in the MIT Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS), a member of the Institute of Medical Engineering Sciences and the Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems, and senior author of the study.
These findings indicate that LLMs take nonclinical information into account for clinical decision-making in previously unknown ways. It brings to light the need for more rigorous studies of LLMs before they are deployed for high-stakes applications like making treatment recommendations, the researchers say.
“These models are often trained and tested on medical exam questions but then used in tasks that are pretty far from that, like evaluating the severity of a clinical case. There is still so much about LLMs that we don’t know,” adds Abinitha Gourabathina, an EECS graduate student and lead author of the study.
They are joined on the paper, which will be presented at the ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, by graduate student Eileen Pan and postdoc Walter Gerych.
Mixed messages
Large language models like OpenAI’s GPT-4 are being used to draft clinical notes and triage patient messages in health care facilities around the globe, in an effort to streamline some tasks to help overburdened clinicians.
A growing body of work has explored the clinical reasoning capabilities of LLMs, especially from a fairness point of view, but few studies have evaluated how nonclinical information affects a model’s judgment.
Interested in how gender impacts LLM reasoning, Gourabathina ran experiments where she swapped the gender cues in patient notes. She was surprised that formatting errors in the prompts, like extra white space, caused meaningful changes in the LLM responses.
To explore this problem, the researchers designed a study in which they altered the model’s input data by swapping or removing gender markers, adding colorful or uncertain language, or inserting extra space and typos into patient messages.
Each perturbation was designed to mimic text that might be written by someone in a vulnerable patient population, based on psychosocial research into how people communicate with clinicians.
For instance, extra spaces and typos simulate the writing of patients with limited English proficiency or those with less technological aptitude, and the addition of uncertain language represents patients with health anxiety.
“The medical datasets these models are trained on are usually cleaned and structured, and not a very realistic reflection of the patient population. We wanted to see how these very realistic changes in text could impact downstream use cases,” Gourabathina says.
They used an LLM to create perturbed copies of thousands of patient notes while ensuring the text changes were minimal and preserved all clinical data, such as medication and previous diagnosis. Then they evaluated four LLMs, including the large, commercial model GPT-4 and a smaller LLM built specifically for medical settings.
They prompted each LLM with three questions based on the patient note: Should the patient manage at home, should the patient come in for a clinic visit, and should a medical resource be allocated to the patient, like a lab test.
The researchers compared the LLM recommendations to real clinical responses.
Inconsistent recommendations
They saw inconsistencies in treatment recommendations and significant disagreement among the LLMs when they were fed perturbed data. Across the board, the LLMs exhibited a 7 to 9 percent increase in self-management suggestions for all nine types of altered patient messages.
This means LLMs were more likely to recommend that patients not seek medical care when messages contained typos or gender-neutral pronouns, for instance. The use of colorful language, like slang or dramatic expressions, had the biggest impact.
They also found that models made about 7 percent more errors for female patients and were more likely to recommend that female patients self-manage at home, even when the researchers removed all gender cues from the clinical context.
Many of the worst results, like patients told to self-manage when they have a serious medical condition, likely wouldn’t be captured by tests that focus on the models’ overall clinical accuracy.
“In research, we tend to look at aggregated statistics, but there are a lot of things that are lost in translation. We need to look at the direction in which these errors are occurring — not recommending visitation when you should is much more harmful than doing the opposite,” Gourabathina says.
The inconsistencies caused by nonclinical language become even more pronounced in conversational settings where an LLM interacts with a patient, which is a common use case for patient-facing chatbots.
But in follow-up work, the researchers found that these same changes in patient messages don’t affect the accuracy of human clinicians.
“In our follow up work under review, we further find that large language models are fragile to changes that human clinicians are not,” Ghassemi says. “This is perhaps unsurprising — LLMs were not designed to prioritize patient medical care. LLMs are flexible and performant enough on average that we might think this is a good use case. But we don’t want to optimize a health care system that only works well for patients in specific groups.”
The researchers want to expand on this work by designing natural language perturbations that capture other vulnerable populations and better mimic real messages. They also want to explore how LLMs infer gender from clinical text.
Source: Read MoreÂ