Understanding Subgroup Fairness in Machine Learning ML
Evaluating fairness in machine learning often involves examining how models perform across different subgroups defined by attributes such as race, gender, or socioeconomic background. This evaluation is essential in contexts such as healthcare, where unequal model performance can lead to disparities in treatment recommendations or diagnostics. Subgroup-level performance analysis helps reveal unintended biases that may be embedded in the data or model design. Understanding this requires careful interpretation because fairness isn’t just about statistical parity—it’s also about ensuring that predictions lead to equitable outcomes when deployed in real-world systems.
Data Distribution and Structural Bias
One major issue arises when model performance differs across subgroups, not due to bias in the model itself but because of real differences in the subgroup data distributions. These differences often reflect broader social and structural inequities that shape the data available for model training and evaluation. In such scenarios, insisting on equal performance across subgroups might lead to misinterpretation. Furthermore, if the data used for model development is not representative of the target population—due to sampling bias or structural exclusions—then models may generalize poorly. Inaccurate performance on unseen or underrepresented groups can introduce or amplify disparities, especially when the structure of the bias is unknown.
Limitations of Traditional Fairness Metrics
Current fairness evaluations often involve disaggregated metrics or conditional independence tests. These metrics are widely used in assessing algorithmic fairness, including accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value, across various subgroups. Frameworks like demographic parity, equalized odds, and sufficiency are common benchmarks. For example, equalized odds ensure that true and false positive rates are similar across groups. However, these methods can produce misleading conclusions in the presence of distribution shifts. If the prevalence of labels differs among subgroups, even accurate models might fail to meet certain fairness criteria, leading practitioners to assume bias where none exists.
A Causal Framework for Fairness Evaluation
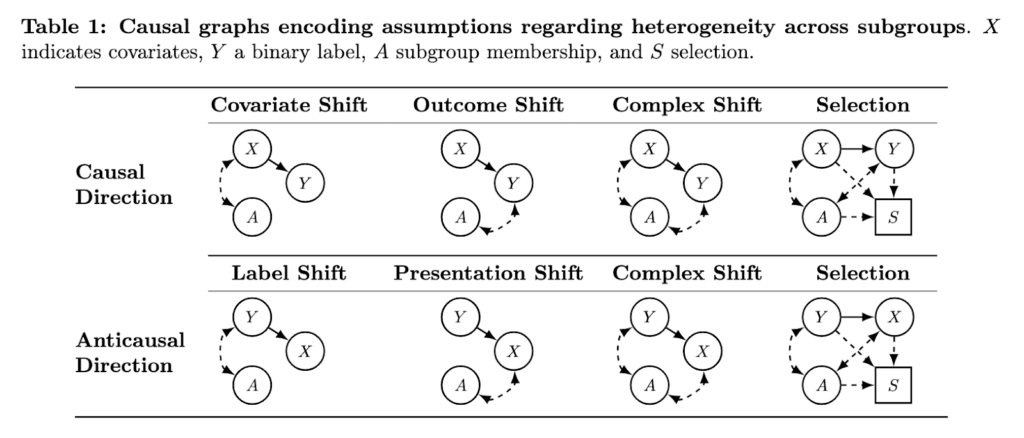
Researchers from Google Research, Google DeepMind, New York University, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, The Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, and Stanford University introduced a new framework that enhances fairness evaluations. The research introduced causal graphical models that explicitly model the structure of data generation, including how subgroup differences and sampling biases influence model behavior. This approach avoids assumptions of uniform distributions and provides a structured way to understand how subgroup performance varies. The researchers propose combining traditional disaggregated evaluations with causal reasoning, encouraging users to think critically about the sources of subgroup disparities rather than relying solely on metric comparisons.
Types of Distribution Shifts Modeled
The framework categorizes types of shifts such as covariate shift, outcome shift, and presentation shift using causal-directed acyclic graphs. These graphs include key variables like subgroup membership, outcome, and covariates. For instance, covariate shift describes situations where the distribution of features differs across subgroups, but the relationship between the outcome and the features remains constant. Outcome shift, by contrast, captures cases where the relationship between features and outcomes changes by subgroup. The graphs also accommodate label shift and selection mechanisms, explaining how subgroup data may be biased during the sampling process. These distinctions allow researchers to predict when subgroup-aware models would improve fairness or when they may not be necessary. The framework systematically identifies the conditions under which standard evaluations are valid or misleading.
Empirical Evaluation and Results
In their experiments, the team evaluated Bayes-optimal models under various causal structures to examine when fairness conditions, such as sufficiency and separation, hold. They found that sufficiency, defined as Y ⊥ A | f*(Z), is satisfied under covariate shift but not under other types of shifts such as outcome or complex shift. In contrast, separation, defined as f*(Z) ⊥ A | Y, only held under label shift when subgroup membership wasn’t included in model input. These results show that subgroup-aware models are essential in most practical settings. The analysis also revealed that when selection bias depends only on variables like X or A, fairness criteria can still be met. However, when selection depends on Y or combinations of variables, subgroup fairness becomes more challenging to maintain.
Conclusion and Practical Implications
This study clarifies that fairness cannot be accurately judged through subgroup metrics alone. Differences in performance may stem from underlying data structures rather than biased models. The proposed causal framework equips practitioners with tools to detect and interpret these nuances. By modeling causal relationships explicitly, researchers provide a path toward evaluations that reflect both statistical and real-world concerns about fairness. The method doesn’t guarantee perfect equity, but it gives a more transparent foundation for understanding how algorithmic decisions impact different populations.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post This AI Paper from Google Introduces a Causal Framework to Interpret Subgroup Fairness in Machine Learning Evaluations More Reliably appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ