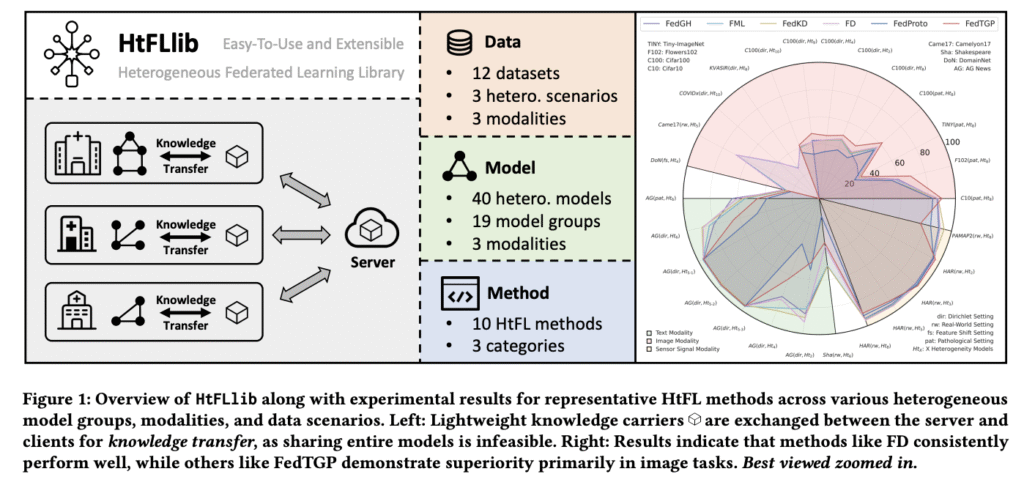
AI institutions develop heterogeneous models for specific tasks but face data scarcity challenges during training. Traditional Federated Learning (FL) supports only homogeneous model collaboration, which needs identical architectures across all clients. However, clients develop model architectures for their unique requirements. Moreover, sharing effort-intensive locally trained models contains intellectual property and reduces participants’ interest in engaging in collaborations. Heterogeneous Federated Learning (HtFL) addresses these limitations, but the literature lacks a unified benchmark for evaluating HtFL across various domains and aspects.
Background and Categories of HtFL Methods
Existing FL benchmarks focus on data heterogeneity using homogeneous client models but neglect real scenarios that involve model heterogeneity. Representative HtFL methods fall into three main categories addressing these limitations. Partial parameter sharing methods such as LG-FedAvg, FedGen, and FedGH maintain heterogeneous feature extractors while assuming homogeneous classifier heads for knowledge transfer. Mutual distillation, such as FML, FedKD, and FedMRL, trains and shares small auxiliary models through distillation techniques. Prototype sharing methods transfer lightweight class-wise prototypes as global knowledge, collecting local prototypes from clients, and collecting them on servers to guide local training. However, it remains unclear whether existing HtFL methods perform consistently across diverse scenarios.
Introducing HtFLlib: A Unified Benchmark
Researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Beihang University, Chongqing University, Tongji University, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, and The Queen’s University of Belfast have proposed the first Heterogeneous Federated Learning Library (HtFLlib), an easy and extensible method for integrating multiple datasets and model heterogeneity scenarios. This method integrates:
- 12 datasets across various domains, modalities, and data heterogeneity scenarios
- 40 model architectures ranging from small to large, across three modalities.
- A modularized and easy-to-extend HtFL codebase with implementations of 10 representative HtFL methods.
- Systematic evaluations covering accuracy, convergence, computation costs, and communication costs.
Datasets and Modalities in HtFLlib
HtFLlib contains detailed data heterogeneity scenarios divided into three settings: Label Skew with Pathological and Dirichlet as subsettings, Feature Shift, and Real-World. It integrates 12 datasets, including Cifar10, Cifar100, Flowers102, Tiny-ImageNet, KVASIR, COVIDx, DomainNet, Camelyon17, AG News, Shakespeare, HAR, and PAMAP2. These datasets vary significantly in domain, data volume, and class numbers, demonstrating HtFLlib’s comprehensive and versatile nature. Moreover, researchers’ main focus is on image data, especially the label skew setting, as image tasks are the most commonly used tasks across various fields. The HtFL methods are evaluated across image, text, and sensor signal tasks to evaluate their respective strengths and weaknesses.
Performance Analysis: Image Modality
For image data, most HtFL methods show decreased accuracy as model heterogeneity increases. The FedMRL shows superior strength through its combination of auxiliary global and local models. When introducing heterogeneous classifiers that make partial parameter sharing methods inapplicable, FedTGP maintains superiority across diverse settings due to its adaptive prototype refinement ability. Medical dataset experiments with black-boxed pre-trained heterogeneous models demonstrate that HtFL enhances model quality compared to pre-trained models and achieves greater improvements than auxiliary models, such as FML. For text data, FedMRL’s advantages in label skew settings diminish in real-world settings, while FedProto and FedTGP perform relatively poorly compared to image tasks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, researchers introduced HtFLlib, a framework that addresses the critical gap in HtFL benchmarking by providing unified evaluation standards across diverse domains and scenarios. HtFLlib’s modular design and extensible architecture provide a detailed benchmark for both research and practical applications in HtFL. Moreover, its ability to support heterogeneous models in collaborative learning opens the way for future research into utilizing complex pre-trained large models, black-box systems, and varied architectures across different tasks and modalities.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post HtFLlib: A Unified Benchmarking Library for Evaluating Heterogeneous Federated Learning Methods Across Modalities appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ