The Challenge of Updating LLM Knowledge
LLMs have shown outstanding performance for various tasks through extensive pre-training on vast datasets. However, these models frequently generate outdated or inaccurate information and can reflect biases during deployment, so their knowledge needs to be updated continuously. Traditional fine-tuning methods are expensive and susceptible to catastrophic forgetting. This has motivated lifelong model editing, which updates model knowledge efficiently and locally. To generate correct predictions, each edit requires reliability, generalizability, and localization. Methods like non-parametric achieve precise localized edits but poor generalization, while parametric methods offer better generalization but suffer from catastrophic forgetting.
Limitations of Prior Model Editing Techniques
Earlier works have explored sparse neural activations in continual learning, with methods like PackNet and Supermasks-in-Superposition allocating disjoint parameter subsets per task. Gradient-based approaches such as GPM and SPARCL improve efficiency through orthogonal updates but are limited to continual learning contexts. Parametric approaches such as ROME, MEMIT, and WISE modify weights through locating-then-editing strategies or auxiliary modules, but suffer from forgetting over extended edit sequences. Non-parametric methods like GRACE and LOKA store knowledge externally to preserve original weights, enabling precise local edits. However, these methods rely on exact input matches, limiting their generalization capabilities.
Introducing MEMOIR: A Structured Approach to Model Editing
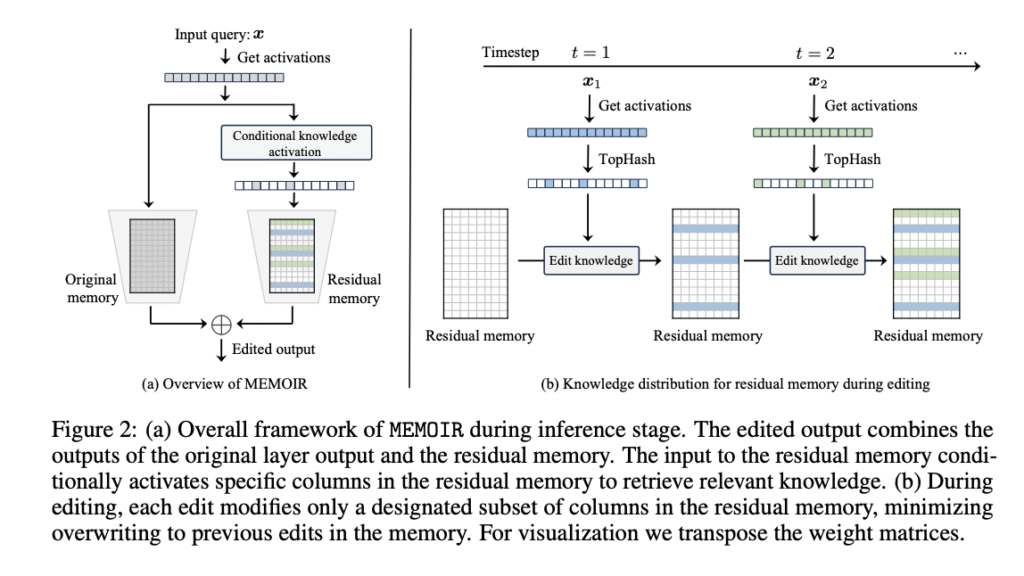
Researchers from EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland, have proposed MEMOIR (Model Editing with Minimal Overwrite and Informed Retention), which achieves an optimal balance between reliability, generalization, and locality for large-scale edits. It introduces a memory module that consists of a fully-connected layer within a single transformer block where all edits occur. MEMOIR solves catastrophic forgetting by allocating distinct parameter subsets to each edit and retrieving them during inference to activate only relevant knowledge for specific prompts. Moreover, the method utilizes structured sparsification with sample-dependent masks during editing, activating only prompt-specific parameter subsets. It distributes new knowledge across the parameter space, reducing overwriting and minimizing catastrophic forgetting.
Evaluation and Experimental Results
MEMOIR operates through a residual memory framework during inference, where the edited output integrates original layer outputs with residual memory outputs. It is evaluated against baselines such as GRACE for external knowledge storage, DEFER for inference-time routing, causal tracing methods like ROME, MEMIT, and ALPHAEDIT, and memory-based methods like WISE. Direct fine-tuning serves as an additional baseline comparison. Experiments are conducted on four autoregressive language models: LLaMA-3-8B-Instruct, Mistral-7B, LLaMA-2-7B, and GPT-J-6B, providing a comprehensive evaluation across different models and scales to show the effectiveness and generalizability of MOMOIR.
On the ZsRE question-answering dataset, MEMOIR achieves an average metric of 0.95 on LLaMA-3 with 1000 edits, outperforming all prior methods by a margin of 0.16. Similar outcomes are seen with Mistral, where this method once again achieves the highest average score, highlighting its robustness and effectiveness across various LLMs. Moreover, MEMOIR maintains optimal balanced performance with increasing edit volumes for hallucination correction using the SelfCheckGPT dataset. MEMOIR sustains saturated locality scores under the most challenging scenario of 600 edits, while achieving perplexity metrics 57% and 77% lower than WISE, the second-best performing method, on LLaMA-3 and Mistral, respectively.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, MEMOIR is a scalable framework for lifelong model editing that effectively balances reliability, generalization, and locality using innovative sparsification techniques. The method retrieves relevant updates through sparse activation pattern comparison, allowing edits to generalize to rephrased queries while maintaining model behavior on unrelated prompts. However, certain limitations exist, like modification of only single linear layers, which may restrict handling of long-horizon edits or knowledge requiring broader model changes. Future directions include extending the approach to multiple layers, hierarchical editing strategies, and application to multi-modal or encoder-decoder models beyond the current decoder-only transformer focus.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post EPFL Researchers Introduce MEMOIR: A Scalable Framework for Lifelong Model Editing in LLMs appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ