A major hurdle in using AI for genomics is the lack of interpretable, step-by-step reasoning from complex DNA data. While DNA foundation models excel at learning rich sequence patterns for tasks such as variant prediction and gene regulation, they often operate as black boxes, offering limited insight into the underlying biological mechanisms. Meanwhile, large language models demonstrate impressive reasoning skills across various domains, but they aren’t designed to handle raw genomic sequences. This gap between strong DNA representation and deep biological reasoning prevents AI from reaching expert-level understanding and limits its potential to drive scientific discovery through meaningful, hypothesis-driven explanations.
DNA foundation models have made significant progress by learning rich representations directly from genomic sequences, showing strong performance across a range of biological tasks. Models like Evo2, with its long-range capabilities, highlight their potential, but their lack of interpretability limits deeper biological insights. Meanwhile, large language models excel in reasoning over biomedical texts but often don’t engage directly with raw genomic data. Attempts, such as GeneGPT and TxGemma, represent early efforts to bridge this gap. Current genomic benchmarks assess task performance but fall short in evaluating reasoning and hypothesis generation.
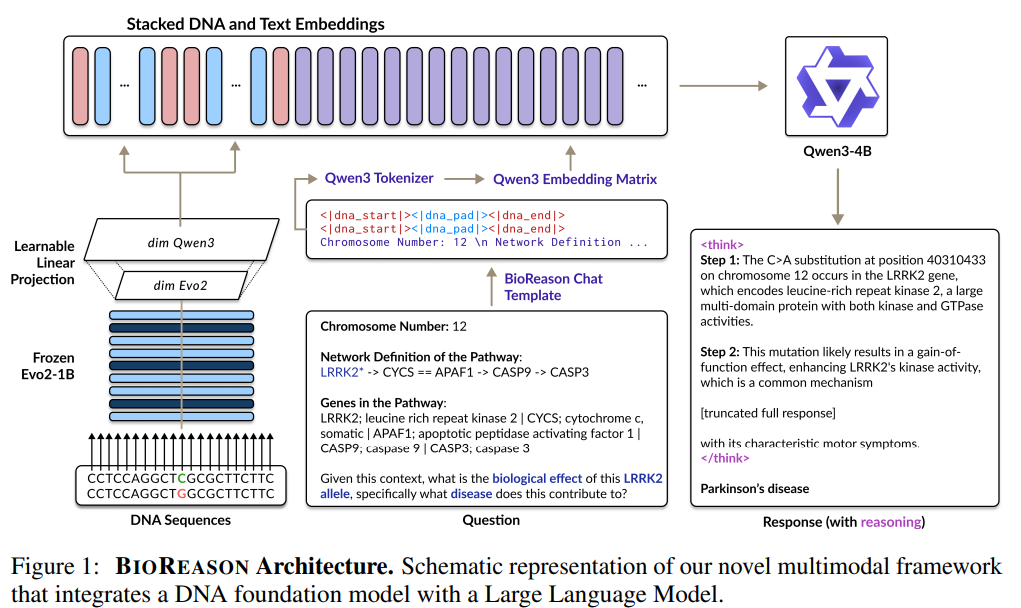
Researchers from the University of Toronto, Vector Institute, University Health Network (UHN), Arc Institute, Cohere, University of California, San Francisco, and Google DeepMind have introduced BIOREASON, a pioneering AI system that unites a DNA foundation model with an LLM. This integration allows BIOREASON to analyze raw genomic sequences while applying LLM-based reasoning to generate clear, biologically grounded insights. Trained through supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning, it achieves a performance gain of 15% or more over traditional models, reaching up to 97% accuracy in KEGG-based disease pathway prediction. This approach offers interpretable, step-by-step outputs that advance biological understanding and facilitate hypothesis generation.
The BIOREASON model is a multimodal framework designed to support deep, interpretable biological reasoning by combining genomic sequences with natural language queries. It uses a DNA foundation model to extract rich, contextual embeddings from raw DNA inputs and integrates these with tokenized textual queries to form a unified input for a LLM, specifically Qwen3. The system is trained to generate step-by-step explanations of biological processes. DNA embeddings are projected into the LLM’s space using a learnable layer, and the combined input is enriched with positional encoding. Additionally, reinforcement learning via Group Relative Policy Optimization refines its reasoning capabilities.
The researchers evaluated BIOREASON on three datasets focused on DNA variant interpretation and biological reasoning. It outperformed both DNA-only and LLM-only models in predicting disease outcomes from genomic variants. The best-performing version, which combined Evo2 and Qwen3-4B, achieved high accuracy and F1-scores across all tasks. A notable case study involved a PFN1 mutation linked to ALS, where BIOREASON accurately predicted the disease and generated a 10-step explanation tracing the variant’s impact on actin dynamics and motor neuron degeneration. This shows its strength not just in accurate predictions but also in providing transparent, biologically grounded reasoning paths.
In conclusion, BIOREASON combines DNA encoders with large language models to enable detailed, interpretable reasoning over genomic data. Unlike traditional models, it not only makes accurate predictions but also explains the biological logic behind them using step-by-step outputs. This helps scientists better understand disease mechanisms and generate new research questions. While powerful, BIOREASON has challenges, like high computational costs and limited uncertainty measures. Future work aims to address these issues by improving scalability, incorporating additional biological data such as RNA and proteins, and applying it to broader tasks, including GWAS. Overall, BIOREASON shows promise in advancing precision medicine and genomic research.
Check out the Paper, GitHub Page and Project Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 95k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post Meet BioReason: The World’s First Reasoning Model in Biology that Enables AI to Reason about Genomics like a Biology Expert appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ