State-of-the-art models show human-competitive accuracy on AIME, GPQA, MATH-500, and OlympiadBench, solving Olympiad-level problems. Recent multimodal foundation models have advanced benchmarks for disciplinary knowledge and mathematical reasoning. However, these evaluations miss a crucial aspect of machine intelligence: physical reasoning, which requires integrating disciplinary knowledge, symbolic operations, and real-world constraints. Physical problem-solving differs fundamentally from pure mathematical reasoning as it demands models to decode implicit conditions in questions. For example, interpreting “smooth surface” as zero friction coefficient, and maintaining physical consistency across reasoning chains because physical laws remain constant regardless of reasoning trajectories.
MLLM shows excellent visual understanding by integrating visual and textual data across various tasks, motivating exploration of its reasoning abilities. However, uncertainty remains regarding whether these models possess genuine advanced reasoning capabilities for visual tasks, particularly in physical domains closer to real-world scenarios. Several LLM benchmarks have emerged to evaluate reasoning abilities, with PHYBench being most relevant for physics reasoning. MLLM scientific benchmarks, such as PhysReason and EMMA, contain multimodal physics problems with figures, however, they include only small physics subsets, which inadequately evaluate MLLMs’ capabilities for reasoning and solving advanced physics problems.
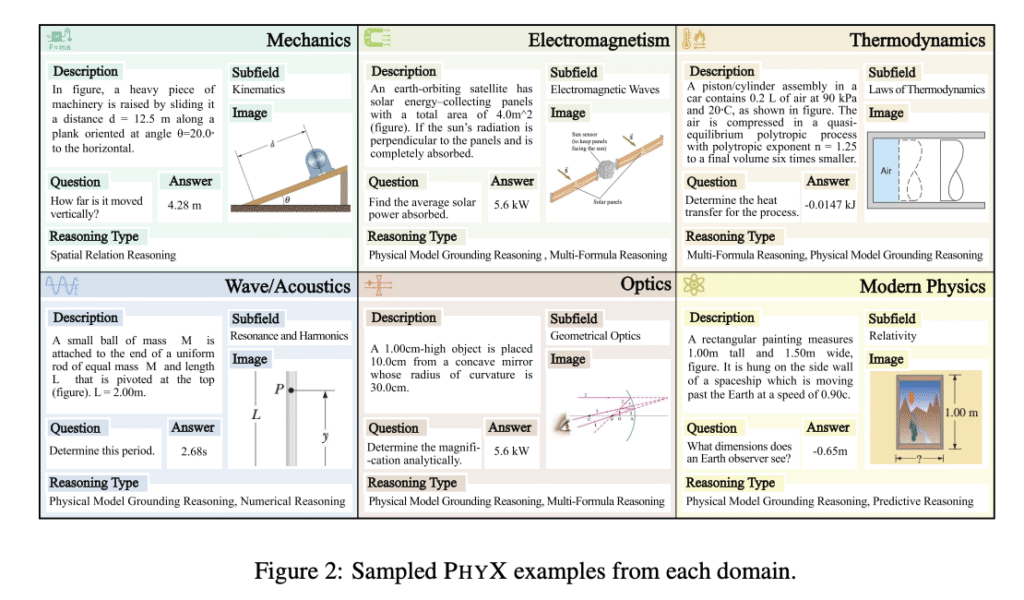
Researchers from the University of Hong Kong, the University of Michigan, the University of Toronto, the University of Waterloo, and the Ohio State University have proposed PHYX, a novel benchmark to evaluate the physical reasoning capabilities of foundation models. It comprises 3,000 visually-grounded physics questions, precisely curated across six distinct physics domains: Mechanics, Electromagnetism, Thermodynamics, Wave/Acoustics, Optics, and Modern Physics. It evaluates physics-based reasoning via multimodal problem-solving with three core innovations: (a) 3,000 newly collected questions with realistic physical scenarios requiring integrated visual analysis and causal reasoning, (b) Expert-validated data design covering six fundamental physics domains, and (c) Strict unified three-step evaluation protocols.
Researchers designed a four-stage data collection process to ensure high-quality data. The process begins with an in-depth survey of core physics disciplines to determine coverage across diverse domains and subfields, followed by the recruitment of STEM graduate students as expert annotators. They comply with copyright restrictions and avoid data contamination by selecting questions without answers that are immediately available. Moreover, quality control involves a three-stage cleaning process including duplicate detection through lexical overlap analysis with manual review by physics Ph.D. students, followed by filtering the shortest 10% of questions based on textual length, resulting in 3,000 high-quality questions from an initial collection of 3,300.
PHYX presents significant challenges for current models, with even the worst-performing human experts achieving 75.6% accuracy, outperforming all evaluated models and showing a gap between human expertise and current model capabilities. The benchmark reveals that multiple-choice formats narrow performance gaps by allowing weaker models to rely on surface-level cues, but open-ended questions demand genuine reasoning and precise answer generation. Comparing GPT-4o’s performance on PHYX to previously reported results on MathVista and MATH-V (both 63.8%), lower accuracy in physical reasoning tasks emphasizes that physical reasoning requires deeper integration of abstract concepts and real-world knowledge, presenting greater challenges than purely mathematical contexts.
In conclusion, researchers introduced PHYX, the first large-scale benchmark for evaluating physical reasoning in multimodal, visually grounded scenarios. Rigorous evaluation reveals that state-of-the-art models show limitations in physical reasoning, relying predominantly on memorized knowledge, mathematical formulas, and superficial visual patterns rather than genuine understanding of physical principles. The benchmark focuses exclusively on English-language prompts and annotations, limiting assessment of multilingual reasoning abilities. Also, while images depict physically realistic scenarios, they are often schematic or textbook-style rather than real-world photographs, which may not fully capture the complexity of perception in natural environments.
Check out the Paper, Code and Project Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 95k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post Multimodal Foundation Models Fall Short on Physical Reasoning: PHYX Benchmark Highlights Key Limitations in Visual and Symbolic Integration appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ