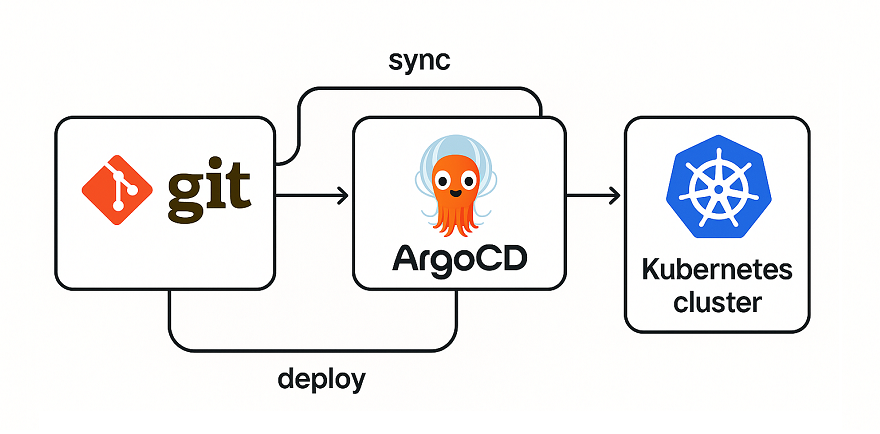
Hey there! Managing Kubernetes clusters can be tough, right? You’ve got so many YAML files, deployments, and changes to track. What if I told you there’s a smarter way to handle all this using GitOps? With GitOps, we use Git as the single source of truth for all our Kubernetes configurations. And ArgoCD is a super cool tool that makes this happen.
In this article, I’ll walk you through how to set up a GitOps workflow with Kubernetes and ArgoCD in a simple, step-by-step way. Let’s make your life easier!

What is GitOps and Why ArgoCD?
GitOps is a way to manage Kubernetes where everything—your app configs, deployments, everything—is stored in a Git repository. If you want to make a change, you update the Git repo, and the changes automatically go to your cluster. No manual commands needed! ArgoCD is a tool that watches your Git repo and applies those changes to your Kubernetes cluster. It’s like having a super-smart assistant who keeps everything in sync.
Prerequisites
Before we start, you’ll need:
- A Kubernetes cluster (version 1.21 or higher). You can use Minikube for testing or any cloud provider like AWS, GCP, or Azure.
- ArgoCD installed (we’ll cover this below).
- A Git repository (like GitHub or GitLab) to store your Kubernetes manifests.
- Basic knowledge of Kubernetes and Git. Don’t worry, I’ll keep it simple!
Step 1: Install ArgoCD
First, we need to get ArgoCD running on our Kubernetes cluster. The easiest way is to use a single YAML file provided by the ArgoCD team.
1. Create the ArgoCD Namespace
Create a namespace called argocd to keep things organized:
kubectl create namespace argocd
2. Install ArgoCD
Apply the official ArgoCD manifest to install all components:
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
This command downloads and applies the ArgoCD setup in the argocd namespace.
3. Verify the Installation
Check if ArgoCD pods are running:
kubectl get pods -n argocd
You should see pods like argocd-server, argocd-repo-server, etc., with a Running status.
4. Access the ArgoCD UI
ArgoCD has a nice web interface. To access it, forward the port:
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443
Now open http://localhost:8080 in your browser. The default username is admin, and you can get the password with:
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d
Step 2: Connect ArgoCD to Your Git Repository
Now, let’s tell ArgoCD where your Kubernetes manifests are stored. These manifests are the YAML files that define your apps, services, and other resources.
1. Set up your Git repo
Create a Git repository (e.g., on GitHub). Inside it, make a folder called manifests and add a simple Kubernetes deployment. Here’s an example:
# manifests/guestbook.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: guestbook
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: guestbook
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: guestbook
spec:
containers:
- name: guestbook
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: guestbook-service
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
app: guestbook
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIP
2. Add the repo to ArgoCD
In the ArgoCD UI, click “New App” and fill in:
- Application Name:
guestbook - Project:
default - Sync Policy:
Manual(we’ll change to auto later) - Repository URL: Your Git repo URL (e.g.,
https://github.com/your-username/your-repo.git) - Path:
manifests - Cluster:
https://kubernetes.default.svc(for in-cluster) - Namespace:
default
Or, you can use this YAML to create the app:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: guestbook
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/your-username/your-repo.git
targetRevision: HEAD
path: manifests
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: default
syncPolicy:
automated: {}
Apply it with:
kubectl apply -f guestbook-app.yaml -n argocd
Step 3: Enable Auto-Sync for True GitOps
The real magic of GitOps is automation. Let’s make ArgoCD automatically apply changes from your Git repo.
1. Turn on auto-sync
In the ArgoCD UI, go to your guestbook app, click “App Details,” and enable “Auto-Sync.” Or, update the YAML above to include:
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
prune: true deletes resources that are no longer in Git.
selfHeal: true fixes any manual changes made directly in the cluster.
2. Test it
Update the replicas: 2 to replicas: 3 in your guestbook.yaml file in the Git repo. Push the change:
git add .
git commit -m "Increase replicas to 3"
git push
In a minute, ArgoCD will notice the change and update your cluster. Check the ArgoCD UI to see the sync status!
Step 4: Advanced Features for Pro Users
ArgoCD has some cool advanced features. Let’s talk about a few:
ApplicationSets for Multiple Clusters
If you have multiple clusters (like dev, staging, prod), ApplicationSets can manage them all. Here’s an example:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: guestbook
namespace: argocd
spec:
generators:
- list:
elements:
- cluster: dev
url: https://dev-cluster:6443
- cluster: prod
url: https://prod-cluster:6443
template:
metadata:
name: '{{cluster}}-guestbook'
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/your-username/your-repo.git
targetRevision: HEAD
path: manifests
destination:
server: '{{url}}'
namespace: guestbook
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
This creates the guestbook app in both dev and prod clusters. Cool, right?
Drift Detection
Sometimes, someone might manually change the cluster (like editing a deployment directly). ArgoCD’s selfHeal: true option will revert those changes to match the Git repo. You can see drift alerts in the UI.
Multi-Tenancy
If you have multiple teams, use ArgoCD Projects to restrict access. For example:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Project
metadata:
name: team-a
namespace: argocd
spec:
destinations:
- namespace: team-a
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
clusterResourceWhitelist:
- group: ''
kind: Namespace
This ensures team-a can only manage their own namespace.
Best Practices
- Organize your Git repo: Keep separate folders like
dev/,staging/,prod/for each environment. - Validate manifests: Use tools like
kubevalin your CI pipeline to catch errors before pushing to Git. - Monitor ArgoCD: Integrate with Prometheus and Grafana to track sync status and errors.
- Secure your repo: Use SSH keys or OIDC for Git authentication to keep things safe.
Common Challenges and Fixes
- Sync fails: Check the ArgoCD logs (
kubectl logs -n argocd) for errors like wrong Git URLs or permissions. - Drift issues: Ensure
prune: trueis set to clean up old resources. - Large repos: Use ApplicationSets or split repos for better scalability.
Conclusion
And there you go! You’ve now set up a GitOps workflow with Kubernetes and ArgoCD. It’s like having a magic wand that keeps your cluster in sync with your Git repo. Start small with one app, then scale up with ApplicationSets and auto-sync. Trust me, once you go GitOps, you’ll never want to go back to manual kubectl apply commands!
References
The post Building a GitOps Workflow with Kubernetes and ArgoCD appeared first on TecAdmin.
Source: Read More