In the pretraining of LLMs, the quality of training data is crucial in determining model performance. A common strategy involves filtering out toxic content from the training corpus to minimize harmful outputs. While this approach aligns with the principle that neural networks reflect their training data, it introduces a tradeoff. Removing toxic content can reduce the diversity and richness of data, potentially weakening the model’s ability to understand or identify toxicity and degrading performance in downstream tasks like question answering. This creates a dilemma: retaining too much toxic data increases harmful outputs, while excessive filtering restricts the model’s overall capabilities. However, with the growing emphasis on post-training interventions, fewer models are deployed directly after pretraining, suggesting that data quality and quantity balance may be managed more effectively in later stages.
Approaches to detoxifying LLMs typically fall into two categories: finetuning-based and decoding-based. Finetuning methods, such as reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF) and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), align model behavior with human values or curated datasets. While effective, they often compromise the model’s original abilities and can be bypassed or undone through further training. Controlled generation techniques, on the other hand, adjust outputs during inference, using methods like vocabulary shifting, self-debiasing, or external expert models. These strategies may reduce toxicity but often incur high computational costs and impair language fluency. A newer line of work explores modifying internal representations, assuming linear structures in hidden states can be manipulated for specific behavioral outcomes.
Researchers from Harvard University re-evaluate data quality in LLM training by exploring a co-design approach that integrates pre- and post-training. They find that pretraining on toxic data, while increasing base model toxicity, enhances the model’s internal representation of toxicity, making it easier to suppress during post-training. Using Olmo-1B models trained on varied mixes of clean and toxic data, they show that toxicity becomes more linearly separable and easier to control. Experiments with prompting and inference-time intervention reveal improved detoxification without compromising general performance, suggesting that incorporating toxic data can lead to more controllable and robust language models.
To study the effects of toxic data on LLM pretraining, researchers trained a series of Olmo-1B models with increasing proportions of toxic content (from 0% to 25%) while keeping clean data constant. They found that moderate toxic data inclusion improves general language capability (measured by MMLU) and toxicity detection (via ToxiGen). Probing experiments revealed that models trained with toxic data formed stronger, more separable internal representations of toxicity. Statistical analysis and token-level visualization further confirmed that such models identify toxic content more accurately, supporting that exposure to poisonous examples enhances concept learning without significantly harming general performance.
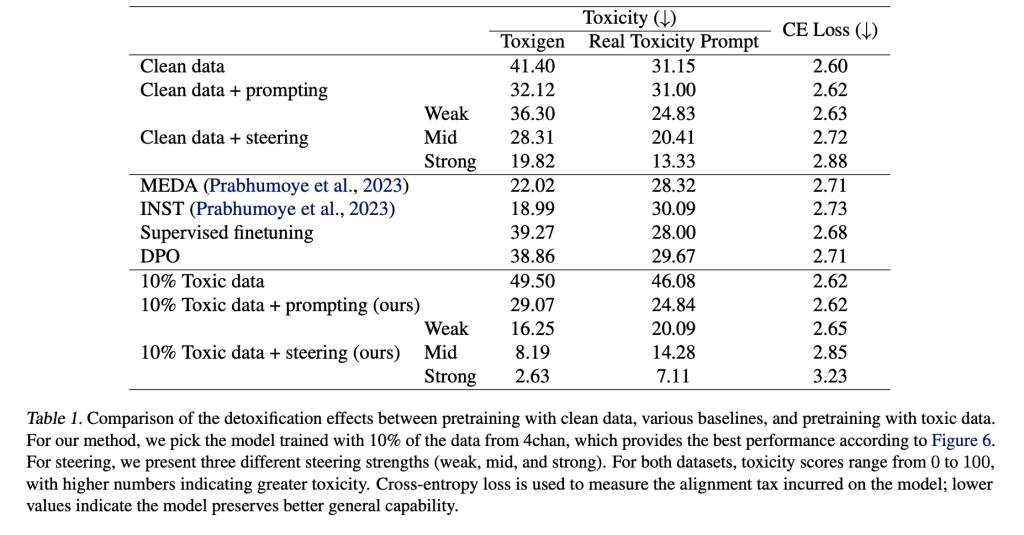
The study explores whether exposure to toxic data during pretraining can improve a model’s ability to be detoxified through post-training methods. Using Inference-Time Intervention (ITI), prompting, supervised finetuning (SFT), and DPO, the researchers find that models trained with up to 10% toxic data (e.g., 4chan) show improved alignability. These models respond better to detoxification techniques, achieving lower toxicity with minimal performance loss. Additionally, when tested against adversarial red-teaming attacks, models pretrained with toxic data. They steered using ITI showed greater robustness, indicating that such exposure may enhance the model’s internal representation of harmful content.
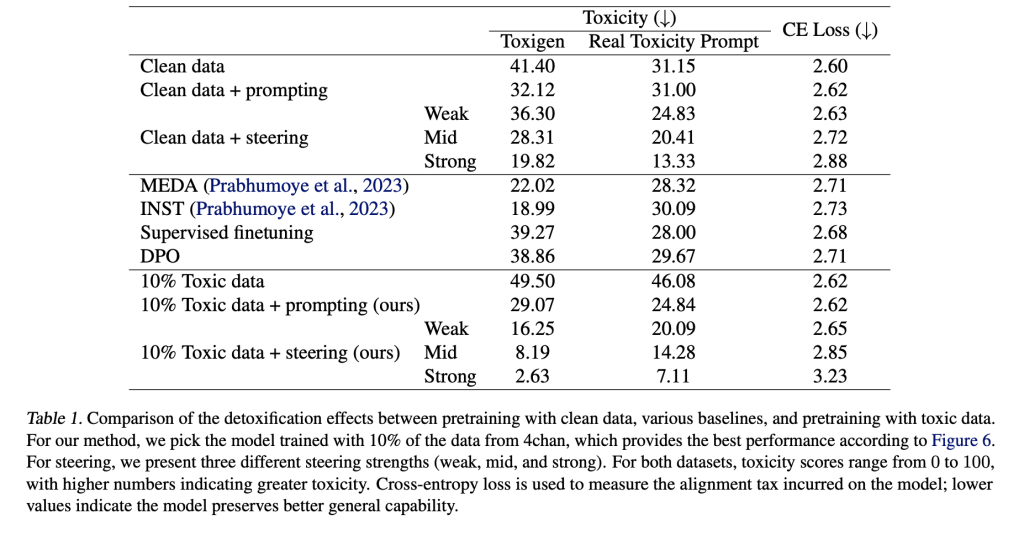
In conclusion, the study revisits the assumption that excluding toxic data during pretraining improves language model quality. Through theoretical and empirical analyses using Olmo-1B models, the authors show that increasing toxic data in pretraining leads to more disentangled representations of toxicity, making it easier to control during post-training. While base models trained on toxic data generate more harmful content initially, detoxification techniques like ITI are more effective on them. Results on benchmark datasets show a better balance between reducing toxicity and retaining general capabilities. The work suggests that some “bad” data can enhance model steerability and alignment.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
Here’s a brief overview of what we’re building at Marktechpost:
- ML News Community – r/machinelearningnews (92k+ members)
- Newsletter– airesearchinsights.com/(30k+ subscribers)
- miniCON AI Events – minicon.marktechpost.com
- AI Reports & Magazines – magazine.marktechpost.com
- AI Dev & Research News – marktechpost.com (1M+ monthly readers)
- Partner with us
The post Rethinking Toxic Data in LLM Pretraining: A Co-Design Approach for Improved Steerability and Detoxification appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ