Researchers at the Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, have introduced LLaMA-Omni2, a family of speech-capable large language models (SpeechLMs) now available on Hugging Face. This research introduces a modular framework that enables real-time spoken dialogue by integrating speech perception and synthesis with language understanding. Unlike earlier cascaded systems, LLaMA-Omni2 operates in an end-to-end pipeline while retaining modular interpretability and low training cost.
Overview of the LLaMA-Omni2 Architecture
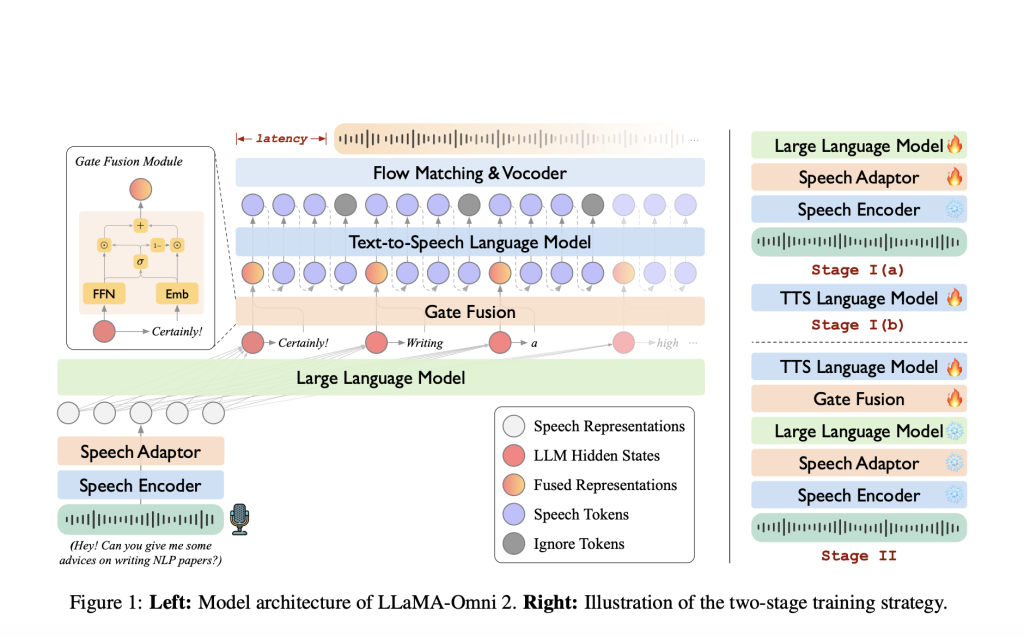
LLaMA-Omni2 encompasses models ranging from 0.5B to 14B parameters, each built atop the Qwen2.5-Instruct series. The architecture consists of:
- Speech Encoder: Utilizes Whisper-large-v3 to transform input speech into token-level acoustic representations.
- Speech Adapter: Processes encoder outputs using a downsampling layer and a feed-forward network to align with the language model’s input space.
- Core LLM: The Qwen2.5 models serve as the main reasoning engine.
- Streaming TTS Decoder: Converts LLM outputs into speech tokens using an autoregressive Transformer and then generates mel spectrograms through a causal flow matching model inspired by CosyVoice2.
A gating mechanism fuses LLM hidden states with textual embeddings before speech synthesis, enhancing contextual fidelity in the generated audio.

Streaming Generation with Read-Write Scheduling
The model adopts a read-write strategy to facilitate streaming output. Specifically, for every R tokens produced by the LLM, W speech tokens are generated. This enables synchronized textual and acoustic generation, minimizing latency without compromising fluency.
Empirical findings suggest that setting R = 3 and W = 10 provides a favorable trade-off between latency (~583 ms), alignment (ASR-WER: 3.26), and perceptual quality (UTMOS: 4.19).
Training Approach
Despite achieving competitive performance, LLaMA-Omni2 is trained on a relatively compact corpus—200K multi-turn speech-to-speech dialogue samples. These samples are synthesized from instruction-following text datasets (Alpaca, UltraChat), with diverse input voices and a consistent output voice generated using FishSpeech and CosyVoice2 models.
Training is executed in two stages:
- Stage I: Independently optimizes the speech-to-text and text-to-speech modules.
- Stage II: Fine-tunes the speech-to-speech generation path, including the gating and autoregressive decoding components.
Benchmark Results
The models are evaluated on spoken question answering and speech instruction following tasks using both speech-to-text (S2T) and speech-to-speech (S2S) modes.
| Model | Llama Q (S2S) | Web Q (S2S) | GPT-4o Score | ASR-WER | Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLM-4-Voice (9B) | 50.7 | 15.9 | 4.09 | 3.48 | 1562.8 |
| LLaMA-Omni (8B) | 49.0 | 23.7 | 3.52 | 3.67 | 346.7 |
| LLaMA-Omni2-7B | 60.7 | 31.3 | 4.15 | 3.26 | 582.9 |
The performance scales consistently with model size. Notably, LLaMA-Omni2-14B outperforms all baselines across tasks, even with substantially less training data than native SpeechLMs such as GLM-4-Voice.
Component Analyses
- Gate Fusion Module: Removing the gating mechanism increases ASR-WER and reduces speech quality, confirming its role in aligning textual and contextual signals.
- TTS Pretraining: Initializing the TTS model from Qwen2.5 and fine-tuning in a streaming setup yields the best performance. Training from scratch fails to converge effectively.
- Read/Write Strategies: Adjusting the R:W ratio impacts latency and quality. Larger W improves UTMOS but at the cost of response delay.
Additionally, the study demonstrates that multi-turn dialogue data is more effective than single-turn data in training speech interaction capabilities, and that performance plateaus around 200K samples.
Conclusion
LLaMA-Omni2 demonstrates that high-quality, low-latency spoken interaction with LLMs is feasible without the need for extensive pretraining on massive speech corpora. By combining modular architecture with autoregressive streaming synthesis, the system offers a practical pathway for real-time speech applications.
Check out the Paper, Model on Hugging Face and GitHub Page. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter.
Here’s a brief overview of what we’re building at Marktechpost:
ML News Community – r/machinelearningnews (92k+ members)
Newsletter– airesearchinsights.com/(30k+ subscribers)
miniCON AI Events – minicon.marktechpost.com
AI Reports & Magazines – magazine.marktechpost.com
AI Dev & Research News – marktechpost.com (1M+ monthly readers)
The post LLMs Can Now Talk in Real-Time with Minimal Latency: Chinese Researchers Release LLaMA-Omni2, a Scalable Modular Speech Language Model appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ