In this hands-on tutorial, we’ll unlock the creative potential of Stability AI’s industry-leading diffusion models, Stable Diffusion v1.5, Stability AI’s v2-base, and the cutting-edge Stable Diffusion 3 Medium, to generate eye-catching imagery. Running entirely in Google Colab with a Gradio interface, we’ll experience side-by-side comparisons of three powerful pipelines, rapid prompt iteration, and seamless GPU-accelerated inference. Whether we’re a marketer looking to elevate our brand’s visual narrative or a developer eager to prototype AI-driven content workflows, this tutorial showcases how Stability AI’s open-source models can be deployed instantly and at no infrastructure cost, allowing you to focus on storytelling, engagement, and driving real-world results.
!pip install huggingface_hub
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
notebook_login()We install the huggingface_hub library and then import and invoke the notebook_login() function, which prompts you to authenticate your notebook session with your Hugging Face account, allowing you to seamlessly access and manage models, datasets, and other hub resources.
!pip uninstall -y torchvision
!pip install --upgrade torch torchvision --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
!pip install --upgrade diffusers transformers accelerate safetensors gradio pillowWe first force-uninstalls any existing torchvision to clear potential conflicts, then reinstalls torch and torchvision from the CUDA 11.8–compatible PyTorch wheels, and finally upgrades key libraries, diffusers, transformers, accelerate, safetensors, gradio, and pillow, to ensure you have the latest versions for building and running GPU-accelerated generative pipelines and web demos.
import torch
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, StableDiffusion3Pipeline
import gradio as gr
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"We import PyTorch alongside both the Stable Diffusion v1 and v3 pipelines from the Diffusers library, as well as Gradio for building interactive demos. It then checks for CUDA availability and sets the device variable to “cuda” if a GPU is present; otherwise, it falls back to “cpu”, ensuring your models run on the optimal hardware.
pipe1 = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
safety_checker=None
).to(device)
pipe1.enable_attention_slicing()We load the Stable Diffusion v1.5 model in half-precision (float16) without the built-in safety checker, transfers it to your selected device (GPU, if available), and then enables attention slicing to reduce peak VRAM usage during image generation.
pipe2 = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-base",
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
safety_checker=None
).to(device)
pipe2.enable_attention_slicing()We load the Stable Diffusion v2 “base” model in 16-bit precision without the default safety filter, transfers it to your chosen device, and activates attention slicing to optimize memory usage during inference.
pipe3 = StableDiffusion3Pipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-3-medium-diffusers",
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
safety_checker=None
).to(device)
pipe3.enable_attention_slicing()We pull in Stability AI’s Stable Diffusion 3 “medium” checkpoint in 16-bit precision (skipping the built-in safety checker), transfers it to your selected device, and enables attention slicing to reduce GPU memory usage during generation.
def generate(prompt, steps, scale):
img1 = pipe1(prompt, num_inference_steps=steps, guidance_scale=scale).images[0]
img2 = pipe2(prompt, num_inference_steps=steps, guidance_scale=scale).images[0]
img3 = pipe3(prompt, num_inference_steps=steps, guidance_scale=scale).images[0]
return img1, img2, img3
Now, this function runs the same text prompt through all three loaded pipelines (pipe1, pipe2, pipe3) using the specified inference steps and guidance scale, then returns the first image from each, making it perfect for comparing outputs across Stable Diffusion v1.5, v2-base, and v3-medium.
def choose(selection):
return f" You selected: **{selection}**"
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
gr.Markdown("## AI Social-Post Generator with 3 Models")
with gr.Row():
prompt = gr.Textbox(label="Prompt", placeholder="A vibrant beach sunset…")
steps = gr.Slider( 1, 100, value=50, step=1, label="Inference Steps")
scale = gr.Slider( 1.0, 20.0, value=7.5, step=0.1, label="Guidance Scale")
btn = gr.Button("Generate Images")
with gr.Row():
out1 = gr.Image(label="Model 1: SD v1.5")
out2 = gr.Image(label="Model 2: SD v2-base")
out3 = gr.Image(label="Model 3: SD v3-medium")
sel = gr.Radio(
["Model 1: SD v1.5","Model 2: SD v2-base","Model 3: SD v3-medium"],
label="Select your favorite"
)
txt = gr.Markdown()
btn.click(fn=generate, inputs=[prompt, steps, scale], outputs=[out1, out2, out3])
sel.change(fn=choose, inputs=sel, outputs=txt)
demo.launch(share=True)
You selected: **{selection}**"
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
gr.Markdown("## AI Social-Post Generator with 3 Models")
with gr.Row():
prompt = gr.Textbox(label="Prompt", placeholder="A vibrant beach sunset…")
steps = gr.Slider( 1, 100, value=50, step=1, label="Inference Steps")
scale = gr.Slider( 1.0, 20.0, value=7.5, step=0.1, label="Guidance Scale")
btn = gr.Button("Generate Images")
with gr.Row():
out1 = gr.Image(label="Model 1: SD v1.5")
out2 = gr.Image(label="Model 2: SD v2-base")
out3 = gr.Image(label="Model 3: SD v3-medium")
sel = gr.Radio(
["Model 1: SD v1.5","Model 2: SD v2-base","Model 3: SD v3-medium"],
label="Select your favorite"
)
txt = gr.Markdown()
btn.click(fn=generate, inputs=[prompt, steps, scale], outputs=[out1, out2, out3])
sel.change(fn=choose, inputs=sel, outputs=txt)
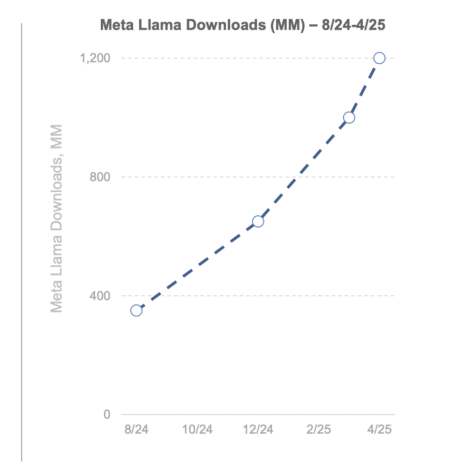
demo.launch(share=True)Finally, this Gradio app builds a three-column UI where you can enter a text prompt, adjust inference steps and guidance scale, then generate and display images from SD v1.5, v2-base, and v3-medium side by side. It also features a radio selector, allowing you to select your preferred model output, and displays a simple confirmation message when a choice is made.
In conclusion, by integrating Stability AI’s state-of-the-art diffusion architectures into an easy-to-use Gradio app, you’ve seen how effortlessly you can prototype, compare, and deploy stunning visuals that resonate on today’s platforms. From A/B-testing creative directions to automating campaign assets at scale, Stability AI provides the performance, flexibility, and vibrant community support to transform your content pipeline.
Check out the Colab Notebook. Don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit. For Promotion and Partnerships, please talk us.
The post A Coding Guide to Compare Three Stability AI Diffusion Models (v1.5, v2-Base & SD3-Medium) Diffusion Capabilities Side-by-Side in Google Colab Using Gradio appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop