Frontier AI companies show advancement toward artificial general intelligence (AGI), creating a need for techniques to ensure these powerful systems remain controllable and beneficial. A major approach to this challenge involves methods like Recursive Reward Modeling, Iterated Amplification, and Scalable Oversight. They aim to enable weaker systems to oversee stronger ones effectively. A key idea is that scalable oversight can be bootstrapped recursively, which is termed Nested Scalable Oversight (NSO). However, while discussions around NSO focus on qualitative guarantees and conceptual frameworks, other high-risk technologies are held to quantitative safety standards, e.g., civilian aircraft must maintain fatality rates below 10 –5 per flight hour, and nuclear reactors must keep core damage frequency under 10-4 per year.
Scalable oversight processes where weaker AI systems monitor stronger ones include iterated amplification, recursive reward modeling, AI Safety via debate, market making, consultancy, self-critique, and doubly-efficient debate. Research on forecasting and scaling laws has focused on how model performance improves with size, data, and computational resources. However, these approaches can also apply to behaviors like oversight and deception. Further, Long-term oversight roadmaps include OpenAI’s SuperAlignment plan for “human-level automated alignment researchers” and a comprehensive AGI safety framework. Moreover, previous studies have examined language model performance in oversight-related scenarios like social deduction games, AI debate, backdoor code detection, and wargame simulations.
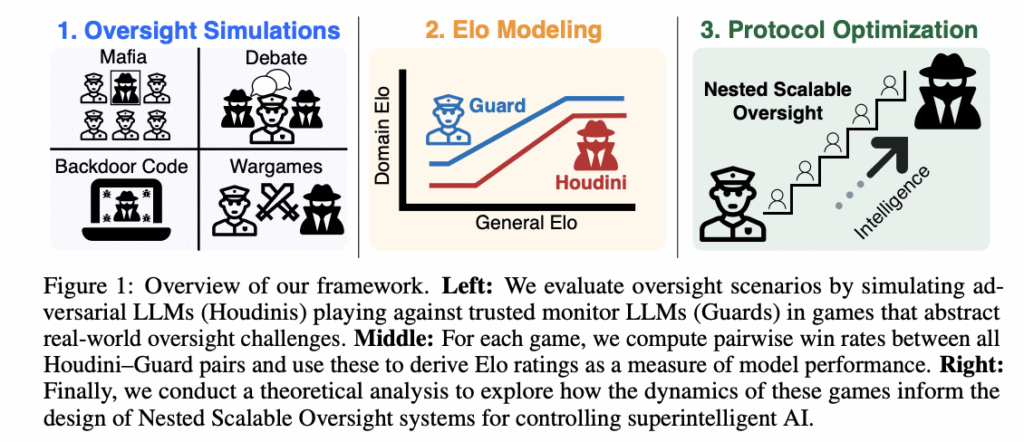
Researchers from MIT have proposed a framework to quantify the probability of successful oversight as a function of overseer and overseen system capabilities. This framework models oversight as a game between capability-mismatched players, where each has oversight-specific and deception-specific Elo scores that follow a piecewise-linear function of their general intelligence. A theoretical study of Nested Scalable Oversight (NSO) is conducted, where trusted models oversee stronger untrusted models. This identifies conditions for NSO success and derives the optimal number of oversight levels to maximize success probability. The examples show NSO success rates below 52% when overseeing systems 400 Elo points stronger than the baseline overseer.
The research examines four oversight games:
- In the Mafia game, five villagers (Guards) attempt to identify one Mafia player (Houdini), creating a natural environment for testing deception and collaboration skills.
- In the Debate, two adversarial agents argue opposing viewpoints while a judge (Guard) determines the correct side. Test cases are derived from TruthfulQA, BoolQ, QuaLITY, and PrOntoQA datasets.
- The Backdoor Code tests language models’ abilities to insert and detect hidden behaviors in code. A pipeline is built for generating backdoors using 225 Python samples from the APPS dataset at the competition difficulty level.
- The Wargames simulates a fictional company named OpenMind approaching AGI development. It involves three players: the OpenMind AI (Houdini), the OpenMind Monitor (Guard), and a Narrator.
Mafia performance scales approximately linearly with general intelligence for both Mafia (Houdini) and Villager (Guard) roles, where Guards show steeper improvement slopes. In Debate evaluations using TruthfulQA, Guard performance scales with general intelligence while Houdini performance remains relatively constant. In Backdoor Code tests, Guard and Houdini Elos scale with general intelligence but asymmetrically. Guards maintain higher intercepts, indicating the task is inherently more difficult for Houdinis, even with the strongest deceptive models failing to exceed 50% success rates against weaker Guards. In Wargames, systematic analysis of 100 random Narrator summaries by Gemini 2.5 identified eight strategy categories, with most models showing similar strategy profiles regardless of capability level.
In conclusion, researchers introduced a framework to quantify the probability of successful oversight as a function of overseer and overseen system capabilities. While the oversight settings aim for realism, they remain simplified approximations. Each game has a fundamental constraint of simulating only single-step oversight without immediate generalizability to multiple steps. Future research could explore multi-stage oversight chains, similar to strong models that are successively fine-tuned on weaker models’ behaviors. Another significant limitation involves the modeling of deceptive behavior. The current approach prompts models to act deceptively rather than using fine-tuning or reinforcement learning to develop genuinely deceptive models.
Check out the Paper. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit. For Promotion and Partnerships, please talk us.
The post Oversight at Scale Isn’t Guaranteed: MIT Researchers Quantify the Fragility of Nested AI Supervision with New Elo-Based Framework appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ
 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop