Autoregressive (AR) models have made significant advances in language generation and are increasingly explored for image synthesis. However, scaling AR models to high-resolution images remains a persistent challenge. Unlike text, where relatively few tokens are required, high-resolution images necessitate thousands of tokens, leading to quadratic growth in computational cost. As a result, most AR-based multimodal models are constrained to low or medium resolutions, limiting their utility for detailed image generation. While diffusion models have shown strong performance at high resolutions, they come with their own limitations, including complex sampling procedures and slower inference. Addressing the token efficiency bottleneck in AR models remains an important open problem for enabling scalable and practical high-resolution image synthesis.
Meta AI Introduces Token-Shuffle
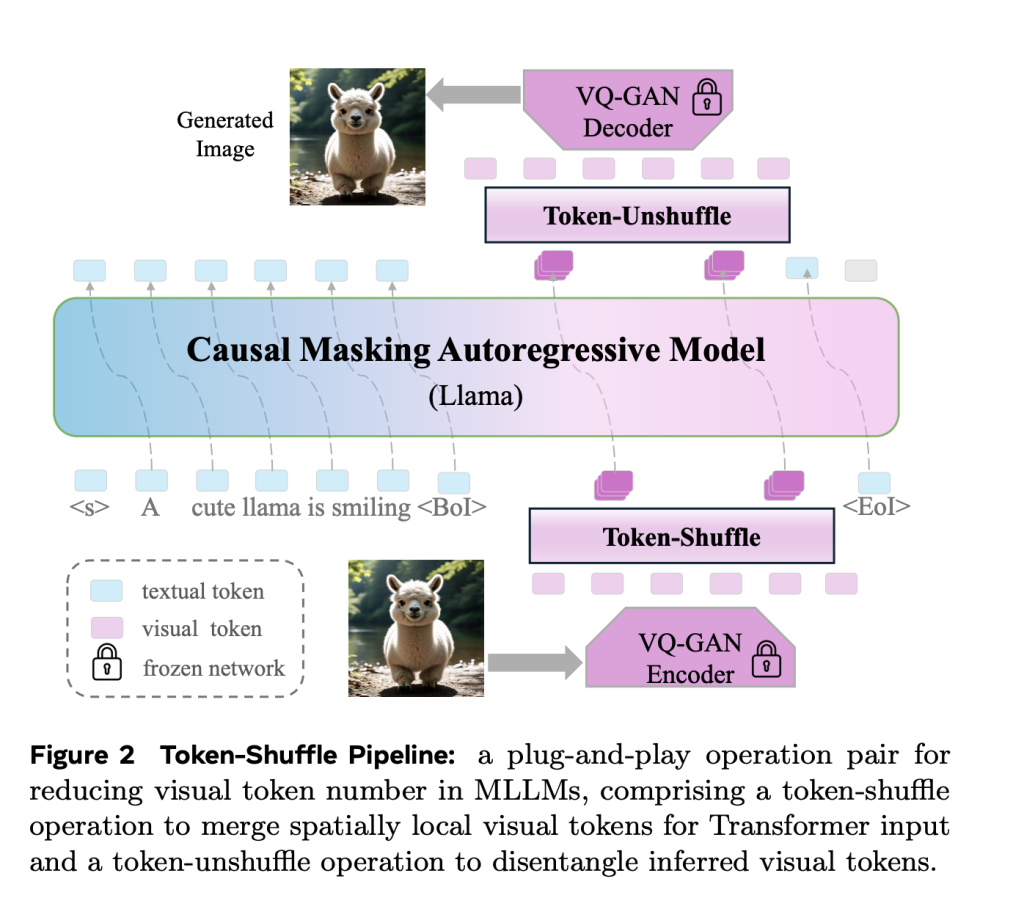
Meta AI introduces Token-Shuffle, a method designed to reduce the number of image tokens processed by Transformers without altering the fundamental next-token prediction reach. The key insight underpinning Token-Shuffle is the recognition of dimensional redundancy in visual vocabularies used by multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Visual tokens, typically derived from vector quantization (VQ) models, occupy high-dimensional spaces but carry a lower intrinsic information density compared to text tokens. Token-Shuffle exploits this by merging spatially local visual tokens along the channel dimension before Transformer processing and subsequently restoring the original spatial structure after inference. This token fusion mechanism allows AR models to handle higher resolutions with significantly reduced computational cost while maintaining visual fidelity.

Technical Details and Benefits
Token-Shuffle consists of two operations: token-shuffle and token-unshuffle. During input preparation, spatially neighboring tokens are merged using an MLP to form a compressed token that preserves essential local information. For a shuffle window size sss, the number of tokens is reduced by a factor of s2s^2s2, leading to a substantial reduction in Transformer FLOPs. After the Transformer layers, the token-unshuffle operation reconstructs the original spatial arrangement, again assisted by lightweight MLPs.
By compressing token sequences during Transformer computation, Token-Shuffle enables the efficient generation of high-resolution images, including those at 2048×2048 resolution. Importantly, this approach does not require modifications to the Transformer architecture itself, nor does it introduce auxiliary loss functions or pretraining of additional encoders.
Furthermore, the method integrates a classifier-free guidance (CFG) scheduler specifically adapted for autoregressive generation. Rather than applying a fixed guidance scale across all tokens, the scheduler progressively adjusts guidance strength, minimizing early token artifacts and improving text-image alignment.
Results and Empirical Insights
Token-Shuffle was evaluated on two major benchmarks: GenAI-Bench and GenEval. On GenAI-Bench, using a 2.7B parameter LLaMA-based model, Token-Shuffle achieved a VQAScore of 0.77 on “hard” prompts, outperforming other autoregressive models such as LlamaGen by a margin of +0.18 and diffusion models like LDM by +0.15. In the GenEval benchmark, it attained an overall score of 0.62, setting a new baseline for AR models operating in the discrete token regime.
Large-scale human evaluation further supported these findings. Compared to LlamaGen, Lumina-mGPT, and diffusion baselines, Token-Shuffle showed improved alignment with textual prompts, reduced visual flaws, and higher subjective image quality in most cases. However, minor degradation in logical consistency was observed relative to diffusion models, suggesting avenues for further refinement.
In terms of visual quality, Token-Shuffle demonstrated the capability to produce detailed and coherent 1024×1024 and 2048×2048 images. Ablation studies revealed that smaller shuffle window sizes (e.g., 2×2) offered the best trade-off between computational efficiency and output quality. Larger window sizes provided additional speedups but introduced minor losses in fine-grained detail.

Conclusion
Token-Shuffle presents a straightforward and effective method to address the scalability limitations of autoregressive image generation. By leveraging the inherent redundancy in visual vocabularies, it achieves substantial reductions in computational cost while preserving, and in some cases improving, generation quality. The method remains fully compatible with existing next-token prediction frameworks, making it easy to integrate into standard AR-based multimodal systems.
The results demonstrate that Token-Shuffle can push AR models beyond prior resolution limits, making high-fidelity, high-resolution generation more practical and accessible. As research continues to advance scalable multimodal generation, Token-Shuffle provides a promising foundation for efficient, unified models capable of handling text and image modalities at large scales.
Check out the Paper. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Meta AI Introduces Token-Shuffle: A Simple AI Approach to Reducing Image Tokens in Transformers appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ
 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop