Multimodal AI enables machines to process and reason across various input formats, such as images, text, videos, and complex documents. This domain has seen increased interest as traditional language models, while powerful, are inadequate when confronted with visual data or when contextual interpretation spans across multiple input types. The real world is inherently multimodal, so systems aiming to assist in real-time tasks, analyzing user interfaces, understanding academic materials, or interpreting complex scenes require intelligence that functions beyond textual reasoning. Newer models are now being developed to simultaneously decode language and vision cues to approach tasks with improved contextual awareness, reasoning depth, and adaptability to different data input forms.
A limitation in multimodal systems today lies in their inability to process long contexts efficiently and to generalize across high-resolution or diverse input structures without compromising performance. Many open-source models limit the input to a few thousand tokens or demand excessive computational resources to maintain performance at scale. These constraints result in models that may perform well on standard benchmarks but struggle with real-world applications that involve complex, multi-image inputs, extended dialogues, or academic tasks like OCR-based document analysis and mathematical problem-solving. There’s also a gap in reasoning ability, particularly long-horizon thinking, which prevents current systems from handling tasks that require step-by-step logic or deep contextual alignment between different data modalities.
Previous tools have attempted to address these challenges but often fell short in scalability or flexibility. The Qwen2.5-VL series and Gemma-3 models, while notable for their dense architectures, lack built-in support for reasoning through longer chains of thought. Models like DeepSeek-VL2 and Aria adopted mixture-of-experts (MoE) strategies but had fixed vision encoders that restricted their ability to adapt to various resolutions and forms of visual input. Also, these models typically supported only short context windows, 4K tokens in DeepSeek-VL2, and had limited success in complex OCR or multi-image scenarios. As such, most existing systems failed to balance low resource consumption with the ability to tackle tasks involving long context and diverse visual data.
Researchers at Moonshot AI introduced Kimi-VL, a novel vision-language model utilizing an MoE architecture. This system activates only 2.8 billion parameters in its decoder, significantly lighter than many competitors while maintaining powerful multimodal capabilities. The two released models based on this architecture on Hugging Face are Kimi-VL-A3B-Thinking and Kimi-VL-A3B-Instruct. It incorporates a native-resolution visual encoder named MoonViT and supports context windows of up to 128K tokens. The model has three integrated components: the MoonViT encoder, an MLP projector for transitioning visual features to language embeddings, and the Moonlight MoE decoder. Researchers further developed an advanced version, Kimi-VL-Thinking, designed specifically for long-horizon reasoning tasks through chain-of-thought supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning. Together, these models aim to redefine efficiency benchmarks in vision-language reasoning.
The architectural innovation in Kimi-VL lies in its adaptability and processing capability. MoonViT processes high-resolution images in their original form, eliminating the need for sub-image fragmentation. To ensure spatial consistency across varied image resolutions, the model uses interpolated absolute positional embeddings combined with two-dimensional rotary positional embeddings across both height and width. These design choices allow MoonViT to preserve fine-grained detail even in large-scale image inputs. Outputs from the vision encoder are passed through a two-layer MLP that uses pixel shuffle operations to downsample spatial dimensions and convert features into LLM-compatible embeddings. On the language side, the 2.8B activated parameter MoE decoder supports 16B total parameters and integrates seamlessly with visual representations, enabling highly efficient training and inference across different input types. The entire training process used an enhanced Muon optimizer with weight decay and ZeRO-1-based memory optimization for handling the large parameter count.
The training data composition reflects a focus on diverse multimodal learning. Starting with 2.0T tokens for ViT training using image-caption pairs, the team added another 0.1T to align the encoder with the decoder. Joint pre-training consumed 1.4T tokens, followed by 0.6T in cooldown and 0.3T in long-context activation, totaling 4.4T tokens. These stages included academic visual datasets, OCR samples, long video data, and synthetic mathematical and code-based QA pairs. For long-context learning, the model was progressively trained to handle sequences from 8K up to 128K tokens, using RoPE embeddings extended from a base frequency of 50,000 to 800,000. This allowed the model to maintain a token recall accuracy of 100% up to 64K tokens, with a slight drop to 87.0% at 128K, still outperforming most alternatives.
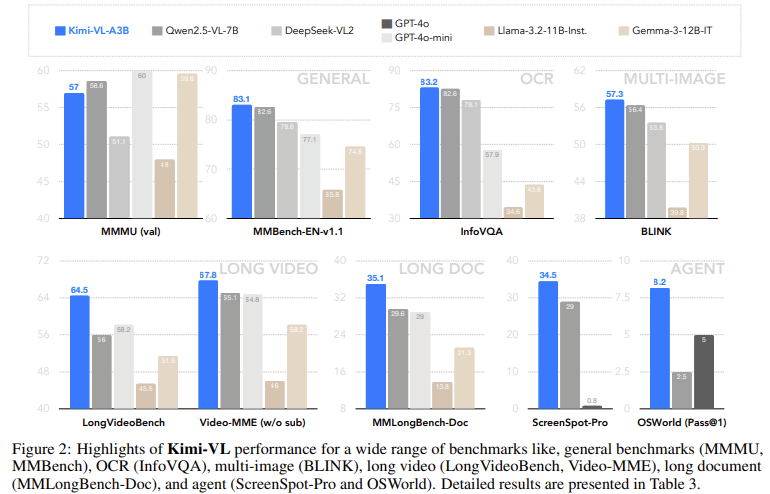
Kimi-VL demonstrated strong results across a range of benchmarks. On the LongVideoBench, it scored 64.5; on MMLongBench-Doc, it achieved 35.1; and on the InfoVQA benchmark, it led with 83.2. On ScreenSpot-Pro, which tests understanding of UI screens, it scored 34.5. The Kimi-VL-Thinking variant excelled in reasoning-intensive benchmarks like MMMU (61.7), MathVision (36.8), and MathVista (71.3). For agent tasks such as OSWorld, the model matched or exceeded performance from larger models like GPT-4o while activating significantly fewer parameters. Its compact design and strong reasoning capabilities make it a leading candidate among open-source multimodal solutions.
Some Key Takeaways from the Research on Kimi-VL:
- Kimi-VL activates only 2.8B parameters during inference, ensuring efficiency without sacrificing capability.
- MoonViT, its vision encoder, natively processes high-resolution images, improving clarity in tasks like OCR and UI interpretation.
- The model supports up to 128K context tokens, achieving 100% recall up to 64K and 87.0% accuracy at 128K on text/video tasks.
- Kimi-VL-Thinking scores 61.7 on MMMU, 36.8 on MathVision, and 71.3 on MathVista, outperforming many larger VLMs.
- It scored 83.2 on InfoVQA and 34.5 on visual tasks on ScreenSpot-Pro, showcasing its precision in perception-based evaluations.
- Total pre-training involved 4.4T tokens across text, video, document, and synthetic multimodal data.
- Optimization was done using a customized Muon optimizer with memory-efficient strategies like ZeRO-1.
- Joint training ensured seamless visual and language feature integration while preserving core language capabilities.
Check out Instruct Model and Reasoning Model. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Moonsight AI Released Kimi-VL: A Compact and Powerful Vision-Language Model Series Redefining Multimodal Reasoning, Long-Context Understanding, and High-Resolution Visual Processing appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ