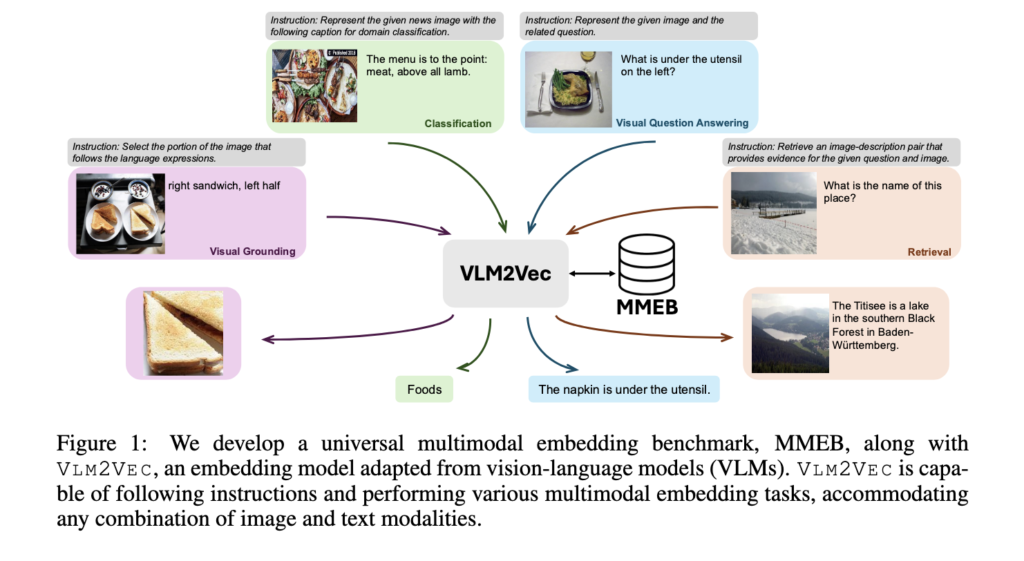
Multimodal embeddings combine visual and textual data into a single representational space, enabling systems to understand and relate images and language meaningfully. These embeddings support various tasks, including visual question answering, retrieval, classification, and grounding. The technology is especially important for AI models that interpret real-world content through visual and linguistic lenses, such as document analysis, digital assistants, or visual search engines.
A pressing challenge has been the inability of current models to generalize across diverse tasks and modalities effectively. Most models are trained for highly specific tasks or underperform when applied to unfamiliar datasets. Furthermore, without a broad and unified benchmark, evaluating performance across multimodal tasks becomes inconsistent and fragmented. This limits the models’ capability to handle the variety of functions required in realistic, cross-domain applications, especially when new data distributions are introduced.
Several tools, such as CLIP, BLIP, and SigLIP, have been proposed for generating visual-textual embeddings. These models typically use separate encoders for images and text, merging their outputs through simple operations like score-level fusion. While these approaches offer baseline utility, they suffer from limited cross-modal reasoning and generalization ability. Their performance in zero-shot conditions tends to decline due to shallow fusion strategies and the lack of task-specific instruction handling during training.
In a collaboration between researchers from Salesforce Research and the University of Waterloo, a new model called VLM2VEC was introduced alongside a comprehensive benchmark named MMEB. MMEB comprises 36 datasets across four major tasks: classification, visual question answering, retrieval, and visual grounding. It divides datasets into 20 used for training and 16 for evaluation, including out-of-distribution tasks. The VLM2VEC framework is designed to convert any vision-language model into an embedding model using contrastive training. It allows it to handle any input combination of text and images while following task instructions.
To build VLM2VEC, the research team used backbone models such as Phi-3.5-V and LLaVA-1.6. The method begins by constructing task-specific instruction-based queries and targets, processed through a vision-language model to generate embeddings. Contrastive training is employed using the InfoNCE loss function with cosine similarity, aligning embeddings by maximizing the similarity between matching query-target pairs while minimizing it for mismatches. To support large batch sizes, critical for training with diverse negatives, the researchers used GradCache, which splits batches into memory-manageable sub-batches and accumulates gradients. This process ensures efficient training even with the high memory demands of multimodal inputs. Task-specific instructions are embedded within the training pipeline to help the model adapt its encoding to the nature of the task, such as grounding or retrieval, further boosting its generalization capabilities.
Performance results demonstrate the advantage of the proposed method. The best-performing version of VLM2VEC used LLaVA-1.6 as its backbone, applied LoRA tuning, and processed images at 1344 × 1344 resolution. This configuration achieved a Precision@1 score of 62.9% across all 36 MMEB datasets. In zero-shot tests on the 16 out-of-distribution datasets, it maintained a strong 57.1% score. Compared to the best-performing baseline model without fine-tuning, which scored 44.7%, VLM2VEC showed an 18.2-point improvement. Compared to the top fine-tuned baseline at 47.2%, the improvement was 15.7 points. Across all task categories—classification, VQA, retrieval, and grounding—the model consistently scored above 50%, a level of performance not matched by any baseline. The results also indicate that LoRA-tuned variants outperformed those trained with full fine-tuning, showing that parameter-efficient training strategies can deliver higher accuracy.
The research clearly outlines a solution to the problem of task-specific multimodal embedding tools that lack generalization. By combining a well-structured training framework and a robust benchmark, the study demonstrates a universal embedding model that handles varied tasks effectively using contrastive training and instruction-following. This development marks a meaningful step forward in scalable, adaptable multimodal AI.
Check out Paper and Project. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit.
The post This AI Paper from Salesforce Introduces VLM2VEC and MMEB: A Contrastive Framework and Benchmark for Universal Multimodal Embeddings appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ