The Debugging Problem in AI Coding Tools
Despite significant progress in code generation and completion, AI coding tools continue to face challenges in debugging—an integral part of software development. While large language models (LLMs) can generate code snippets and occasionally offer fixes, they often falter when addressing runtime errors or navigating through logical faults using traditional debugging tools. Human developers routinely rely on interactive debuggers like Python’s pdb to inspect variables, trace execution, and understand program flow. These tools facilitate exploratory reasoning—a dimension largely absent from the capabilities of current LLMs. This gap highlights a fundamental limitation: most LLMs operate in static environments with limited support for dynamic feedback, making it difficult to engage in the iterative reasoning required for effective debugging.
Debug-Gym—A Framework for Tool-Using Agents
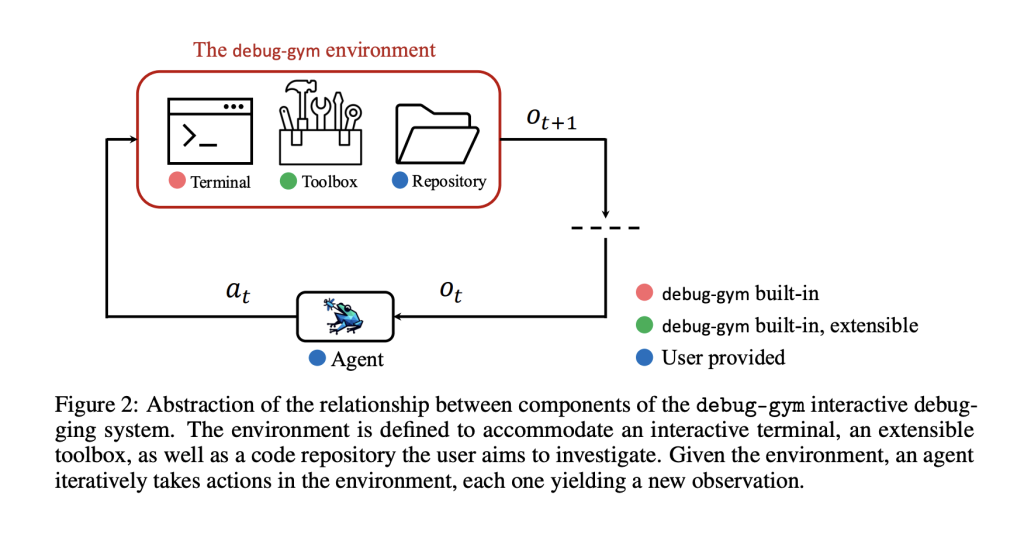
To explore the extent to which LLMs can make use of interactive debugging tools such as pdb, Microsoft has introduced Debug-Gym—a Python-based environment designed to evaluate how AI agents perform in realistic code-repair tasks. Debug-Gym provides a structured setting where LLM-based agents can employ debugging commands, examine runtime behavior, and refine their approach through active exploration. Rather than simply predicting corrections, agents in Debug-Gym can interact with their environment to gather evidence before proposing solutions. This model of active, tool-assisted debugging more closely mirrors the human approach to software repair and allows for the assessment of reasoning strategies in complex scenarios.

Technical Architecture and Features
Debug-Gym is built to support experimentation with interactive, tool-aware coding agents. It presents agents with error-prone Python programs and grants access to debugging tools via a controlled interface. Core components of the system include:
- Buggy program scenarios: A curated set of Python scripts with known faults, spanning syntax, runtime, and logical errors.
- Debugger access: A tool interface exposing commands akin to those used in Python’s
pdb, including stack inspection, step-through execution, and variable evaluation. - Observation and action spaces: Structured inputs such as traceback data and variable values are provided to the agent, which can then respond with commands or code edits.
The architecture supports deterministic execution and is modular, enabling easy substitution or augmentation of agents and debugging tools. The environment is publicly available under an open-source license, encouraging collaboration and comparative evaluation.

Evaluation and Observations
Initial experiments using Debug-Gym suggest that agents capable of leveraging interactive tools are better equipped to resolve complex bugs. According to Microsoft’s evaluation, LLMs that issued and interpreted debugging commands—such as variable prints or navigation through stack frames—demonstrated more accurate and efficient code repairs compared to static counterparts. In a benchmark consisting of 150 diverse bug cases, interactive agents achieved a notably higher success rate, resolving over half the problems with fewer iterations.
The framework also provides visibility into agent behavior. Researchers can analyze tool usage patterns, investigate where agents deviate from productive debugging strategies, and identify common failure points. This level of introspection supports iterative development of agent policies and opens pathways for fine-tuning models using richer feedback than text alone.
Furthermore, Debug-Gym supports training paradigms such as reinforcement learning from interaction histories, allowing future models to learn not just from human demonstrations, but also from the structured sequences of debugging actions.
Conclusion
Debug-Gym offers a practical and forward-looking approach to advancing LLM-based coding tools. By incorporating support for interactive debugging, it aligns more closely with real-world developer workflows. The environment enables precise measurement of agent capabilities in dynamic code repair and provides the scaffolding needed to train and evaluate agents that learn from exploration.
While current systems still face limitations in understanding nuanced runtime contexts, Debug-Gym lays the groundwork for developing agents that can systematically reason through bugs using external tools. This shift from passive code suggestion to active problem-solving represents a meaningful step toward integrating LLMs into professional software development environments.
Check out Paper and Project. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Can LLMs Debug Like Humans? Microsoft Introduces Debug-Gym for AI Coding Agents appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ