Understanding the Limits of Language Model Transparency
As large language models (LLMs) become central to a growing number of applications—ranging from enterprise decision support to education and scientific research—the need to understand their internal decision-making becomes more pressing. A core challenge remains: how can we determine where a model’s response comes from? Most LLMs are trained on massive datasets consisting of trillions of tokens, yet there has been no practical tool to map model outputs back to the data that shaped them. This opacity complicates efforts to evaluate trustworthiness, trace factual origins, and investigate potential memorization or bias.
OLMoTrace – A Tool for Real-Time Output Tracing
The Allen Institute for AI (Ai2) recently introduced OLMoTrace, a system designed to trace segments of LLM-generated responses back to their training data in real time. The system is built on top of Ai2’s open-source OLMo models and provides an interface for identifying verbatim overlaps between generated text and the documents used during model training. Unlike retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) approaches, which inject external context during inference, OLMoTrace is designed for post-hoc interpretability—it identifies connections between model behavior and prior exposure during training.
OLMoTrace is integrated into the Ai2 Playground, where users can examine specific spans in an LLM output, view matched training documents, and inspect those documents in extended context. The system supports OLMo models including OLMo-2-32B-Instruct and leverages their full training data—over 4.6 trillion tokens across 3.2 billion documents.

Technical Architecture and Design Considerations
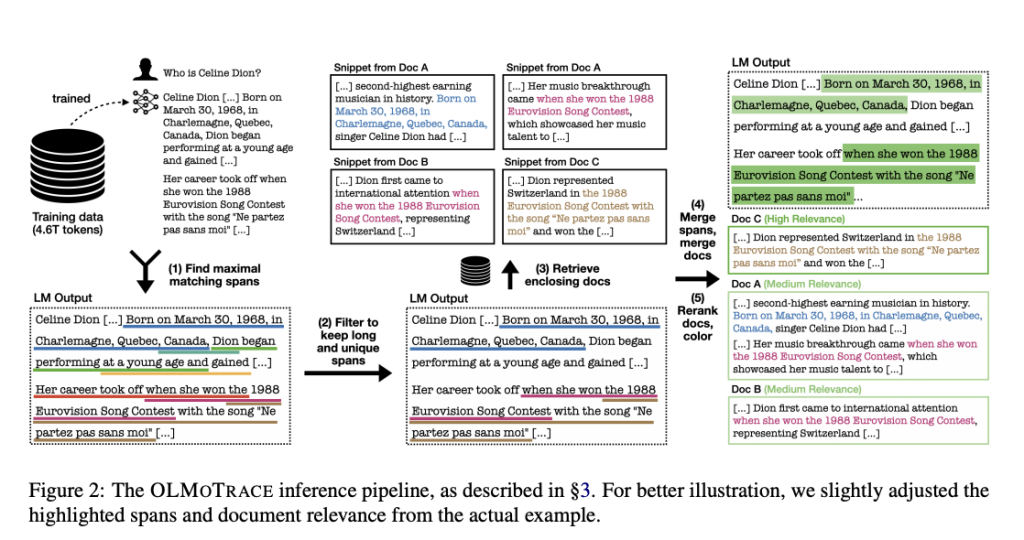
At the heart of OLMoTrace is infini-gram, an indexing and search engine built for extreme-scale text corpora. The system uses a suffix array-based structure to efficiently search for exact spans from the model’s outputs in the training data. The core inference pipeline comprises five stages:
- Span Identification: Extracts all maximal spans from a model’s output that match verbatim sequences in the training data. The algorithm avoids spans that are incomplete, overly common, or nested.
- Span Filtering: Ranks spans based on “span unigram probability,” which prioritizes longer and less frequent phrases, as a proxy for informativeness.
- Document Retrieval: For each span, the system retrieves up to 10 relevant documents containing the phrase, balancing precision and runtime.
- Merging: Consolidates overlapping spans and duplicates to reduce redundancy in the user interface.
- Relevance Ranking: Applies BM25 scoring to rank the retrieved documents based on their similarity to the original prompt and response.
This design ensures that tracing results are not only accurate but also surfaced within an average latency of 4.5 seconds for a 450-token model output. All processing is performed on CPU-based nodes, using SSDs to accommodate the large index files with low-latency access.
Evaluation, Insights, and Use Cases
Ai2 benchmarked OLMoTrace using 98 LLM-generated conversations from internal usage. Document relevance was scored both by human annotators and by a model-based “LLM-as-a-Judge” evaluator (gpt-4o). The top retrieved document received an average relevance score of 1.82 (on a 0–3 scale), and the top-5 documents averaged 1.50—indicating reasonable alignment between model output and retrieved training context.
Three illustrative use cases demonstrate the system’s utility:
- Fact Verification: Users can determine whether a factual statement was likely memorized from the training data by inspecting its source documents.
- Creative Expression Analysis: Even seemingly novel or stylized language (e.g., Tolkien-like phrasing) can sometimes be traced back to fan fiction or literary samples in the training corpus.
- Mathematical Reasoning: OLMoTrace can surface exact matches for symbolic computation steps or structured problem-solving examples, shedding light on how LLMs learn mathematical tasks.
These use cases highlight the practical value of tracing model outputs to training data in understanding memorization, data provenance, and generalization behavior.
Implications for Open Models and Model Auditing
OLMoTrace underscores the importance of transparency in LLM development, particularly for open-source models. While the tool only surfaces lexical matches and not causal relationships, it provides a concrete mechanism to investigate how and when language models reuse training material. This is especially relevant in contexts involving compliance, copyright auditing, or quality assurance.
The system’s open-source foundation, built under the Apache 2.0 license, also invites further exploration. Researchers may extend it to approximate matching or influence-based techniques, while developers can integrate it into broader LLM evaluation pipelines.
In a landscape where model behavior is often opaque, OLMoTrace sets a precedent for inspectable, data-grounded LLMs—raising the bar for transparency in model development and deployment
Check out Paper and Playground. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit. Note:
The post Allen Institute for AI (Ai2) Launches OLMoTrace: Real-Time Tracing of LLM Outputs Back to Training Data appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ