While the outputs of large language models (LLMs) appear coherent and useful, the underlying mechanisms guiding these behaviors remain largely unknown. As these models are increasingly deployed in sensitive and high-stakes environments, it has become crucial to understand what they do and how they do it.
The main challenge lies in uncovering the internal steps that lead a model to a specific response. The computations happen across hundreds of layers and billions of parameters, making it difficult to isolate the processes involved. Without a clear understanding of these steps, trusting or debugging their behavior becomes harder, especially in tasks requiring reasoning, planning, or factual reliability. Researchers are thus focused on reverse-engineering these models to identify how information flows and decisions are made internally.
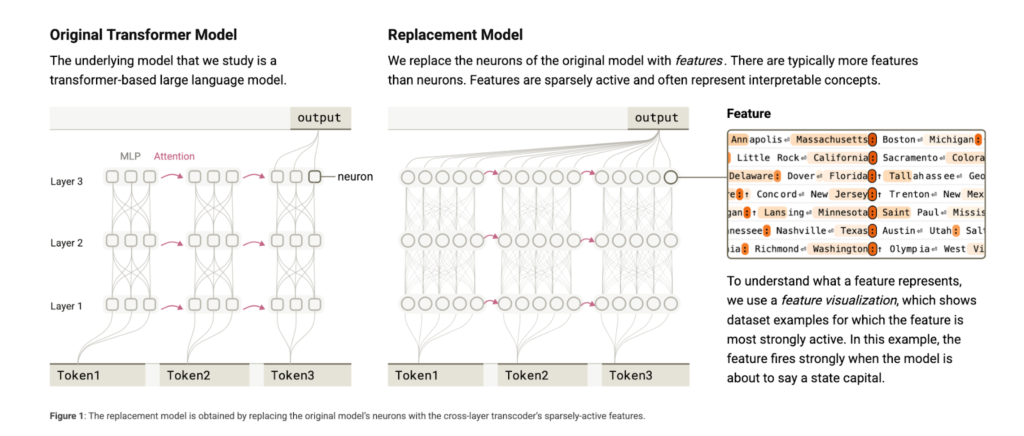
Existing interpretability methods like attention maps and feature attribution offer partial views into model behavior. While these tools help highlight which input tokens contribute to outputs, they often fail to trace the full chain of reasoning or identify intermediate steps. Moreover, these tools usually focus on surface-level behaviors and do not provide consistent insight into deeper computational structures. This has created the need for more structured, fine-grained methods to trace logic through internal representations over multiple steps.
To address this, researchers from Anthropic introduced a new technique called attribution graphs. These graphs allow researchers to trace the internal flow of information between features within a model during a single forward pass. By doing so, they attempt to identify intermediate concepts or reasoning steps that are not visible from the model’s outputs alone. The attribution graphs generate hypotheses about the computational pathways a model follows, which are then tested using perturbation experiments. This approach marks a significant step toward revealing the “wiring diagram” of large models, much like how neuroscientists map brain activity.
The researchers applied attribution graphs to Claude 3.5 Haiku, a lightweight language model released by Anthropic in October 2024. The method begins by identifying interpretable features activated by a specific input. These features are then traced to determine their influence on the final output. For example, when prompted with a riddle or poem, the model selects a set of rhyming words before writing lines, a form of planning. In another example, the model identifies “Texas” as an intermediate step to answer the question, “What’s the capital of the state containing Dallas?” which it correctly resolves as “Austin.” The graphs reveal the model outputs and how it internally represents and transitions between ideas.
The performance results from attribution graphs uncovered several advanced behaviors within Claude 3.5 Haiku. In poetry tasks, the model pre-plans rhyming words before composing each line, showing anticipatory reasoning. In multi-hop questions, the model forms internal intermediate representations, such as associating Dallas with Texas before determining Austin as the answer. It leverages both language-specific and abstract circuits for multilingual inputs, with the latter becoming more prominent in Claude 3.5 Haiku than in earlier models. Further, the model generates diagnoses internally in medical reasoning tasks and uses them to inform follow-up questions. These findings suggest that the model can abstract planning, internal goal-setting, and stepwise logical deductions without explicit instruction.
This research presents attribution graphs as a valuable interpretability tool that reveals the hidden layers of reasoning in language models. By applying this method, the team from Anthropic has shown that models like Claude 3.5 Haiku don’t merely mimic human responses—they compute through layered, structured steps. This opens the door to deeper audits of model behavior, allowing more transparent and responsible deployment of advanced AI systems.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit.
The post This AI Paper from Anthropic Introduces Attribution Graphs: A New Interpretability Method to Trace Internal Reasoning in Claude 3.5 Haiku appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ
 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]
