GPUs are widely recognized for their efficiency in handling high-performance computing workloads, such as those found in artificial intelligence and scientific simulations. These processors are designed to execute thousands of threads simultaneously, with hardware support for features like register file access optimization, memory coalescing, and warp-based scheduling. Their structure allows them to support extensive data parallelism and achieve high throughput on complex computational tasks increasingly prevalent across diverse scientific and engineering domains.
A major challenge in academic research involving GPU microarchitectures is the dependence on outdated architecture models. Many studies still use the Tesla-based pipeline as their baseline, which was released more than fifteen years ago. Since then, GPU architectures have evolved significantly, including introducing sub-core components, new control bits for compiler-hardware coordination, and enhanced cache mechanisms. Continuing to simulate modern workloads on obsolete architectures misguides performance evaluations and hinders innovation in architecture-aware software design.
Some simulators have tried to keep pace with these architectural changes. Tools like GPGPU-Sim and Accel-sim are commonly used in academia. Still, their updated versions lack fidelity in modeling key aspects of modern architectures such as Ampere or Turing. These tools often fail to accurately represent instruction fetch mechanisms, register file cache behaviors, and the coordination between compiler control bits and hardware components. A simulator that fails to represent such features can result in gross errors in estimated cycle counts and execution bottlenecks.
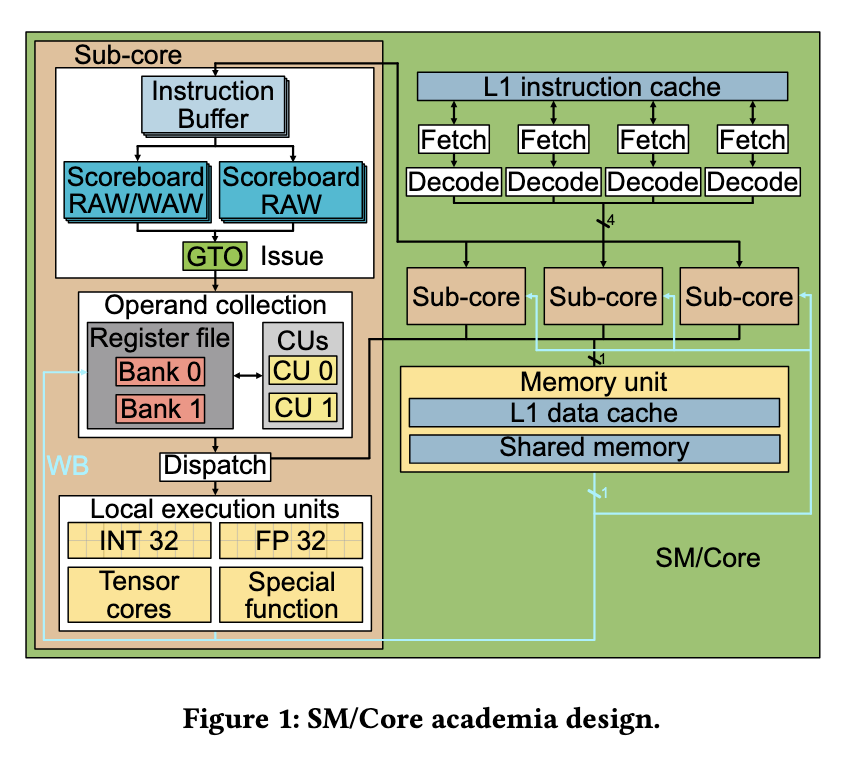
Research introduced by a team from the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya seeks to close this gap by reverse engineering the microarchitecture of modern NVIDIA GPUs. Their work dissects architectural features in detail, including the design of the issue and fetch stages, the behavior of the register file and its cache, and a refined understanding of how warps are scheduled based on readiness and dependencies. They also studied the effect of hardware control bits, revealing how these compiler hints influence hardware behavior and instruction scheduling.
To build their simulation model, the researchers created microbenchmarks composed of carefully selected SASS instructions. These were executed on actual Ampere GPUs while recording clock counters to determine latency. Experiments used stream buffers to test specific behaviors such as read-after-write hazards, register bank conflicts, and instruction prefetching behavior. They also evaluated the operation of the dependence management mechanism, which uses a scoreboard to track in-flight consumers and prevent write-after-read hazards. This granular measurement enabled them to propose a model that reflects internal execution details far more precisely than existing simulators.
In terms of accuracy, the model developed by the researchers significantly outperformed existing tools. Compared with real hardware using the NVIDIA RTX A6000, the model achieved a mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of 13.98%, which is 18.24% better than Accel-sim. The worst-case error in the proposed model never exceeded 62%, while Accel-sim reached errors up to 543% in some applications. Furthermore, their simulation showed a 90th percentile error of 31.47%, compared to 82.64% for Accel-sim. These results underline the enhanced precision of the proposed simulation framework in predicting GPU performance characteristics. The researchers verified that the model works effectively with other NVIDIA architectures like Turing, proving its portability and adaptability.
The paper highlights a clear mismatch between academic tools and modern GPU hardware and presents a practical solution to bridge that gap. The proposed simulation model improves performance prediction accuracy and helps understand modern GPUs’ detailed design. This contribution can support future innovations in both GPU architecture and software optimization.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit.
The post This AI Paper Unveils a Reverse-Engineered Simulator Model for Modern NVIDIA GPUs: Enhancing Microarchitecture Accuracy and Performance Prediction appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]