As LLMs scale, their computational and bandwidth demands increase significantly, posing challenges for AI training infrastructure. Following scaling laws, LLMs improve comprehension, reasoning, and generation by expanding parameters and datasets, necessitating robust computing systems. Large-scale AI clusters now require tens of thousands of GPUs or NPUs, as seen in LLAMA-3’s 16K GPU training setup, which took 54 days. With AI data centers deploying over 100K GPUs, scalable infrastructure is essential. Additionally, interconnect bandwidth requirements surpass 3.2 Tbps per node, far exceeding traditional CPU-based systems. The rising costs of symmetrical Clos network architectures make cost-effective solutions critical, alongside optimizing operational expenses such as energy and maintenance. Moreover, high availability is a key concern, as massive training clusters experience frequent hardware failures, demanding fault-tolerant network designs.
Addressing these challenges requires rethinking AI data center architecture. First, network topologies should align with LLM training’s structured traffic patterns, which differ from traditional workloads. Tensor parallelism, responsible for most data transfers, operates within small clusters, while data parallelism involves minimal but long-range communication. Second, computing and networking systems must be co-optimized, ensuring effective parallelism strategies and resource distribution to avoid congestion and underutilization. Lastly, AI clusters must feature self-healing mechanisms for fault tolerance, automatically rerouting traffic or activating backup NPUs when failures occur. These principles—localized network architectures, topology-aware computation, and self-healing systems—are essential for building efficient, resilient AI training infrastructures.
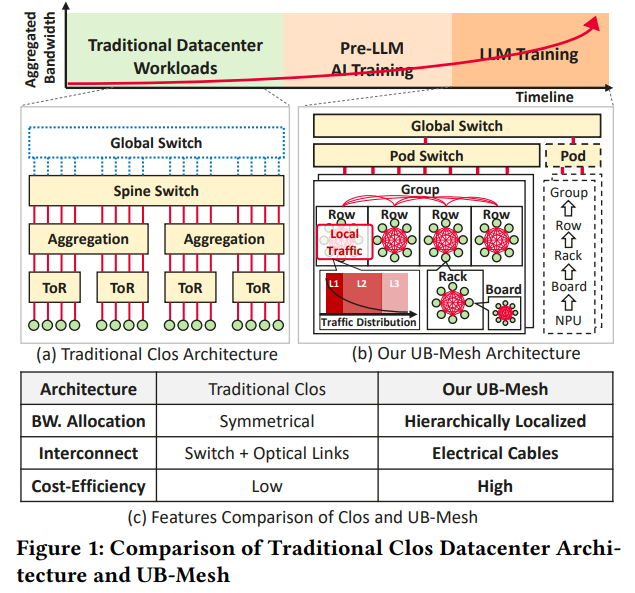
Huawei researchers introduced UB-Mesh, an AI data center network architecture designed for scalability, efficiency, and reliability. Unlike traditional symmetrical networks, UB-Mesh employs a hierarchically localized nD-FullMesh topology, optimizing short-range interconnects to minimize switch dependency. Based on a 4D-FullMesh design, its UB-Mesh-Pod integrates specialized hardware and a Unified Bus (UB) technique for flexible bandwidth allocation. The All-Path Routing (APR) mechanism enhances data traffic management, while a 64+1 backup system ensures fault tolerance. Compared to Clos networks, UB-Mesh reduces switch usage by 98% and optical module reliance by 93%, achieving 2.04× cost efficiency with minimal performance trade-offs in LLM training.
UB-Mesh is a high-dimensional full-mesh interconnect architecture designed to enhance efficiency in large-scale AI training. It employs an nD-FullMesh topology, minimizing reliance on costly switches and optical modules by maximizing direct electrical connections. The system is built on modular hardware components linked through a UB interconnect, streamlining communication across CPUs, NPUs, and switches. A 2D full-mesh structure connects 64 NPUs within a rack, extending to a 4D full-mesh at the Pod level. For scalability, a SuperPod structure integrates multiple Pods using a hybrid Clos topology, balancing performance, flexibility, and cost-efficiency in AI data centers.
To enhance the efficiency of UB-Mesh in large-scale AI training, we employ topology-aware strategies for optimizing collective communication and parallelization. For AllReduce, a Multi-Ring algorithm minimizes congestion by efficiently mapping paths and utilizing idle links to enhance bandwidth. In all-to-all communication, a multi-path approach boosts data transmission rates, while hierarchical methods optimize bandwidth for broadcasting and reduce operations. Additionally, the study refines parallelization through a systematic search, prioritizing high-bandwidth configurations. Comparisons with Clos architecture reveal that UB-Mesh maintains competitive performance while significantly reducing hardware costs, making it a cost-effective alternative for large-scale model training.
In conclusion, the UB IO controller incorporates a specialized co-processor, the Collective Communication Unit (CCU), to optimize collective communication tasks. The CCU manages data transfers, inter-NPU transmissions, and in-line data reduction using an on-chip SRAM buffer, minimizing redundant memory copies and reducing HBM bandwidth consumption. It also enhances computer-communication overlap. Additionally, UB-Mesh efficiently supports massive-expert MoE models by leveraging hierarchical all-to-all optimization and load/store-based data transfer. The study introduces UB-Mesh, an nD-FullMesh network architecture for LLM training, offering cost-efficient, high-performance networking with 95%+ linearity, 7.2% improved availability, and 2.04× better cost efficiency than Clos networks.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit.
The post UB-Mesh: A Cost-Efficient, Scalable Network Architecture for Large-Scale LLM Training appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ
 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]
