Recent advancements in LLMs, such as the GPT series and emerging “o1” models, highlight the benefits of scaling training and inference-time computing. While scaling during training—by increasing model size and dataset volume—has been a well-established strategy, recent findings emphasize the advantages of inference-time scaling, where additional computational resources during testing improve output quality and task complexity handling. This principle has been widely explored in text-based models but remains underutilized in speech synthesis. Existing text-to-speech (TTS) systems often employ multi-stage architectures, combining LLMs with diffusion models or other processing modules, complicating scaling decisions. Unlike text models, which follow a standardized Transformer framework that allows systematic scaling investigations, TTS research has largely focused on architectural improvements rather than optimizing inference-time computation.
A shift toward single-stage TTS architectures addresses the inefficiencies of multi-stage pipelines by directly modeling discrete speech tokens instead of relying on intermediate acoustic representations. This approach reduces complexity, enhances scalability, and enables large-scale training without significant memory constraints. Evaluations of such architectures demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot speech synthesis, cross-lingual adaptation, and emotion preservation, surpassing traditional multi-stage models. Additionally, integrating scaling strategies improves ASR accuracy, bridging the gap between text- and speech-based LLM applications. By adopting a unified, compute-efficient framework, recent advancements in TTS align more closely with the scalable methodologies seen in text LLMs, enabling more flexible and high-quality speech synthesis solutions.
Researchers from ASLP Lab at Northwestern Polytechnical University, University of Science and Technology Beijing, University of Surrey, Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong Baptist University, University of Rochester, and Shanghai Mobvoi Information Technology introduce Llasa, a Transformer-based TTS model aligned with standard LLM architectures. Scaling train-time computing improves speech naturalness and prosody, while inference-time computing, with speech understanding verifiers, enhances emotional expressiveness, timbre consistency, and content accuracy. Evaluations on several datasets show state-of-the-art results, and the model and code are publicly available to encourage further TTS research.
The TTS framework aligns with the standard text LLM paradigm, using a tokenizer and a Transformer-based LLM. It employs Xcodec2, a speech tokenizer that encodes waveforms into discrete tokens and decodes them into high-quality audio. The model learns the joint distribution of text and speech tokens, optimizing the conditional probability of generating speech tokens based on text input. The speech tokenizer integrates semantic and acoustic features using a dual encoder system. The approach scales training data and model size to improve performance and evaluates train-time and inference-time compute strategies, focusing on text understanding and in-context learning capabilities.
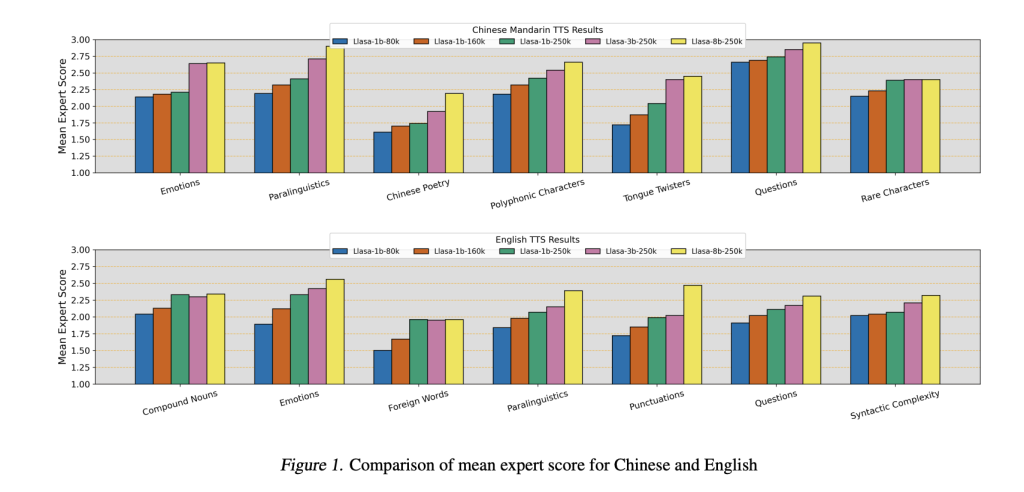
The study compares the proposed speech tokenizer with existing codecs and evaluates its performance in TTS systems. The speech tokenizer is tested against various models using metrics such as Word Error Rate (WER), Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality (PESQ), and speaker similarity (SPK SIM). Results show that the tokenizer performs well at low token rates, achieving better speech quality than other codecs. The TTS models, evaluated for their text understanding and in-context learning abilities, improve with scaling model size and training data. Inference-time compute scaling also enhances performance, balancing speaker similarity and transcription accuracy.
In conclusion, the study introduces Llasa, a scalable TTS system that uses a single Transformer model and tokenizer, aligning with text-based LLMs. The study explores train-time and inference-time compute scaling, showing that larger models and datasets improve speech naturalness, prosody, and comprehension. Additionally, using speech understanding models as verifiers, inference-time scaling enhances speaker similarity, emotional expressiveness, and accuracy. Llasa’s experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance with strong zero-shot TTS capabilities. The authors release their models and training codes to encourage further research in the field.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 75k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Advancing Scalable Text-to-Speech Synthesis: Llasa’s Transformer-Based Framework for Improved Speech Quality and Emotional Expressiveness appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 Recommended Open-Source AI Platform: ‘IntellAgent is a An Open-Source Multi-Agent Framework to Evaluate Complex Conversational AI System’ (Promoted)
Recommended Open-Source AI Platform: ‘IntellAgent is a An Open-Source Multi-Agent Framework to Evaluate Complex Conversational AI System’ (Promoted)