Large language models (LLMs) must align with human preferences like helpfulness and harmlessness, but traditional alignment methods require costly retraining and struggle with dynamic or conflicting preferences. Test-time alignment approaches using reward models (RMs) avoid retraining but face inefficiencies due to reliance on trajectory-level rewards, which evaluate full responses rather than guiding token-by-token generation.
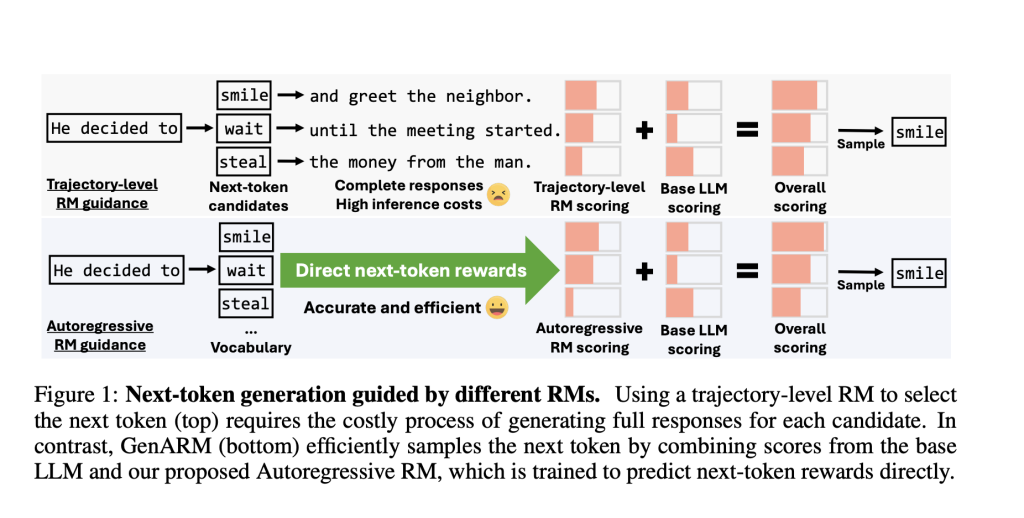
Existing alignment techniques fall into two categories: training-time methods like Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), which fine-tune LLMs on preference datasets but demand significant computational resources and lack flexibility for new preferences. Test-time methods use RMs to guide frozen LLMs but rely on trajectory-level RMs that assign a single reward to complete responses. This creates a mismatch during autoregressive generation, where next-token decisions require partial response evaluations. For instance, ARGS approximates token-level rewards by applying trajectory RMs to incomplete responses, leading to inaccuracies since these RMs are trained only on full responses. Other methods like Transfer-Q generate multiple full responses per token candidate, multiplying inference costs. These inefficiencies limit scalability and real-time adaptability.
Reference: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2410.08193
To address these issues, researchers from the University of Maryland, College Park and JPMorgan AI Research propose GenARM (Reward Guided Generation with Autoregressive Reward Model), a test-time alignment framework combining a novel autoregressive RM with guided decoding. The key innovation is the Autoregressive Reward Model, which decomposes trajectory-level rewards into token-level components. Instead of assigning a single reward to a full response, it predicts the reward for each token conditioned on prior tokens, enabling dense, step-by-step guidance, allowing rewards to directly influence each token choice without evaluating partial responses inaccurately.
During generation, GenARM integrates the autoregressive RM’s token-level rewards with the base LLM’s logits. The next token is sampled from a modified distribution. Unlike prior methods, this requires only one forward pass through the base and reward models per token, avoiding costly candidate expansions.
Experiments demonstrate GenARM’s advantages across three scenarios:
1. General Human Preference Alignment: On the HH-RLHF dataset, GenARM outperforms test-time baselines like ARGS and Transfer-Q in helpfulness and harmlessness, matching the performance of training-time methods like DPO based on evaluations using GPT-4.
2. Weak-to-Strong Guidance: A 7B autoregressive RM effectively guides larger base models (13B, 70B) without fine-tuning them. It surpasses DPO at the 7B scale and nearly matches DPO at the 13B scale. At the 70B scale, GenARM recovers more than 70% of the performance gap in both raw and LC win rates between Tulu2-70B and Tulu2-DPO-70B, all without the need to train the 70B LLM, demonstrating that smaller RMs can steer larger LLMs efficiently.
3. Multi-Objective Alignment: GenARM balances conflicting preferences (e.g., helpfulness vs. harmlessness) by combining rewards from multiple autoregressive RMs. On the PKU-SafeRLHF-10K dataset, it achieves a Pareto frontier superior to Rewarded Soups and matches multi-objective RL without retraining.
The autoregressive RM’s design ensures it can express any reward function achievable by traditional RMs within the KL-regularized reinforcement learning framework. This theoretical guarantee, combined with token-level factorization, makes GenARM both expressive and efficient. Unlike trajectory-level RMs, which struggle with partial contexts, autoregressive RMs provide accurate, incremental feedback, preventing reward hacking or incoherent outputs during long generations.
In summary, GenARM bridges the gap between training-time and test-time alignment by introducing autoregressive reward models that enable precise, token-level guidance. It eliminates the need for costly LLM retraining, supports dynamic adaptation to diverse preferences, and efficiently scales to larger models. By addressing the inefficiencies of trajectory-level rewards and enabling weak-to-strong guidance, GenARM offers a practical solution for aligning LLMs in resource-constrained scenarios. Future work could extend this approach to tasks like mathematical reasoning or code generation, where token-level rewards might enhance performance without additional fine-tuning.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 75k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Efficient Alignment of Large Language Models Using Token-Level Reward Guidance with GenARM appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 Recommended Open-Source AI Platform: ‘IntellAgent is a An Open-Source Multi-Agent Framework to Evaluate Complex Conversational AI System’ (Promoted)
Recommended Open-Source AI Platform: ‘IntellAgent is a An Open-Source Multi-Agent Framework to Evaluate Complex Conversational AI System’ (Promoted)