

Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized artificial intelligence by demonstrating remarkable capabilities in text generation and problem-solving. However, a critical limitation persists in their default “fast thinking” approach—generating outputs based on a single query without iterative refinement. While recent “slow thinking” methods like chain-of-thought prompting break problems into smaller steps, they remain constrained by static initial knowledge and cannot dynamically integrate new information during reasoning. This gap becomes pronounced in complex tasks requiring real-time knowledge updates, such as multi-hop question answering or adaptive code generation.
Current approaches to enhancing LLM reasoning fall into two categories. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems pre-load external knowledge but often introduce irrelevant information that hampers efficiency and accuracy. Tree-based search algorithms like Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) enable structured exploration of reasoning paths but lack mechanisms for contextual knowledge integration. For instance, while LATS (LLM-driven MCTS) introduced evaluation and reflection stages, it still operates within the model’s initial knowledge boundaries. These methods struggle with balancing exploration breadth, contextual relevance, and computational efficiency—often producing either overly broad or insufficiently informed responses.
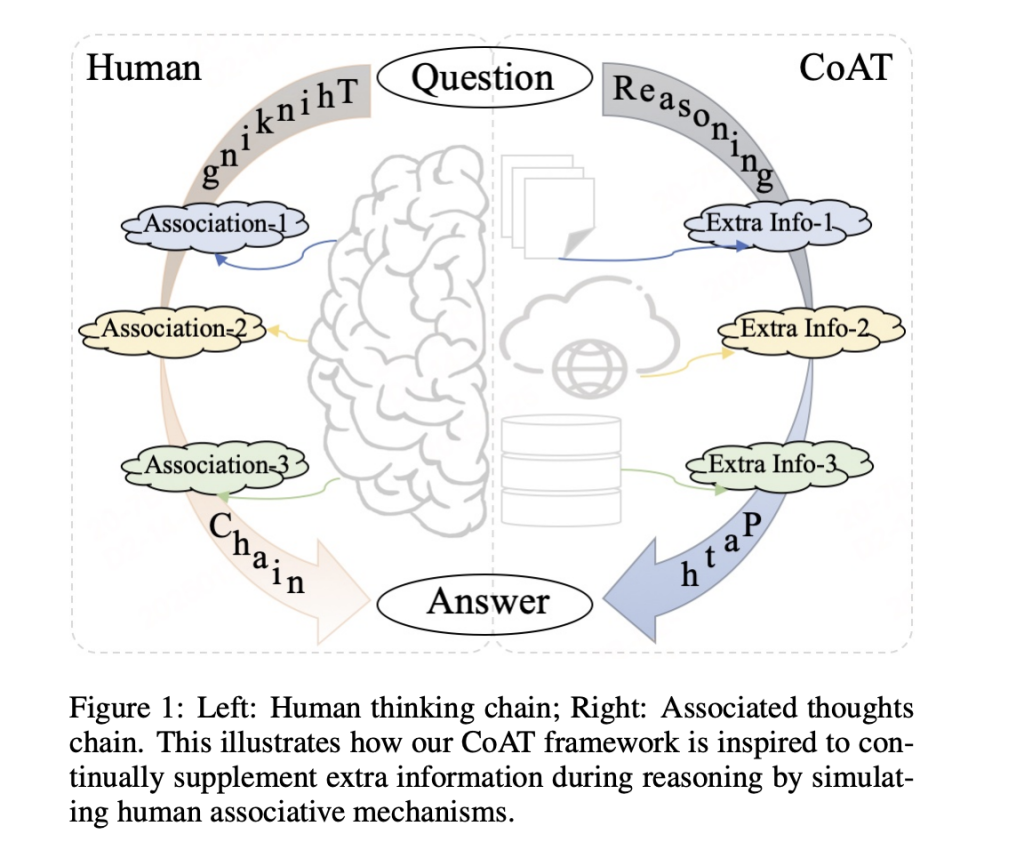
In this paper, a team of researchers from Digital Security Group, Qihoo 360 proposed the Chain-of-Associated-Thoughts (CoAT) framework to address these limitations through two key innovations. First, an associative memory mechanism enables dynamic knowledge integration during reasoning, mimicking human cognitive associations. Unlike static RAG approaches that retrieve information upfront, CoAT activates knowledge retrieval in response to specific reasoning steps—equivalent to a mathematician recalling relevant theorems only when needed in a proof. Second, an optimized MCTS algorithm incorporates this associative process through a novel four-stage cycle: selection, expansion with knowledge association, quality evaluation, and value backpropagation. This creates a feedback loop where each reasoning step can trigger targeted knowledge updates, as shown in Figure 4 of the original implementation.
At the core of CoAT lies a dual-stream reasoning architecture. When processing a query, the system simultaneously explores possible reasoning paths through the MCTS tree while maintaining an associative memory bank. Each node in the search tree (representing a reasoning step) generates both content (G(n)), associated knowledge (AM(n)) and
assigns scores balancing answer quality (Fg) and knowledge relevance (Fa), with β controlling their relative importance. This ensures that associations remain tightly coupled to the evolving reasoning process rather than introducing tangential information.
Performance evaluation of CoAT highlights its superiority over existing reasoning enhancement techniques. The framework was benchmarked on qualitative and quantitative metrics across various tasks. Qualitative assessments involved complex query responses, where CoAT demonstrated richer and more comprehensive answers compared to baseline models like Qwen2.5-32B and ChatGPT. Notably, it introduced additional categories of reasoning, such as ethical and regulatory considerations, which were absent in other models. Quantitative evaluations were conducted in two primary domains: knowledge-intensive question answering and code generation. For retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) tasks, CoAT was compared against NativeRAG, IRCoT, HippoRAG, LATS, and KAG on the HotpotQA and 2WikiMultiHopQA datasets. Metrics such as Exact Match (EM) and F1 scores confirmed CoAT’s superior performance, demonstrating its ability to generate precise and contextually relevant answers. In code generation, CoAT-enhanced models outperformed fine-tuned counterparts (Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct, Qwen2.5-Coder-14B-Instruct) on datasets like HumanEval, MBPP, and HumanEval-X, underscoring its adaptability to domain-specific reasoning tasks.
This work establishes a new paradigm for LLM reasoning by integrating dynamic knowledge association with structured search. Unlike previous static augmentation methods, CoAT’s real-time memory updates enable context-aware reasoning that adapts to emerging information needs. The technical innovations in MCTS optimization and dual-content evaluation provide a blueprint for combining external knowledge systems with modern LLMs. While current implementations rely on predefined external brains, the architecture naturally supports plug-and-play integration with emerging tools like LLM agents and real-time web search. These advancements suggest that the next frontier in AI reasoning may lie in systems that dynamically interleave internal computation with targeted external knowledge retrieval—much like human experts consulting references during complex problem-solving.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 75k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Chain-of-Associated-Thoughts (CoAT): An AI Framework to Enhance LLM Reasoning appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 Recommended Open-Source AI Platform: ‘IntellAgent is a An Open-Source Multi-Agent Framework to Evaluate Complex Conversational AI System’ (Promoted)
Recommended Open-Source AI Platform: ‘IntellAgent is a An Open-Source Multi-Agent Framework to Evaluate Complex Conversational AI System’ (Promoted)