As enterprises rapidly expand their applications, platforms, and infrastructure, it becomes increasingly challenging to keep up with technology trends, best practices, and programming standards. Enterprises typically provide their developers, engineers, and architects with a variety of knowledge resources such as user guides, technical wikis, code repositories, and specialized tools. However, over time these resources often become siloed within individual teams or organizational silos, making it difficult for employees to easily access relevant information across the broader organization. This lack of knowledge sharing can lead to duplicated efforts, reduced productivity, and missed opportunities to use institutional expertise.
Imagine you’re a developer tasked with troubleshooting a complex issue in your company’s cloud infrastructure. You scour through outdated user guides and scattered conversations, but can’t find the right answer. Minutes turn into hours, sometimes days, as you struggle to piece together the information you need, all while your project falls behind.
To address these challenges, the MuleSoft team integrated Amazon Q Apps, a capability within Amazon Q Business, a generative AI-powered assistant service, directly into their Cloud Central portal—an individualized portal that shows assets owned, costs and usage, and AWS Well-Architected recommendations to over 100 engineer teams. Amazon Q Apps is designed to use Amazon Q Business and its ability to draw upon an enterprise’s own internal data, documents, and systems to provide conversational assistance to users. By tapping into these rich information sources, you can enable your users to create Amazon Q Apps that can answer questions, summarize key points, generate custom content, and even securely complete certain tasks—all without the user having to navigate through disparate repositories or systems. Prior to Amazon Q Apps, MuleSoft was using a chatbot that used Slack, Amazon Lex V2, and Amazon Kendra. The chatbot solution didn’t meet the needs of the engineering and development teams, which prompted the exploration of Amazon Q Apps.
In this post, we demonstrate how Amazon Q Apps can help maximize the value of existing knowledge resources and improve productivity among various teams, ranging from finance to DevOps to support engineers. We share specific examples of how the generative AI assistant can enable surface relevant information, distill complex topics, generate custom content, and execute workflows—all while maintaining robust security and data governance controls.
In addition to demonstrating the power of Amazon Q Apps, we provide guidance on prompt engineering and system prompts reflective of real-world use cases using the rich features of Amazon Q Apps. For instance, let’s consider the scenario of troubleshooting network connectivity. By considering personas and their specific lines of business, we can derive the optimal tone and language to provide a targeted, actionable response. This level of personalization is key to delivering optimized customer experiences and building trust.
Improve production with Amazon Q Apps
Amazon Q Apps is a feature within Amazon Q Business that assists you in creating lightweight, purpose-built applications within Amazon Q Business. You can create these apps in several ways like creating applications with your own words to fit specific requirements, or by transforming your conversations with an Amazon Q Business assistant into prompts that then can be used to generate an application.
With Amazon Q Apps, you can build, share, and customize applications on enterprise data to streamline tasks and boost individual and team productivity. You can also publish applications to an admin-managed library and share them with their coworkers. Amazon Q Apps inherits user permissions, access controls, and enterprise guardrails from Amazon Q Business for secure sharing and adherence to data governance policies.
Amazon Q Apps is only available to users with a Pro subscription. If you have the Lite subscription, you will not be able to view or use Amazon Q Apps.
MuleSoft’s use case with Amazon Q Apps
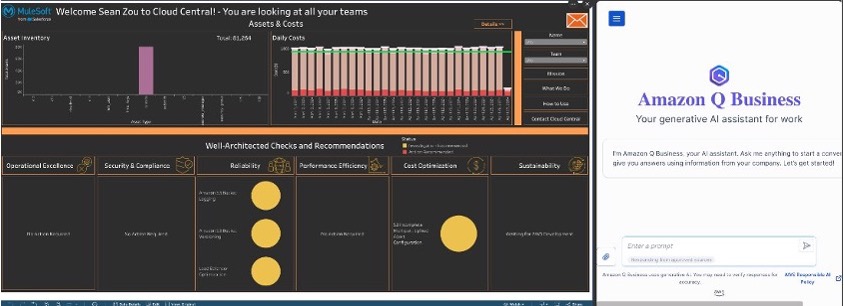
The team needed a more personalized approach to Amazon Q Business. Upon the announcement of Amazon Q Apps, the team determined it could solve an immediate need across teams. Their Cloud Central portal is already geared for a personalized experience for its users. MuleSoft completed a successful proof of concept integrating Amazon Q Apps into their overall Cloud Central portal. Cloud Central (see the following screenshot) serves as a single pane of glass for both managers and team members to visualize and understand each persona’s personalized cloud assets, cost metrics, and Well-Architected status based on application or infrastructure.

Fig 1: Salesforce MuleSoft Cloud Central Portal
The MuleSoft support team was looking for a way to help them troubleshoot network traffic latency when they rolled out a new customer into their production environment. The MuleSoft team found Amazon Q Apps helpful in providing possible causes for network latency for virtual private clouds (VPCs) as well as in providing prescriptive guidance on how to troubleshoot VPC network latencies. We explore a similar network latency use case in this post.
Solution overview
In this post, we focus on creating Amazon Q applications from the Amazon Q Business Chat and Amazon Q Apps Creator:
- Amazon Q Business Chat – You can use the Amazon Q Apps icon in the Amazon Q Business Chat assistant to generate a prompt that can be used to create an application. This feature summarizes the Amazon Q Business Chat conversation to create a prompt that you can review and edit before generating an application.
- Amazon Q Apps Creator – With Amazon Q Apps Creator, you can describe the type of application you want to build using your own words to generate an application. Amazon Q Apps will generate an application for you based on the provided prompt.
Pre-requisites
Make sure you have an AWS account. If not, you can sign up one. Refer to Pre-requisites for Amazon Q Apps for the steps to complete prior to deploying Amazon Q Apps. For more information, see Getting started with Amazon Q Business.
Create an application using Amazon Q Business Chat
You can choose the Amazon Q Apps icon from an Amazon Q chat conversation to generate an application prompt and using it to create an Amazon Q application. The icon is available in the conversations pane on the left, above the Amazon Q Assistant Chat conversation in the upper-right corner, or on the prompt dropdown menu.

Let’s explore an example of using an Amazon Q chat assistant conversation to create an application.
- Begin by asking the Amazon Q Business assistant a question related to the data that is provided in the Amazon Q Business application.
For this example, we ask about steps to troubleshoot network latency.

- After you’ve finished your conversation, choose the Amazon Q Apps icon in either the conversation pane or in the upper-right corner to launch Amazon Q App Creator.

- Review the generated prompt from the conversation and update the prompt to match your application purpose as needed.

- Choose Generate to create the application.

- To test the application, we enter under User input “I am unable to reach my EC2 host via port 22,” and choose Run.
- Review the generated text output and confirm that the troubleshooting steps look correct.

- Share the app with all in the library, choose Publish.

The Amazon Q Apps library will show all published applications shared by your teammates. Only users who have access to the Amazon Q Business application will be able to view your published application.
- You can choose labels where the application will reside, relating to teams, personas, or categories.

Create an application using Amazon Q Apps Creator
You can start building an Amazon Q application with Amazon Q Apps Creator by describing the task you want to create an application for. Complete the following steps:
- Choose Apps in the navigation pane.
- Enter your prompt or use an example prompt.

For this post, we enter the prompt “Create an app that crafts insightful content for users to troubleshoot AWS services. It takes inputs like as a use case to work backwards from on a solution. Based on these inputs, the app generates a tailored response for resolving the AWS service use case, providing steps to remediate and content links.”
- Choose Generate to create the application.

The Amazon Q application was created with AWS Use Case, Troubleshooting Steps, and Additional Resources sections translated from your prompt.


- To test the application, we enter under User input “which AWS tool to manage many AWS accounts and take advantage of consolidated billing,” and choose Run.
The Troubleshooting Steps section highlights using AWS Organizations and provides a walkthrough. The Additional Resources section provides more information about your use case, while citing AWS customer references.


- Choose Share to publish your application and choose the appropriate labels.
Results
MuleSoft offers a prime example of the transformative impact of Amazon Q Apps. With this solution, MuleSoft was able to realize a 50% reduction in team inquiries—from 100 down to just 50. These inquiries spanned a wide range, from basic AWS service information to complex networking troubleshooting and even Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volume migrations from gp2 to gp3.
Pricing
Amazon Q Business offers subscription options for you to customize your access. For more details, see Amazon Q Business pricing.
Conclusion
Amazon Q Business empowers enterprises to maximize the value of their knowledge resources by democratizing access to powerful conversational AI capabilities. Through Amazon Q Apps, organizations can create purpose-built applications using internal data and systems, unlocking new solutions and accelerating innovation.
The MuleSoft team demonstrated this by integrating Amazon Q Apps into their Cloud Central portal, enhancing user experience, streamlining collaboration, and optimizing cloud infrastructure while maintaining robust security and data governance.
Amazon Q Apps provides flexible generative AI application development using natural language, allowing organizations to build and securely publish custom applications tailored to their unique needs. This approach enables teams to boost innovation, productivity, and knowledge sharing across job functions.
By leveraging Amazon Q Business, enterprises can find answers, build applications, and drive productivity using their own enterprise data and conversational AI capabilities.
To learn about other Amazon Q Business customers’ success stories, see Amazon Q Developer customers.
*Note Amazon Q Apps is only available to users with the Pro subscription, if you have the Lite subscription you will not be able to view or use Amazon Q Apps.
About the Authors
 Rueben Jimenez is an AWS Sr Solutions Architect. Designing and implementing complex Data Analytics, Machine learning, Generative AI, and cloud infrastructure solutions.
Rueben Jimenez is an AWS Sr Solutions Architect. Designing and implementing complex Data Analytics, Machine learning, Generative AI, and cloud infrastructure solutions.
 Tiffany Myers is an AWS Product Manager for Amazon Q Apps. Launching generative AI solutions for business users.
Tiffany Myers is an AWS Product Manager for Amazon Q Apps. Launching generative AI solutions for business users.
 Summer Petersil is a Strategic Account Representative (SAR) on the AWS Salesforce team, where she leads Generative AI (GenAI) enablement efforts.
Summer Petersil is a Strategic Account Representative (SAR) on the AWS Salesforce team, where she leads Generative AI (GenAI) enablement efforts.
Source: Read MoreÂ