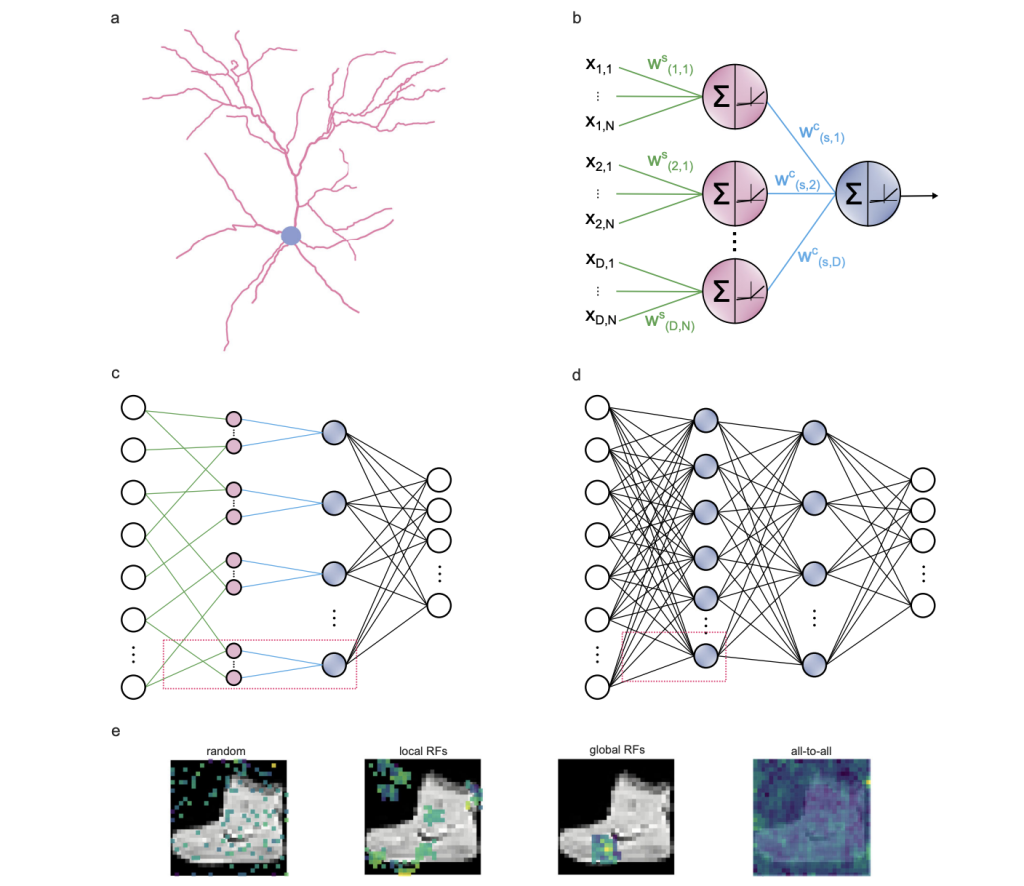
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) have their roots established in the inspiration developed from biological neural networks. Although highly efficient, ANNs fail to embody the neuronal structures in their architects truly. ANNs rely on vast training parameters, which lead to their high performance, but they consume a lot of energy and are prone to overfitting. Due to the continuous increase in the complexity and depth of ANNs, there has been an exponential growth in energy usage, which is becoming increasingly difficult to sustain. Therefore, researchers from Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas, Heraklion, Crete, Greece have developed a novel solution, dendritic ANNs, that has significantly captured the characteristics of dendritics in the neurons.
Traditional ANNs excel at solving complex tasks but require massive amounts of trainable parameters to achieve high accuracy. Each node in the complex network represents a specific class, which is an efficient way of distinguishing features. Still, it is inflexible as it faces problems adapting to different tasks. Moreover, it makes them prone to overfitting, making generalizability an issue. Therefore, there is a need for a new method that can maintain or increase its performance when the number of parameters is reduced and has improved generalizability to unseen data.
The proposed solution, dendritic ANNs, is designed to better leverage the structural and functional efficiency observed in neurons. The most significant innovation of ANNs is multi-class responsiveness, which allows for more precise and resilient learning. The dANNs try to mimic the structural connectivity of biological neurons, reducing random connections to process information more efficiently. The dendrites focus only on a subset of input data, which filters out the noise and focuses only on relevant information. These breakthroughs allow the model to train on a significantly smaller number of parameters compared to traditional ANNs.
To better understand the different features of the biological neurons that can be leveraged in ANNs, the researchers came up with four variants. The key features of each of the variants are:
- dANN-LRF (Local Receptive Fields): Each dendrite focuses on a small input sample, demonstrating the power of localised processing in reducing parameter count while maintaining high accuracy. This variant achieves the highest efficiency,
- dANN-R (Random Sampling): Input features are randomly sampled for each dendrite. This variant serves the purpose of understanding whether the sampling increases the efficiency or the dendritic structure itself. It proved to be beneficial for tasks having unclear spatial relationships of features.
- dANN-GRF (Global Receptive Fields): It focuses on capturing localised features to understand the spatial arrangement, for example, of objects in an image.
- pdANN (Pyramidal dANN): Investigates whether adding more biological realism through hierarchical structure can improve performance or generalisation. Although there was no significant improvement in accuracy, it reduced overfitting.
The dANNs were tested on several datasets, including CIFAR-10 and Fashion-MNIST. Their accuracy and performance consistently matched or exceeded that of the best vanilla ANNs (vANNs) across all datasets. dANN-LRF achieved peak accuracy and minimal loss and it used greatly fewer trainable parameters than vANNs. dANNs showed improved performance and stability as the number of layers increased, effectively dealing with scalability issues often found in biologically-inspired models. dANNs showed better efficiency when performing complex tasks, like those using the CIFAR10 dataset.
dANNs offer a new way to build artificial neural networks. This approach uses ideas from how biological dendrites work. Their learning is highly accurate, remarkably strong and exceptionally parameter-efficient. This substantially improves conventional architectures, creating stronger and more sustainable AI systems. Bio-inspired design offers important promise for improvements in artificial intelligence. This approach could lead to the development of several clever, energy-efficient systems.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 75k+ ML SubReddit.
 Meet IntellAgent: An Open-Source Multi-Agent Framework to Evaluate Complex Conversational AI System (Promoted)
Meet IntellAgent: An Open-Source Multi-Agent Framework to Evaluate Complex Conversational AI System (Promoted)
The post Dendritic Neural Networks: A Step Closer to Brain-Like AI appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ