A fundamental challenge in advancing AI research lies in developing systems that can autonomously perform structured reasoning and dynamically expand domain knowledge. Traditional AI models often rely on implicit reasoning processes, which limit their ability to explain decisions, adapt across domains, and generalize relational patterns. These shortcomings hinder their applicability to complex scientific problems that require interdisciplinary approaches, such as hypothesis generation, causal inference, and creative reasoning. Overcoming these limitations necessitates systems that can explicitly encode, refine, and transfer relational knowledge across diverse domains while maintaining adaptability and interpretability.
Existing approaches, including transformers and graph neural networks (GNNs), have achieved remarkable progress in natural language processing and relational tasks like property prediction. However, transformers primarily excel at linguistic fluency but rely heavily on implicit reasoning processes, restricting their ability to encode explicit structures. GNNs, while capable of representing relational systems, often struggle with distinguishing non-isomorphic graphs, limiting their capacity for hierarchical inference and abstraction. Additionally, both methods exhibit limitations in adaptability to new domains and often require substantial labeled data, reducing their efficiency for tasks that demand real-time reasoning or interdisciplinary synthesis.
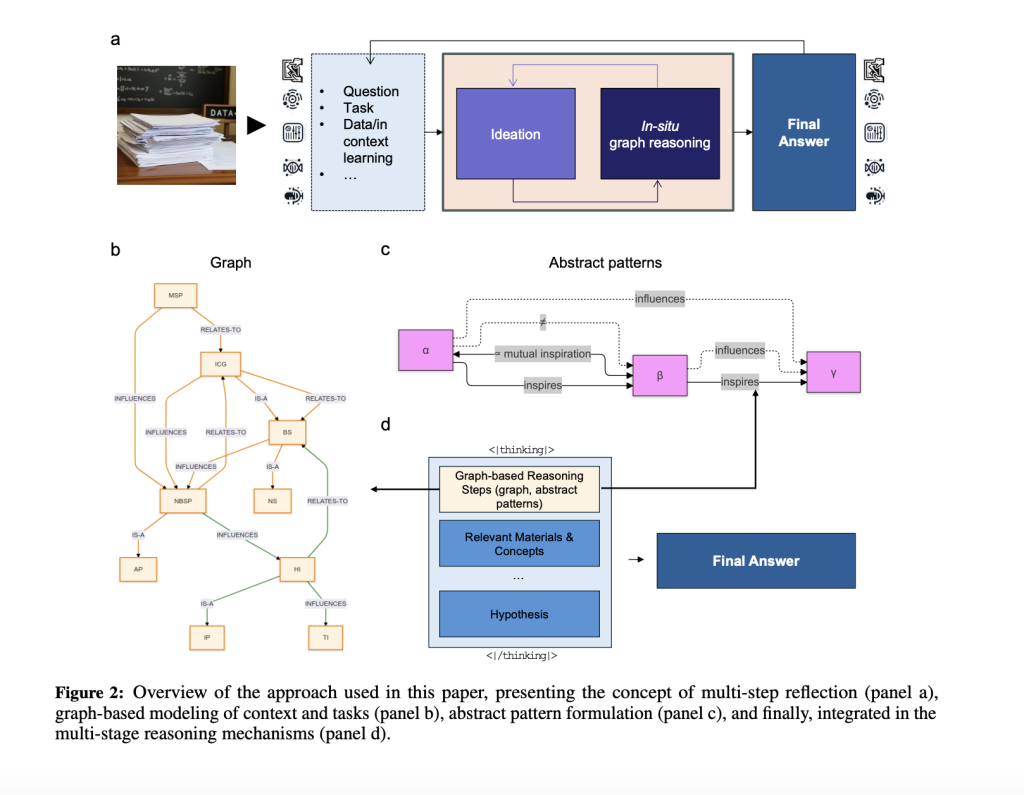
Researchers from MIT propose Graph-PReFLexOR, an innovative framework that integrates graph-based reasoning with symbolic abstraction to address these challenges. This framework formalizes reasoning as a structured mapping M: T→(G, P, A), where tasks generate knowledge graphs (G), abstract patterns (P), and final answers ( A). Inspired by category theory, it encodes concepts as nodes and relationships as edges, supporting hierarchical inference and adaptive generalization. Graph-PReFLexOR introduces explicit graph construction during the reasoning process to enhance interpretability and employs recursive reflection to refine reasoning iteratively. Bridging symbolic reasoning and neural architectures allows interdisciplinary applications, such as linking mythological concepts to materials science or uncovering patterns across domains. This paradigm enhances reasoning depth and adaptability, pushing beyond the capabilities of existing AI frameworks.
Graph-PReFLexOR combines graph-based reasoning with the fluency of transformer architectures, employing graph isomorphism networks (GINs) to identify structural equivalence across domains. The reasoning process involves constructing dynamic knowledge graphs where nodes represent core concepts and edges encode relationships such as IS-A or RELATES-TO. These graphs preserve relational structures, making detecting universal features like recurring subgraphs and algebraic patterns easier. The framework balances linguistic fluency with structured reasoning by embedding graph reasoning into transformers. The authors trained the system with a database of 1,000 bio-inspired materials science research papers using retrieval-augmented generation and recursive reasoning mechanisms. The model independently generates and improves knowledge graphs, promoting adaptability and consistency in difficult reasoning tasks.
Graph-PReFLexOR demonstrated excellent reasoning strengths on various tasks, effectively combining structured graph reasoning and symbolic abstraction for interdisciplinary uses. The system demonstrated the ability to generalize across diverse domains, effectively linking music with material properties, identifying isomorphic patterns, and dynamically generating knowledge graphs for hypothesis generation. It delivered significant improvements in reasoning depth, adaptability, and accuracy compared to conventional methods. The framework also bridged seemingly unrelated fields, such as mythology and materials science, uncovering innovative connections and providing insights into biomimetic material design. Its capacity to grow and refine knowledge graphs dynamically highlights its potential as a versatile tool for advancing interdisciplinary research and discovery.
Graph-PReFLexOR represents a major advancement in AI reasoning, addressing the critical challenge of enabling structured, interpretable, and interdisciplinary reasoning. By combining graph-based reasoning with symbolic abstraction, it achieves impressive adaptability and generalization across domains. With applications ranging from materials science to creative reasoning and hypothesis generation, this approach opens new pathways for AI-driven discovery. Future work can explore scaling this system to larger datasets and real-time applications, further unlocking its potential to drive innovation across scientific and interdisciplinary fields.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 65k+ ML SubReddit.
The post MIT Researchers Propose Graph-PReFLexOR: A Machine Learning Model Designed for Graph-Native Reasoning in Science and Engineering appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ