Chemical reasoning involves intricate, multi-step processes requiring precise calculations, where small errors can lead to significant issues. LLMs often struggle with domain-specific challenges, such as accurately handling chemical formulas, reasoning through complex steps, and integrating code effectively. Despite advancements in scientific reasoning, benchmarks like SciBench reveal LLMs’ limitations in solving chemical problems, highlighting the need for innovative approaches. Recent frameworks, such as StructChem, attempt to address these challenges by structuring problem-solving into stages like formula generation and confidence-based reviews. Other techniques, including advanced prompting strategies and Python-based reasoning tools, have also been explored. For instance, ChemCrow leverages function calling and precise code generation for tackling chemistry-specific tasks, while combining LLMs with external tools like Wolfram Alpha shows potential for improving accuracy in scientific problem-solving, though integration remains a challenge.
Decomposing complex problems into smaller tasks has enhanced model reasoning and accuracy, particularly in multi-step chemical problems. Studies emphasize the benefits of breaking down queries into manageable components, improving understanding and performance in domains like reading comprehension and complex question answering. Additionally, self-evolution techniques, where LLMs refine their outputs through iterative improvement and prompt evolution, have shown promise. Memory-enhanced frameworks, tool-assisted critiquing, and self-verification methods strengthen LLM capabilities by enabling error correction and refinement. These advancements provide a foundation for developing scalable systems capable of handling the complexities of chemical reasoning while maintaining accuracy and efficiency.
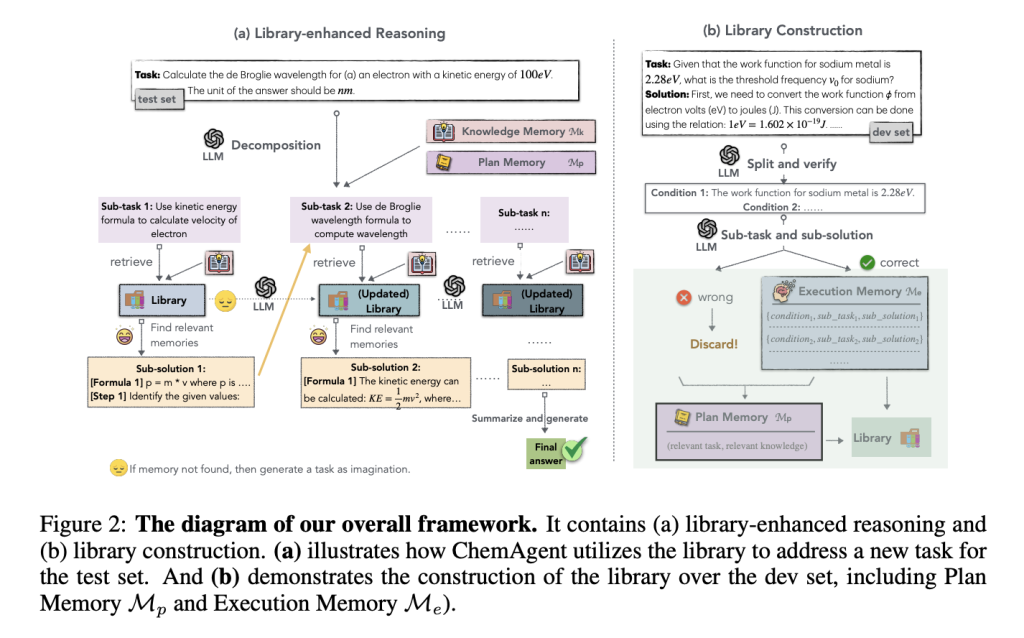
Researchers from Yale University, UIUC, Stanford University, and Shanghai Jiao Tong University introduced ChemAgent, a framework that enhances LLM performance through a dynamic, self-updating library. ChemAgent decomposes chemical tasks into sub-tasks, storing these and their solutions in a structured memory system. This system includes Planning Memory for strategies, Execution Memory for task-specific solutions, and Knowledge Memory for foundational principles. When solving new problems, ChemAgent retrieves, refines, and updates relevant information, enabling iterative learning. Tested on SciBench datasets, ChemAgent improved accuracy by up to 46% (GPT-4), outperforming state-of-the-art methods and demonstrating potential for applications like drug discovery.
ChemAgent is a system designed to improve LLMs for solving complex chemical problems. It organizes tasks into a structured memory with three components: Planning Memory (strategies), Execution Memory (solutions), and Knowledge Memory (chemical principles). Problems are broken into smaller sub-tasks in a library built from verified solutions. Relevant tasks are retrieved, refined, and dynamically updated during inference to enhance adaptability. ChemAgent outperforms baseline models (Few-shot, StructChem) on four datasets, achieving high accuracy through structured memory and iterative refinement. Its hierarchical approach and memory integration establish an effective framework for advanced chemical reasoning tasks.
The study evaluates ChemAgent’s memory components (Mp, Me, Mk) to identify their contributions, with GPT-4 as the base model. Results show that removing any component reduces performance, with Mk being the most impactful, particularly in datasets like ATKINS with limited memory pools. Memory quality is crucial, as GPT-4-generated memories outperform GPT-3.5, while hybrid memories degrade accuracy due to conflicting inputs. ChemAgent demonstrates consistent performance improvement across different LLMs, with the most notable gains on powerful models like GPT-4. The self-updating memory mechanism enhances problem-solving capabilities, particularly in complex datasets requiring specialized chemical knowledge and logical reasoning.
In conclusion, ChemAgent is a framework that enhances LLMs in solving complex chemical problems through self-exploration and a dynamic, self-updating memory library. By decomposing tasks into planning, execution, and knowledge components, ChemAgent builds a structured library to improve task decomposition and solution generation. Experiments on datasets like SciBench show significant performance gains, up to a 46% improvement using GPT-4. The framework effectively addresses challenges in chemical reasoning, such as handling domain-specific formulas and multi-step processes. It holds promise for broader applications in drug discovery and materials science.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 65k+ ML SubReddit.
 Recommend Open-Source Platform: Parlant is a framework that transforms how AI agents make decisions in customer-facing scenarios. (Promoted)
Recommend Open-Source Platform: Parlant is a framework that transforms how AI agents make decisions in customer-facing scenarios. (Promoted)
The post ChemAgent: Enhancing Large Language Models for Complex Chemical Reasoning with Dynamic Memory Frameworks appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ