The o1 model’s impressive performance in complex reasoning highlights the potential of test-time computing scaling, which enhances System-2 thinking by allocating greater computational effort during inference. While deep learning’s scaling effects have driven advancements in AI, particularly in LLMs like GPT, further scaling during training faces limitations due to data scarcity and computational constraints. Additionally, current models often fail in robustness and handling intricate tasks, primarily relying on fast, intuitive System-1 thinking. The o1 model, introduced by OpenAI in 2024, incorporates System-2 thinking, enabling superior performance in complex reasoning tasks through test-time computing scaling. This approach demonstrates that increasing computational effort during inference improves model accuracy, addressing some of the limitations of traditional training-phase scaling.
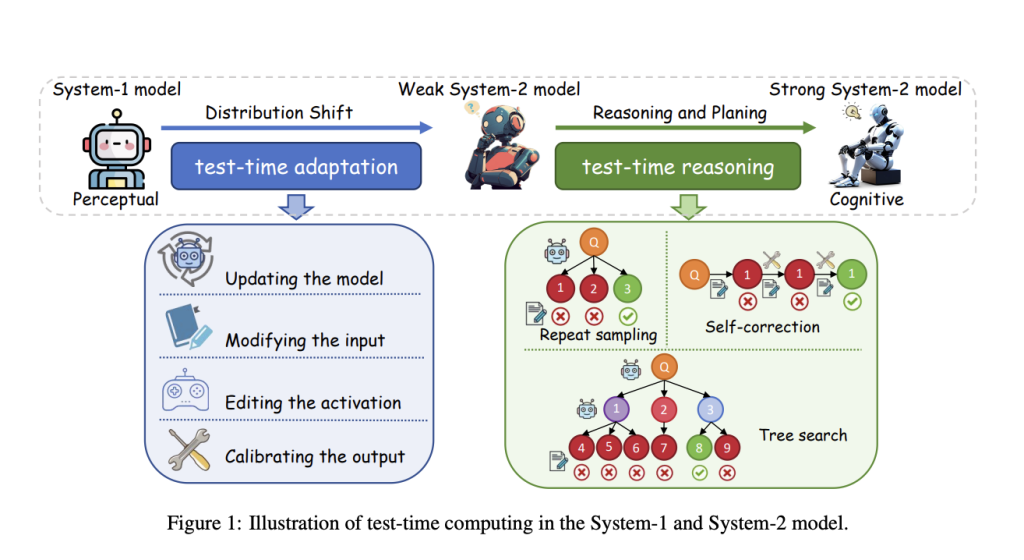
System-1 and System-2 thinking, derived from cognitive psychology, are used in AI to describe different processing strategies. System-1 models rely on pattern recognition and fast, intuitive responses, lacking robustness and adaptability to distribution shifts. Earlier efforts to enhance robustness, such as test-time adaptation (TTA), focused on parameter updates or external input adjustments. However, these models were limited to weak System-2 capabilities. With the rise of LLMs, System-2 models have gained traction, allowing for incremental reasoning and the generation of intermediate steps, as seen in Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting. While this approach improves reasoning compared to direct output methods, it remains prone to cumulative errors. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) partially addresses factual inaccuracies, but its impact on reasoning abilities is limited, leaving CoT-enabled models at an early stage of System-2 thinking.
Researchers from Soochow University, the National University of Singapore, and Ant Group explored test-time computing, tracing its evolution from System-1 to System-2 models. Initially applied to System-1 models to address distribution shifts and enhance robustness through parameter updates, input modifications, and output calibration, test-time computing now strengthens reasoning in System-2 models using strategies like repeated sampling, self-correction, and tree search. These methods enable models to solve complex problems by simulating diverse thinking patterns, reflecting on errors, and improving reasoning depth. The survey highlights this progression and further discusses future research directions for developing robust, cognitively capable AI systems.
TTA fine-tunes models during inference using test sample information. Key considerations include learning signals, parameter updates, and ensuring efficiency. Learning signals like Test-time Training (TTT) use auxiliary tasks, while Fully Test-time Adaptation (FTTA) leverages internal feedback (e.g., entropy minimization) but requires safeguards against model collapse. Human feedback is also utilized for tasks like QA and cross-modal retrieval. To improve efficiency, parameter updates target specific layers (e.g., normalization or adapters). Techniques such as episodic TTA or exponential moving averages address catastrophic forgetting. Methods like FOA further refine adaptation by optimizing prompts without backpropagation.
Test-time reasoning involves leveraging extended inference time to identify human-like reasoning within the decoding search space. Its two core components are feedback modeling and search strategies. Feedback modeling evaluates outputs through score-based and verbal feedback. Score-based feedback uses verifiers to score outputs based on correctness or reasoning process quality, with outcome-based and process-based approaches. Verbal feedback provides interpretability and correction suggestions via natural language critiques, often utilizing LLMs like GPT-4. Search strategies include repeated sampling and self-correction, where diverse responses are generated and refined. Multi-agent debates and self-critiques enhance reasoning by leveraging external feedback or intrinsic evaluation mechanisms.
In conclusion, The future of test-time computing involves several key directions. First, enhancing the generalization of System-2 models beyond domain-specific tasks like math and code to support scientific discovery and weak-to-strong generalization is vital. Second, expanding multimodal reasoning by integrating modalities like speech and video and aligning processes with human cognition holds promise. Third, balancing efficiency and performance by optimizing resource allocation and integrating acceleration strategies is critical. Fourth, establishing universal scaling laws remains challenging due to diverse strategies and influencing factors. Lastly, combining multiple test-time strategies and adaptation methods can improve reasoning, advancing LLMs toward cognitive intelligence.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 60k+ ML SubReddit.
 FREE UPCOMING AI WEBINAR (JAN 15, 2025): Boost LLM Accuracy with Synthetic Data and Evaluation Intelligence–Join this webinar to gain actionable insights into boosting LLM model performance and accuracy while safeguarding data privacy.
FREE UPCOMING AI WEBINAR (JAN 15, 2025): Boost LLM Accuracy with Synthetic Data and Evaluation Intelligence–Join this webinar to gain actionable insights into boosting LLM model performance and accuracy while safeguarding data privacy.
The post Advancing Test-Time Computing: Scaling System-2 Thinking for Robust and Cognitive AI appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ