Disaggregated systems are a new type of architecture designed to meet the high resource demands of modern applications like social networking, search, and in-memory databases. The systems intend to overcome the physical restrictions of the traditional servers by pooling and managing resources like memory and CPUs among multiple machines. Flexibility, better utilization of resources, and cost-effectiveness make this approach suitable for scalable cloud infrastructure, but this distributed design introduces significant challenges. Non-uniform memory access (NUMA) and remote resource access create latency and performance issues, which are hard to optimize. Contention for shared resources, memory locality problems, and scalability limits further complicate the use of disaggregated systems, leading to unpredictable application performance and resource management difficulties.
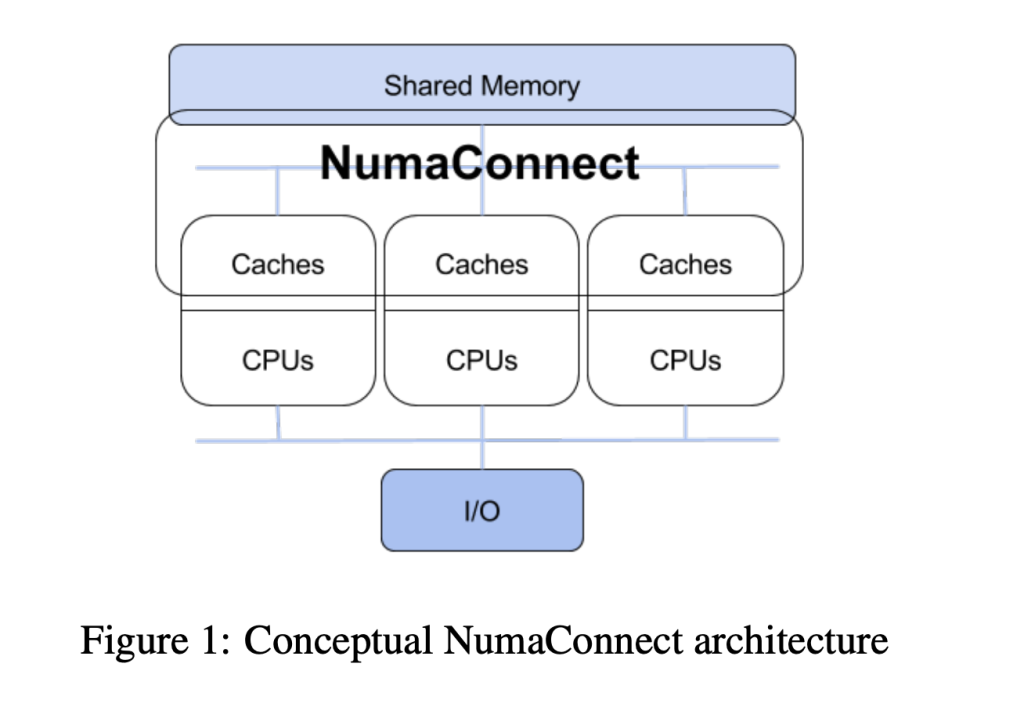
Currently, the resource contention in memory hierarchies and locality optimizations through UMA and NUMA-aware techniques in modern systems face major drawbacks. UMA does not consider the impact of remote memory and, thus, cannot be effective on large-scale architectures. However, NUMA-based techniques are aimed at small settings or simulations instead of the real world. As single-core performance stagnated, multicore systems became standard, introducing programming and scaling challenges. Technologies such as NumaConnect unify resources with shared memory and cache coherency but depend highly on workload characteristics. Application classification schemes, such as animal classes, simplify the categorization of workloads but lack adaptability, failing to address variability in resource sensitivity.
To address challenges posed by complex NUMA topologies on application performance, researchers from Umea University, Sweden, proposed a NUMA-aware resource mapping algorithm for virtualized environments on disaggregated systems. Researchers conducted detailed research to explore resource contention in shared environments. Researchers analyzed cache contention, memory hierarchy latency differences, and NUMA distances, all influencing performance.
The NUMA-aware algorithm optimized resource allocation by pinning virtual cores and migrating memory, thereby reducing memory slicing across nodes and minimizing application interference. Applications were categorized (e.g., “Sheep,” “Rabbit,” “Devil”) and carefully placed based on compatibility matrices to minimize contention. The response time, clock rate, and power usage were tracked in real-time along with IPC and MPI to enable the necessary changes in resource allocation. Evaluations performed on a disaggregated sixnode system demonstrated that significant improvements in application performance could be realized with memory-intensive workloads compared to default schedulers.
Researchers conducted experiments with various VM types, small, medium, large, and huge running workloads like Neo4j, Sockshop, SPECjvm2008, and Stream, to simulate real-world applications. The shared memory algorithm optimized virtual-to-physical resource mapping, reduced the NUMA distance and resource contention, and ensured affinity between cores and memory. It differed from the default Linux scheduler, where the core mappings are random, and performance is variable. The algorithm provided stable mappings and minimized interference.
Results showed significant performance improvements with the shared memory algorithm variants (SM-IPC and SM-MPI), achieving up to 241x enhancement in cases like Derby and Neo4j. While the vanilla scheduler exhibited unpredictable performance with standard deviation ratios above 0.4, the shared memory algorithms maintained consistent performance with ratios below 0.04. In addition, VM size affected the performance of the vanilla scheduler but had little effect on the shared memory algorithms, which reflected their efficiency in resource allocation across diverse environments.
In conclusion, the algorithm proposed by researchers enables resource composition from disaggregated servers, resulting in up to a 50x improvement in application performance compared to the default Linux scheduler. Results proved that the algorithm increases resource efficiency, application co-location, and user capacity. This method can act as a baseline for future advancements in resource mapping and performance optimization in NUMA disaggregated systems.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 60k+ ML SubReddit.
 FREE UPCOMING AI WEBINAR (JAN 15, 2025): Boost LLM Accuracy with Synthetic Data and Evaluation Intelligence–Join this webinar to gain actionable insights into boosting LLM model performance and accuracy while safeguarding data privacy.
FREE UPCOMING AI WEBINAR (JAN 15, 2025): Boost LLM Accuracy with Synthetic Data and Evaluation Intelligence–Join this webinar to gain actionable insights into boosting LLM model performance and accuracy while safeguarding data privacy.
The post Unlocking Cloud Efficiency: Optimized NUMA Resource Mapping for Virtualized Environments appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ