LLMs have demonstrated impressive capabilities in answering medical questions accurately, even outperforming average human scores in some medical examinations. However, their adoption in medical documentation tasks, such as clinical note generation, faces challenges due to the risk of generating incorrect or inconsistent information. Studies reveal that 20% of patients reading clinical notes identified errors, with 40% considering them serious, often related to misdiagnoses. This raises significant concerns, especially as LLMs increasingly support medical documentation tasks. While these models have shown strong performance in answering medical exam questions and imitating clinical reasoning, they are prone to generating hallucinations and potentially harmful content, which could adversely impact clinical decision-making. This highlights the critical need for robust validation frameworks to ensure the accuracy and safety of LLM-generated medical content.
Recent efforts have explored benchmarks for consistency evaluation in general domains, such as semantic, logical, and factual consistency, but these approaches often fall short of ensuring reliability across test cases. While models like ChatGPT and GPT-4 exhibit improved reasoning and language understanding, studies show they struggle with logical consistency. In the medical domain, assessments of LLMs, such as ChatGPT and GPT-4, have demonstrated accurate performance in structured medical examinations like the USMLE. However, limitations emerge when handling complex medical queries, and LLM-generated drafts in patient communication have shown potential risks, including severe harm if errors remain uncorrected. Despite advancements, the lack of publicly available benchmarks for validating the correctness and consistency of medical texts generated by LLMs underscores the need for reliable, automated validation systems to address these challenges effectively.
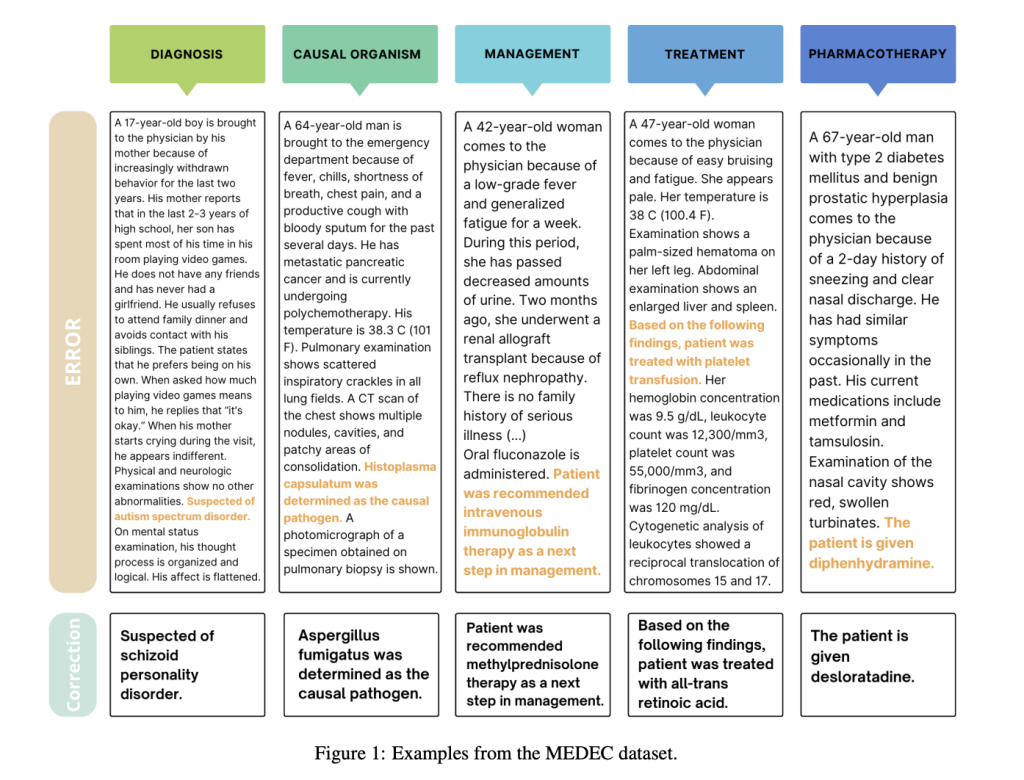
Researchers from Microsoft and the University of Washington have developed MEDEC, the first publicly available benchmark for detecting and correcting medical errors in clinical notes. MEDEC includes 3,848 clinical texts covering five error types: Diagnosis, Management, Treatment, Pharmacotherapy, and Causal Organism. Evaluations using advanced LLMs, such as GPT-4 and Claude 3.5 Sonnet, revealed their capability to address these tasks, but human medical experts outperform them. This benchmark highlights the challenges in validating and correcting clinical texts, emphasizing the need for models with robust medical reasoning. Insights from these experiments offer guidance for improving future error detection systems.
The MEDEC dataset contains 3,848 clinical texts, annotated with five error types: Diagnosis, Management, Treatment, Pharmacotherapy, and Causal Organism. Errors were introduced by leveraging medical board exams (MS) and modifying real clinical notes from University of Washington hospitals (UW). Annotators manually created errors by injecting incorrect medical entities into the text while ensuring consistency with other parts of the note. MEDEC is designed to evaluate models on error detection and correction, divided into predicting errors, identifying error sentences, and generating corrections.
The experiments utilized various small and LLMs, including Phi-3-7B, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, Gemini 2.0 Flash, and OpenAI’s GPT-4 series, to evaluate their performance on medical error detection and correction tasks. These models were tested on subtasks such as identifying errors, pinpointing erroneous sentences, and generating corrections. Metrics like accuracy, recall, ROUGE-1, BLEURT, and BERTScore were employed to assess their capabilities, alongside an aggregate score combining these metrics for correction quality. Claude 3.5 Sonnet achieved the highest accuracy in detecting error flags (70.16%) and sentences (65.62%), while o1-preview excelled in error correction with an aggregate score of 0.698. Comparisons with expert medical annotations highlighted that while LLMs performed well, they were still surpassed by medical doctors in detection and correction tasks.
The performance gap is likely due to the limited availability of error-specific medical data in LLM pretraining and the challenge of analyzing pre-existing clinical texts rather than generating responses. Among the models, the o1-preview demonstrated superior recall across all error types but struggled with precision, often overestimating error occurrences compared to medical experts. This precision deficit, alongside the models’ dependency on public datasets, resulted in a performance disparity across subsets, with models performing better on public datasets (e.g., MEDEC-MS) than private collections like MEDEC-UW.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 60k+ ML SubReddit.
 FREE UPCOMING AI WEBINAR (JAN 15, 2025): Boost LLM Accuracy with Synthetic Data and Evaluation Intelligence–Join this webinar to gain actionable insights into boosting LLM model performance and accuracy while safeguarding data privacy.
FREE UPCOMING AI WEBINAR (JAN 15, 2025): Boost LLM Accuracy with Synthetic Data and Evaluation Intelligence–Join this webinar to gain actionable insights into boosting LLM model performance and accuracy while safeguarding data privacy.
The post MEDEC: A Benchmark for Detecting and Correcting Medical Errors in Clinical Notes Using LLMs appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ